mRNA profiling reveals determinants of trastuzumab efficiency in HER2-positive breast cancer
- PMID: 25710561
- PMCID: PMC4339844
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117818
mRNA profiling reveals determinants of trastuzumab efficiency in HER2-positive breast cancer
Abstract
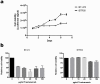
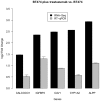
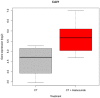
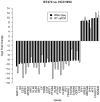
Intrinsic and acquired resistance to the monoclonal antibody drug trastuzumab is a major problem in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer. A deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms could help to develop new agents. Our intention was to detect genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) affecting trastuzumab efficiency in cell culture. Three HER2-positive breast cancer cell lines with different resistance phenotypes were analyzed. We chose BT474 as model of trastuzumab sensitivity, HCC1954 as model of intrinsic resistance, and BTR50, derived from BT474, as model of acquired resistance. Based on RNA-Seq data, we performed differential expression analyses on these cell lines with and without trastuzumab treatment. Differentially expressed genes between the resistant cell lines and BT474 are expected to contribute to resistance. Differentially expressed genes between untreated and trastuzumab treated BT474 are expected to contribute to drug efficacy. To exclude false positives from the candidate gene set, we removed genes that were also differentially expressed between untreated and trastuzumab treated BTR50. We further searched for SNPs in the untreated cell lines which could contribute to trastuzumab resistance. The analysis resulted in 54 differentially expressed candidate genes that might be connected to trastuzumab efficiency. 90% of 40 selected candidates were validated by RT-qPCR. ALPP, CALCOCO1, CAV1, CYP1A2 and IGFBP3 were significantly higher expressed in the trastuzumab treated than in the untreated BT474 cell line. GDF15, IL8, LCN2, PTGS2 and 20 other genes were significantly higher expressed in HCC1954 than in BT474, while NCAM2, COLEC12, AFF3, TFF3, NRCAM, GREB1 and TFF1 were significantly lower expressed. Additionally, we inferred SNPs in HCC1954 for CAV1, PTGS2, IL8 and IGFBP3. The latter also had a variation in BTR50. 20% of the validated subset have already been mentioned in literature. For half of them we called and analyzed SNPs. These results contribute to a better understanding of trastuzumab action and resistance mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Erythropoietin receptor expression and its relationship with trastuzumab response and resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Dec;136(3):739-48. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2316-x. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 23117856
-
ErbB-2 inhibition activates Notch-1 and sensitizes breast cancer cells to a gamma-secretase inhibitor.Oncogene. 2008 Aug 28;27(37):5019-32. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.149. Epub 2008 May 12. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18469855
-
Overcoming trastuzumab resistance in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells by using a novel celecoxib-derived phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 inhibitor.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;70(5):1534-41. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.023911. Epub 2006 Aug 3. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16887935
-
HER2-directed therapy: current treatment options for HER2-positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2015 Mar;22(2):101-16. doi: 10.1007/s12282-015-0587-x. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Breast Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25634227 Review.
-
Emerging insights into mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive cancers.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Sep;122:110602. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110602. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37437432 Review.
Cited by
-
Caveolin-1 mediates cellular distribution of HER2 and affects trastuzumab binding and therapeutic efficacy.Nat Commun. 2018 Dec 3;9(1):5137. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07608-w. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30510281 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid-phase electron microscopy of molecular drug response in breast cancer cells reveals irresponsive cell subpopulations related to lack of HER2 homodimers.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Aug 9;28(23):3193-202. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-06-0381. Online ahead of print. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28794264 Free PMC article.
-
HER2/PD1 bispecific antibody in IgG4 subclass with superior anti-tumour activities.Clin Transl Med. 2022 Apr;12(4):e791. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.791. Clin Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35384333 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
NHF-derived carbon dots: prevalidation approach in breast cancer treatment.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 29;10(1):12662. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69670-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32728167 Free PMC article.
-
ER-phagy: mechanisms, regulation, and diseases connected to the lysosomal clearance of the endoplasmic reticulum.Physiol Rev. 2022 Jul 1;102(3):1393-1448. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00038.2021. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Physiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35188422 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

