Elevated NIBP/TRAPPC9 mediates tumorigenesis of cancer cells through NFκB signaling
- PMID: 25704885
- PMCID: PMC4467429
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3349
Elevated NIBP/TRAPPC9 mediates tumorigenesis of cancer cells through NFκB signaling
Abstract
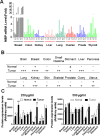
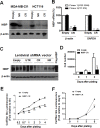
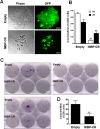
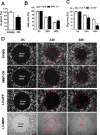
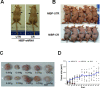
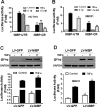
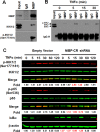
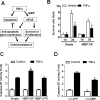
Regulatory mechanisms underlying constitutive and inducible NFκB activation in cancer remain largely unknown. Here we investigated whether a novel NIK- and IKK2-binding protein (NIBP) is required for maintaining malignancy of cancer cells in an NFκB-dependent manner. Real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of a human cancer survey tissue-scan cDNA array, immunostaining of a human frozen tumor tissue array and immunoblotting of a high-density reverse-phase cancer protein lysate array showed that NIBP is extensively expressed in most tumor tissues, particularly in breast and colon cancer. Lentivirus-mediated NIBP shRNA knockdown significantly inhibited the growth/proliferation, invasion/migration, colony formation and xenograft tumorigenesis of breast (MDA-MB-231) or colon (HCT116) cancer cells. NIBP overexpression in HCT116 cells promoted cell proliferation, migration and colony formation. Mechanistically, NIBP knockdown in cancer cells inhibited cytokine-induced activation of NFκB luciferase reporter, thus sensitizing the cells to TNFα-induced apoptosis. Endogenous NIBP bound specifically to the phosphorylated IKK2 in a TNFα-dependent manner. NIBP knockdown transiently attenuated TNFα-stimulated phosphorylation of IKK2/p65 and degradation of IκBα. In contrast, NIBP overexpression enhanced TNFα-induced NFκB activation, thus inhibiting constitutive and TNFα-induced apoptosis. Collectively, our data identified important roles of NIBP in promoting tumorigenesis via NFκΒ signaling, spotlighting NIBP as a promising target in cancer therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: NFκB; TRAPPC9; cancer cells; trans-Golgi network; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockdown of NIK and IKKβ-Binding Protein (NIBP) Reduces Colorectal Cancer Metastasis through Down-Regulation of the Canonical NF-κΒ Signaling Pathway and Suppression of MAPK Signaling Mediated through ERK and JNK.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 26;12(1):e0170595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170595. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28125661 Free PMC article.
-
NIK‑ and IKKβ‑binding protein contributes to gastric cancer chemoresistance by promoting epithelial‑mesenchymal transition through the NF‑κB signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2018 Jun;39(6):2721-2730. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6348. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29620292
-
Expression and function of NIK- and IKK2-binding protein (NIBP) in mouse enteric nervous system.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014 Jan;26(1):77-97. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12234. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014. PMID: 24011459 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of NIK/IKK2-binding protein (NIBP)/trafficking protein particle complex 9 (TRAPPC9) in nervous system diseases.Transl Res. 2020 Oct;224:55-70. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.05.001. Epub 2020 May 17. Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32434006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteopontin: it's role in regulation of cell motility and nuclear factor kappa B-mediated urokinase type plasminogen activator expression.IUBMB Life. 2005 Jun;57(6):441-7. doi: 10.1080/15216540500159424. IUBMB Life. 2005. PMID: 16012053 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of NIBP and its clinical significance in human early colorectal cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Aug 1;10(8):8633-8639. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966720 Free PMC article.
-
NIK- and IKKβ-binding protein promotes colon cancer metastasis by activating the classical NF-κB pathway and MMPs.Tumour Biol. 2016 May;37(5):5979-90. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4433-8. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26596835
-
Knockdown of NIK and IKKβ-Binding Protein (NIBP) Reduces Colorectal Cancer Metastasis through Down-Regulation of the Canonical NF-κΒ Signaling Pathway and Suppression of MAPK Signaling Mediated through ERK and JNK.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 26;12(1):e0170595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170595. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28125661 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of TPX2 and NIBP in esophageal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Oct;18(4):4221-4229. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10747. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31516617 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-17-3p suppresses NF-κB-mediated endothelial inflammation by targeting NIK and IKKβ binding protein.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Dec;42(12):2046-2057. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00611-w. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 33623121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonizzi G, Karin M. The two NF-kappaB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004;25(6):280–288. - PubMed
-
- Mattson MP, Meffert MK. Roles for NF-kappaB in nerve cell survival, plasticity, and disease. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13(5):852–860. - PubMed
-
- O'Sullivan NC, Croydon L, McGettigan PA, Pickering M, Murphy KJ. Hippocampal region-specific regulation of NF-kappaB may contribute to learning-associated synaptic reorganisation. Brain Res Bull. 2010;81(4-5):385–390. - PubMed
-
- Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature. 2006;441(7092):431–436. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani A, Balkwill F. RalB signaling: a bridge between inflammation and cancer. Cell. 2006;127(1):42–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

