Synergistic anticancer effect of cisplatin and Chal-24 combination through IAP and c-FLIPL degradation, Ripoptosome formation and autophagy-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 25682199
- PMCID: PMC4359321
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2746
Synergistic anticancer effect of cisplatin and Chal-24 combination through IAP and c-FLIPL degradation, Ripoptosome formation and autophagy-mediated apoptosis
Abstract
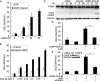
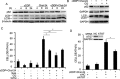
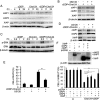
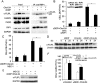
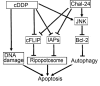
Drug resistance is a major hurdle in anticancer chemotherapy. Combined therapy using drugs with distinct mechanisms of function may increase anticancer efficacy. We have recently identified the novel chalcone derivative, chalcone-24 (Chal-24), as a potential therapeutic that kills cancer cells through activation of an autophagy-mediated necroptosis pathway. In this report, we investigated if Chal-24 can be combined with the frontline genotoxic anticancer drug, cisplatin for cancer therapy. The combination of Chal-24 and cisplatin synergistically induced apoptotic cytotoxicity in lung cancer cell lines, which was dependent on Chal-24-induced autophagy. While cisplatin slightly potentiated the JNK/Bcl2/Beclin1 pathway for autophagy activation, its combination with Chal-24 strongly triggered proteasomal degradation of the cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (c-IAPs) and formation of the Ripoptosome complex that contains RIP1, FADD and caspase 8. Furthermore, the cisplatin and Chal-24 combination induced dramatic degradation of cellular FLICE (FADD-like IL-1β-converting enzyme)-inhibitory protein large (cFLIPL) which suppresses Ripoptosome-mediated apoptosis activation. These results establish a novel mechanism for potentiation of anticancer activity with the combination of Chal-24 and cisplatin: to enhance apoptosis signaling through Ripoptosome formation and to release the apoptosis brake through c-FLIPL degradation. Altogether, our work suggests that the combination of Chal-24 and cisplatin could be employed to improve chemotherapy efficacy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Autophagy-Mediated Degradation of IAPs and c-FLIP(L) Potentiates Apoptosis Induced by Combination of TRAIL and Chal-24.J Cell Biochem. 2016 May;117(5):1136-44. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25397. Epub 2015 Nov 2. J Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26448608 Free PMC article.
-
A JNK-mediated autophagy pathway that triggers c-IAP degradation and necroptosis for anticancer chemotherapy.Oncogene. 2014 Jun 5;33(23):3004-13. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.256. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23831571 Free PMC article.
-
Cordycepin induces autophagy-mediated c-FLIPL degradation and leads to apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 24;8(4):6691-6699. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14262. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28035061 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the ripoptosome and its components: implications for anti-inflammatory and cancer therapy.Methods Enzymol. 2014;545:83-102. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-801430-1.00004-4. Methods Enzymol. 2014. PMID: 25065887 Review.
-
c-FLIP, a master anti-apoptotic regulator.Exp Oncol. 2012 Oct;34(3):176-84. Exp Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23070002 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
3-Oxoacid CoA transferase 1 as a therapeutic target gene for cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Feb;15(2):2611-2618. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7560. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29434981 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-Mediated Degradation of IAPs and c-FLIP(L) Potentiates Apoptosis Induced by Combination of TRAIL and Chal-24.J Cell Biochem. 2016 May;117(5):1136-44. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25397. Epub 2015 Nov 2. J Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26448608 Free PMC article.
-
TR4 nuclear receptor enhances the cisplatin chemo-sensitivity via altering the ATF3 expression to better suppress HCC cell growth.Oncotarget. 2016 May 31;7(22):32088-99. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8525. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27050071 Free PMC article.
-
Whole exome sequencing identifies novel candidate genes that modify chronic obstructive pulmonary disease susceptibility.Hum Genomics. 2016 Jan 7;10:1. doi: 10.1186/s40246-015-0058-7. Hum Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26744305 Free PMC article.
-
Induction Effect to Apoptosis by Maitake Polysaccharide: Synergistic Effect of Its Combination With Vitamin C in Neuroglioma Cell.J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2017 Oct;22(4):667-674. doi: 10.1177/2156587217708524. Epub 2017 May 22. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28528571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seve P, Dumontet C. Chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2005;5:73–88. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Ghavami S, Hashemi M, Ande SR, Yeganeh B, Xiao W, Eshraghi M, Bus CJ, Kadkhoda K, Wiechec E, Halayko AJ, Los M. Apoptosis and cancer: mutations within caspase genes. J Med Genet. 2009;46:497–510. - PubMed
-
- Ocker M, Hopfner M. Apoptosis-modulating drugs for improved cancer therapy. Eur Surg Res. 2012;48:111–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

