Characteristics of immunogenic and tolerogenic dendritic cells within the arterial wall in atherosclerosis and in vitro
- PMID: 25663981
- PMCID: PMC4307428
Characteristics of immunogenic and tolerogenic dendritic cells within the arterial wall in atherosclerosis and in vitro
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the characteristic of mature dendritic cell (mDC) and tolerogenic dendritic cell (TDC) in human lower limb atherosclerosis occlusion syndrome (ASO) and diabetic foot and in vitro.
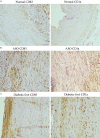
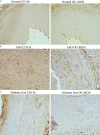
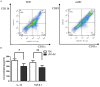
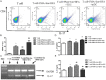
Methods: 58 human ASO and diabetic foot arterial specimens were collected from surgical operation and autopsy. Immunohistochemical and Western blotting method were used to examine the distribution and the content of CD83 and CD1a positive reaction mDC and CD11b and DC-SIGN positive reaction TDC. Furthermore, bone marrow-derived DCs were induced by rmGM-CSF and rmIL-4 in the presence or absence of LPS in vitro. The percent of CD11c(+)CD11b(+)TDC and CD11c(+)CD83(+)mDC were analyzed by flow cytometry. The effects of TDC and mDC on T lymphocytes were analyzed by the IL-17 level, the percent of Th17, and IL-17 mRNA expression.
Results: Immunogenicity mDC was heavily found in intima plaque and around the small vessel of adventitia on artherosclerosis aorta of lesion group, and was positively correlated to the progress of the disease. However, there were low expression of TDC and was negatively correlated to the progress of the disease. Meanwhile, we found that there is a close relationship between high glucose and disease progression. TDC expressed high levels of IL-10 and TGF-β1 and down-regulated the percent of CD4(+)IL-17(+) Th17, IL-17 mRNA and the level of IL-17 in vitro.
Conclusion: TDC and mDC are assembled in the process of ASO, and the progression of the disease might be aggravated by DC-maturation. High glucose might closely relate to the progression of atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Dendritic cells; diabetic foot; immune response; immunogenicity; lower limb atherosclerosis occlusion syndrome; tolerogenicity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[The role of third-party tolerogenic dendritic cells in the prevention of acute graft-versus-host-disease following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in mice].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Jun;33(6):461-6. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22967381 Chinese.
-
TRAF6 regulates the effects of polarized maturation of tolerability: Marrow-derived dendritic cells on collagen-induced arthritis in mice.Biomed Rep. 2017 Feb;6(2):206-210. doi: 10.3892/br.2017.836. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Biomed Rep. 2017. PMID: 28357074 Free PMC article.
-
Tolerogenic dendritic cells modified by tacrolimus suppress CD4(+) T-cell proliferation and inhibit collagen-induced arthritis in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Jul;21(1):247-54. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 May 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24836681
-
The suppression effect of dendritic cells maturation by adipose-derived stem cells through TGF-β1 related pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2018 Sep 15;370(2):708-717. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.07.037. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Exp Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 30053444
-
Tolerogenic dendritic cells induce antigen-specific hyporesponsiveness in insulin- and glutamic acid decarboxylase 65-autoreactive T lymphocytes from type 1 diabetic patients.Clin Immunol. 2014 Sep;154(1):72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24993292
Cited by
-
Dioscin attenuates oxLDL uptake and the inflammatory reaction of dendritic cells under high glucose conditions by blocking p38 MAPK.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Jan;21(1):304-310. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10806. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 31746382 Free PMC article.
-
A myriad of roles of dendritic cells in atherosclerosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2021 Oct;206(1):12-27. doi: 10.1111/cei.13634. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34109619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nickel T, Schmauss D, Hanssen H, Sicic Z, Krebs B, Jankl S, Summo C, Fraunberger P, Walli AK, Pfeiler S, Weis M. oxLDL uptake by dendritic cells induces upregulation of scavenger-receptors, maturation and differentiation. Atherosclerosis. 2009;205:442–450. - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1685–1695. - PubMed
-
- Miloud T, Hammerling GJ, Garbi N. Review of murine dendritic cells: types, location, and development. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;595:21–42. - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz A, Lipfert B, Cicha I, Schubert K, Klein M, Raithel D, Daniel WG, Garlichs CD. Accumulation of immune cells and high expression of chemokines/chemokine receptors in the upstream shoulder of atherosclerotic carotid plaques. Exp Mol Pathol. 2007;82:245–255. - PubMed
-
- Min SY, Park KS, Cho ML, Kang JW, Cho YG, Hwang SY, Park MJ, Yoon CH, Min JK, Lee SH, Park SH, Kim HY. Antigen-induced, tolerogenic CD11c+, CD11b+ dendritic cells are abundant in Peyer’s patches during the induction of oral tolerance to type II collagen and suppress experimental collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:887–898. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
