miR-122 stimulates hepatitis C virus RNA synthesis by altering the balance of viral RNAs engaged in replication versus translation
- PMID: 25662750
- PMCID: PMC4326553
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.12.014
miR-122 stimulates hepatitis C virus RNA synthesis by altering the balance of viral RNAs engaged in replication versus translation
Abstract
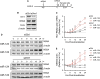
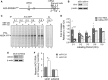
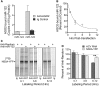
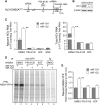
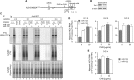
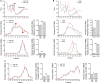
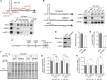
The liver-specific microRNA, miR-122, stabilizes hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA genomes by recruiting host argonaute 2 (AGO2) to the 5' end and preventing decay mediated by exonuclease Xrn1. However, HCV replication requires miR-122 in Xrn1-depleted cells, indicating additional functions. We show that miR-122 enhances HCV RNA levels by altering the fraction of HCV genomes available for RNA synthesis. Exogenous miR-122 increases viral RNA and protein levels in Xrn1-depleted cells, with enhanced RNA synthesis occurring before heightened protein synthesis. Inhibiting protein translation with puromycin blocks miR-122-mediated increases in RNA synthesis, but independently enhances RNA synthesis by releasing ribosomes from viral genomes. Additionally, miR-122 reduces the fraction of viral genomes engaged in protein translation. Depleting AGO2 or PCBP2, which binds HCV RNA in competition with miR-122 and promotes translation, eliminates miR-122 stimulation of RNA synthesis. Thus, by displacing PCBP2, miR-122 reduces HCV genomes engaged in translation while increasing the fraction available for RNA synthesis.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Hepatitis C Virus Genome Replication by Xrn1 and MicroRNA-122 Binding to Individual Sites in the 5' Untranslated Region.J Virol. 2015 Jun;89(12):6294-311. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03631-14. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25855736 Free PMC article.
-
[Regulation of hepatitis C virus genome replication by microRNA-122].Uirusu. 2015;65(2):277-286. doi: 10.2222/jsv.65.277. Uirusu. 2015. PMID: 27760927 Review. Japanese.
-
Human Ago2 is required for efficient microRNA 122 regulation of hepatitis C virus RNA accumulation and translation.J Virol. 2011 Mar;85(5):2342-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02046-10. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21177824 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the roles of the 5' exoribonucleases Xrn1 and Xrn2 in restricting hepatitis C virus replication.J Virol. 2015 May;89(9):4857-65. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03692-14. Epub 2015 Feb 11. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25673723 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of host cell microRNAs with the HCV RNA genome during infection of liver cells.Semin Liver Dis. 2015 Feb;35(1):75-80. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1397351. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Semin Liver Dis. 2015. PMID: 25632937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Interference in Hepatic Host-Pathogen Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 30;22(7):3554. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073554. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4AII contributes to microRNA-122 regulation of hepatitis C virus replication.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 6;46(12):6330-6343. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky262. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29669014 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-122 amplifies hepatitis C virus translation by shaping the structure of the internal ribosomal entry site.Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 4;9(1):2613. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05053-3. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29973597 Free PMC article.
-
Diminished viral replication and compartmentalization of hepatitis C virus in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 2;113(5):1375-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516879113. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26787866 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-122 Regulation of HCV Infections: Insights from Studies of miR-122-Independent Replication.Pathogens. 2022 Sep 2;11(9):1005. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11091005. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36145436 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chang J., Nicolas E., Marks D., Sander C., Lerro A., Buendia M.A., Xu C., Mason W.S., Moloshok T., Bort R. miR-122, a mammalian liver-specific microRNA, is processed from hcr mRNA and may downregulate the high affinity cationic amino acid transporter CAT-1. RNA Biol. 2004;1:106–113. - PubMed
-
- Fukushi S., Okada M., Kageyama T., Hoshino F.B., Nagai K., Katayama K. Interaction of poly(rC)-binding protein 2 with the 5′-terminal stem loop of the hepatitis C-virus genome. Virus Res. 2001;73:67–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

