Norepinephrine preferentially modulates memory CD8 T cell function inducing inflammatory cytokine production and reducing proliferation in response to activation
- PMID: 25653192
- PMCID: PMC4414741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.01.015
Norepinephrine preferentially modulates memory CD8 T cell function inducing inflammatory cytokine production and reducing proliferation in response to activation
Abstract
Background: Norepinephrine (NE) is one of the primary catecholamines of the sympathetic nervous system released during a stress response and plays an important role in modulating immune function. NE binds to the adrenergic receptors on immune cells, including T cells, resulting in either suppressed or enhanced function depending on the type of cell, activation status of the cell, duration of NE exposure and concentration of NE. Here, we aim to analyze the effects of NE on the functionality of naïve (Tn), central memory (Tcm) and effector memory (Tem) CD8 T cells.
Methods: We isolated CD8 T cell subsets from healthy human adults and treated cells in vitro with NE (1×10(-6)M) for 16h; we then stimulated NE treated and untreated CD8 T cell subsets with antibodies for CD3 and CD28 for 24 and 72h. We assessed the level of beta-2 adrenergic receptor (ADRB2) expression in these cells as well as global gene expression changes in NE treated Tcm cells by microarray analysis. Altered expressed genes after NE treatment were identified and further confirmed by RT-qPCR, and by ELISA for protein changes. We further determined whether the observed NE effects on memory CD8 T cells are mediated by ADRB2 using specific adrenergic receptor agonist and antagonists. Finally, we examined the levels of mRNA and protein of the NE-induced genes in healthy adults with high serum levels of NE (>150pg/mL) compared to low levels (<150pg/mL).
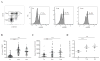
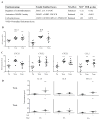
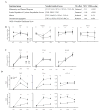
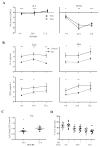
Results: We found that memory (Tcm and Tem) CD8 T cells expressed a significantly higher level of ADRB2 compared to naïve cells. Consequently, memory CD8 T cells were significantly more sensitive than naïve cells to NE induced changes in gene expressions in vitro. Global gene expression analysis revealed that NE induced an elevated expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in resting and activated memory CD8 T cells in addition to a reduced expression of growth-related cytokines. The effects of NE on memory CD8 T cells were primarily mediated by ADRB2 as confirmed by the adrenergic receptor agonist and antagonist assays. Finally, individuals with high serum levels of NE had similar elevated gene expressions observed in vitro compared to the low NE group.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that NE preferentially modulates the functions of memory CD8 T cells by inducing inflammatory cytokine production and reducing activation-induced memory CD8 T cell expansion.
Keywords: CD8 T cells; Inflammation; Norepinephrine; Stress.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sympathetic neural signaling via the β2-adrenergic receptor suppresses T-cell receptor-mediated human and mouse CD8(+) T-cell effector function.Eur J Immunol. 2016 Aug;46(8):1948-58. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646395. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27222010 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Superoxide Signaling Contributes to Norepinephrine-Mediated T-Lymphocyte Cytokine Profiles.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 11;11(10):e0164609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164609. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27727316 Free PMC article.
-
β-Adrenergic signaling blocks murine CD8+ T-cell metabolic reprogramming during activation: a mechanism for immunosuppression by adrenergic stress.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019 Jan;68(1):11-22. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2243-8. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30229289 Free PMC article.
-
The immune system in extreme longevity.Exp Gerontol. 2008 Feb;43(2):61-5. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2007.06.008. Epub 2007 Jul 4. Exp Gerontol. 2008. PMID: 17870272 Review.
-
The beta2-adrenergic receptor on T and B lymphocytes: do we understand it yet?Brain Behav Immun. 2012 Feb;26(2):195-200. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.08.001. Epub 2011 Aug 10. Brain Behav Immun. 2012. PMID: 21855626 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of norepinephrine on immunity and oxidative metabolism in sepsis.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 7;14:1271098. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1271098. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The β2-adrenergic receptor controls inflammation by driving rapid IL-10 secretion.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Nov;74:176-185. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 30195028 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenergic Signaling: A Targetable Checkpoint Limiting Development of the Antitumor Immune Response.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 6;9:164. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00164. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29479349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoimmune Epilepsy - Novel Multidisciplinary Analysis, Discoveries and Insights.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 12;12:762743. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.762743. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic roles of miRNAs in regulating T cell immunity.Immunol Rev. 2021 Nov;304(1):126-140. doi: 10.1111/imr.13029. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Immunol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34549446 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anstead MI, Hunt TA, Carlson SL, Burki NK. Variability of peripheral blood lymphocyte beta-2-adrenergic receptor density in humans. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:990–992. - PubMed
-
- Araki Y, Wang Z, Zang C, Wood WH, III, Schones D, Cui K, Roh TY, Lhotsky B, Wersto RP, Peng W, Becker KG, Zhao K, Weng NP. Genome-wide analysis of histone methylation reveals chromatin state-based regulation of gene transcription and function of memory CD8+ T cells. Immunity. 2009;30:912–925. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asao H, Fu XY. Interferon-gamma has dual potentials in inhibiting or promoting cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:867–874. - PubMed
-
- Bonneau RH, Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Glaser R. Stress-induced modulation of the immune response. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;594:253–269. - PubMed
-
- Carlson SL, Brooks WH, Roszman TL. Neurotransmitter-lymphocyte interactions: dual receptor modulation of lymphocyte proliferation and cAMP production. J Neuroimmunol. 1989;24:155–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

