Jagged-1 signaling suppresses the IL-6 and TGF-β treatment-induced Th17 cell differentiation via the reduction of RORγt/IL-17A/IL-17F/IL-23a/IL-12rb1
- PMID: 25648768
- PMCID: PMC4316398
- DOI: 10.1038/srep08234
Jagged-1 signaling suppresses the IL-6 and TGF-β treatment-induced Th17 cell differentiation via the reduction of RORγt/IL-17A/IL-17F/IL-23a/IL-12rb1
Abstract
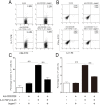
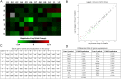
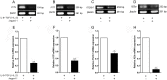
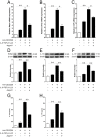
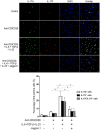
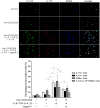
Jagged-1 signaling has recently been reported to be involved in the Th17 cell differentiation. However, little is known about its mechanisms. Soluble Jagged-1 was used to activate the Jagged-1-Notch signaling to interfere with the IL-6 and TGF-β-induced Th17 cell skewing. Genes relevant to the autoimmunity or inflammation were screened for the first time in this system by qPCR array for the differential expressions. The 18 genes out of 84, including Clec7a, Il12b, Il12rb1, Il12rb2, Csf3, Il15, Il17a, Il17f, Il17rc, Il17rd, Il17re, Il23a, Myd88, Socs1, Stat4, Stat5a, Sykb and Tbx21, were downregulated, but only Cxcl2, Cxcl12 and Mmp3 were upregulated. The expressions of the genes, Rorγt, Il17a, Il17f, Il12rb1 and Il23a, induced by simultaneous IL-6 and TGF-β treatment were significantly suppressed by Jagged-1, followed by the reduction of RORγt, IL-17A, and IL-17F. Consistent with the attenuation of RORγt, and the reduced production and secretion of IL-17A and IL-17F in the cell supernatant and the in situ stained cells, the number of CD4(+)IL-17(+) cells was also diminished. It is concluded that the Jagged-1-Notch signaling can suppress the IL-6 and TGF-β treatment-induced Th17 cell skewing through the attenuation of RORγt and, hence by, the down-regulation of IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-23a, and IL-12rb1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Jagged-1-HES-1 signaling inhibits the differentiation of TH17 cells via ROR gammat.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013 Jan-Mar;27(1):79-93. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013. PMID: 23489689
-
Pharmacologic inhibition of RORγt regulates Th17 signature gene expression and suppresses cutaneous inflammation in vivo.J Immunol. 2014 Mar 15;192(6):2564-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302190. Epub 2014 Feb 10. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24516202
-
[Generation of engineering Th17 cells and its function evaluation].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Dec;32(12):825-9. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22339955 Chinese.
-
Genes associated with T helper 17 cell differentiation and function.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2016 Jun 1;8(3):427-35. doi: 10.2741/E777. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2016. PMID: 27100349 Review.
-
[Research progress of Th17 cells and glomerulonephritis].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013 Apr;38(4):432-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2013.04.016. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013. PMID: 23645246 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Notch Signaling in T Helper Cell Subsets: Instructor or Unbiased Amplifier?Front Immunol. 2017 Apr 18;8:419. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00419. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28458667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th17/Treg cell balance in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: a new potential biomarker and therapeutic target.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 29;14:1325575. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1325575. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39534095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch signaling pathway regulates CD4+CD25+CD127dim/- regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cells function in gastric cancer patients.Biosci Rep. 2019 May 14;39(5):BSR20182044. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182044. Print 2019 May 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30988066 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17 receptor D (Sef) is a multi-functional regulator of cell signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Jan 12;19(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00695-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 33436016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide promotes T-hel per17 cell differentiation by upregulating Delta-like ligand 4 expression on CD14+ monocytes.PeerJ. 2021 Apr 23;9:e11094. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11094. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33981487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harrington L. E. et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol 6, 1123–1132 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Veldhoen M. et al. TGFbeta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity 24, 179–189 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Li M. O. et al. Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 24, 99–146 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Bettelli E. et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 441, 235–238 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

