The role of hypoxia in inflammatory disease (review)
- PMID: 25625467
- PMCID: PMC4356629
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2079
The role of hypoxia in inflammatory disease (review)
Abstract
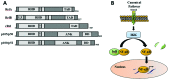
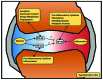
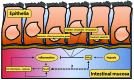
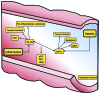
Mammals have developed evolutionarily conserved programs of transcriptional response to hypoxia and inflammation. These stimuli commonly occur together in vivo and there is significant crosstalk between the transcription factors that are classically understood to respond to either hypoxia or inflammation. This crosstalk can be used to modulate the overall response to environmental stress. Several common disease processes are characterised by aberrant transcriptional programs in response to environmental stress. In this review, we discuss the current understanding of the role of the hypoxia-responsive (hypoxia-inducible factor) and inflammatory (nuclear factor-κB) transcription factor families and their crosstalk in rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer, with relevance for future therapies for the management of these conditions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interdependent roles for hypoxia inducible factor and nuclear factor-kappaB in hypoxic inflammation.J Physiol. 2008 Sep 1;586(17):4055-9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.157669. Epub 2008 Jul 3. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18599532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIF3α: the little we know.FEBS J. 2016 Mar;283(6):993-1003. doi: 10.1111/febs.13572. Epub 2015 Nov 14. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26507580 Review.
-
Chronic and Cycling Hypoxia: Drivers of Cancer Chronic Inflammation through HIF-1 and NF-κB Activation: A Review of the Molecular Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10701. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910701. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumour necrosis factor-α suppresses the hypoxic response by NF-κB-dependent induction of inhibitory PAS domain protein in PC12 cells.J Biochem. 2011 Sep;150(3):311-8. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvr061. Epub 2011 May 10. J Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21558328
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2 promotes liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis liver disease via the NF-κB signalling pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Feb 12;540:67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33450482
Cited by
-
The Molecular Adaptive Responses of Skeletal Muscle to High-Intensity Exercise/Training and Hypoxia.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jul 24;9(8):656. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080656. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32722013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathways by small molecules and natural compounds as a therapeutic approach for breast cancer cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Oct;46(5):4809-4816. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04929-x. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31313132
-
Ambulatory Surgery Has Minimal Impact on Sleep Parameters: A Prospective Observational Trial.J Clin Sleep Med. 2018 Apr 15;14(4):593-602. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.7052. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018. PMID: 29609705 Free PMC article.
-
Ex Vivo Production of IL-1β and IL-10 by Activated Blood Cells of Wistar Rats with Different Resistance to Hypoxia after Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2023 Dec;176(2):290-296. doi: 10.1007/s10517-024-06010-5. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 38194074
-
Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Patients with Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Danish Nationwide Cohort Study.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 21;12(9):2700. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092700. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32967227 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

