Estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα) and ERRγ are essential coordinators of cardiac metabolism and function
- PMID: 25624346
- PMCID: PMC4355525
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01156-14
Estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα) and ERRγ are essential coordinators of cardiac metabolism and function
Abstract
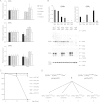
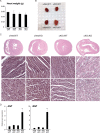
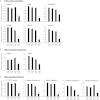
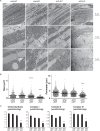
Almost all cellular functions are powered by a continuous energy supply derived from cellular metabolism. However, it is little understood how cellular energy production is coordinated with diverse energy-consuming cellular functions. Here, using the cardiac muscle system, we demonstrate that nuclear receptors estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα) and ERRγ are essential transcriptional coordinators of cardiac energy production and consumption. On the one hand, ERRα and ERRγ together are vital for intact cardiomyocyte metabolism by directly controlling expression of genes important for mitochondrial functions and dynamics. On the other hand, ERRα and ERRγ influence major cardiomyocyte energy consumption functions through direct transcriptional regulation of key contraction, calcium homeostasis, and conduction genes. Mice lacking both ERRα and cardiac ERRγ develop severe bradycardia, lethal cardiomyopathy, and heart failure featuring metabolic, contractile, and conduction dysfunctions. These results illustrate that the ERR transcriptional pathway is essential to couple cellular energy metabolism with energy consumption processes in order to maintain normal cardiac function.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cardiac-Specific Overexpression of ERRγ in Mice Induces Severe Heart Dysfunction and Early Lethality.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 28;22(15):8047. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158047. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360813 Free PMC article.
-
A Critical Role for Estrogen-Related Receptor Signaling in Cardiac Maturation.Circ Res. 2020 Jun 5;126(12):1685-1702. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316100. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32212902 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-related receptor gamma induces cardiac hypertrophy by activating GATA4.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 Dec;65:88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.09.011. Epub 2013 Sep 29. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 24083978
-
Transcriptional control of energy homeostasis by the estrogen-related receptors.Endocr Rev. 2008 Oct;29(6):677-96. doi: 10.1210/er.2008-0017. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Endocr Rev. 2008. PMID: 18664618 Review.
-
The estrogen-related receptors in metabolism and cancer: newer insights.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2018 Apr;38(2):95-100. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2018.1456552. Epub 2018 Apr 5. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2018. PMID: 29619877 Review.
Cited by
-
How Hypertension Affects Heart Metabolism.Front Physiol. 2019 Apr 16;10:435. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00435. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31040794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the activation mechanism of human estrogen-related receptor γ by environmental endocrine disruptors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Dec;76(23):4769-4781. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03129-x. Epub 2019 May 24. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31127318 Free PMC article.
-
Contractile Work Contributes to Maturation of Energy Metabolism in hiPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes.Stem Cell Reports. 2018 Mar 13;10(3):834-847. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.01.039. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Stem Cell Reports. 2018. PMID: 29503093 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary Roles of Estrogen-Related Receptors in Brown Adipocyte Thermogenic Function.Endocrinology. 2016 Dec;157(12):4770-4781. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1767. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 27763777 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyocyte Maturation: New Phase in Development.Circ Res. 2020 Apr 10;126(8):1086-1106. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315862. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32271675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
