Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans control adhesion and invasion of breast carcinoma cells
- PMID: 25623282
- PMCID: PMC4326193
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-014-0279-8
Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans control adhesion and invasion of breast carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: Cell surface proteoglycans interact with numerous regulators of cell behavior through their glycosaminoglycan chains. The syndecan family of transmembrane proteoglycans are virtually ubiquitous cell surface receptors that are implicated in the progression of some tumors, including breast carcinoma. This may derive from their regulation of cell adhesion, but roles for specific syndecans are unresolved.
Methods: The MDA-MB231 human breast carcinoma cell line was exposed to exogenous glycosaminoglycans and changes in cell behavior monitored by western blotting, immunocytochemistry, invasion and collagen degradation assays. Selected receptors including PAR-1 and syndecans were depleted by siRNA treatments to assess cell morphology and behavior. Immunohistochemistry for syndecan-2 and its interacting partner, caveolin-2 was performed on human breast tumor tissue arrays. Two-tailed paired t-test and one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test were used in the analysis of data.
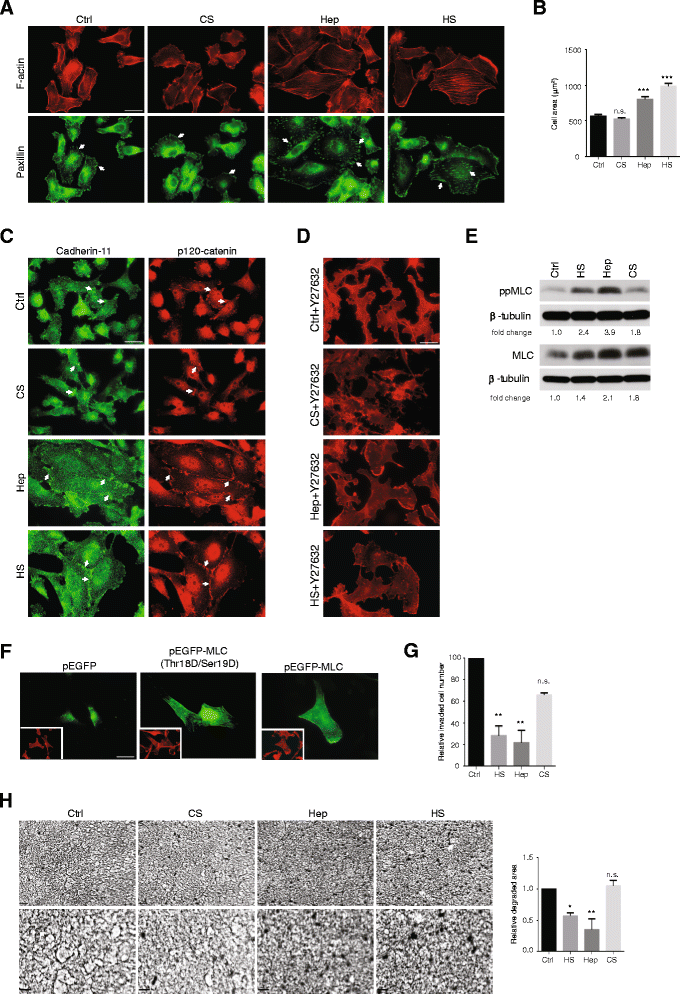
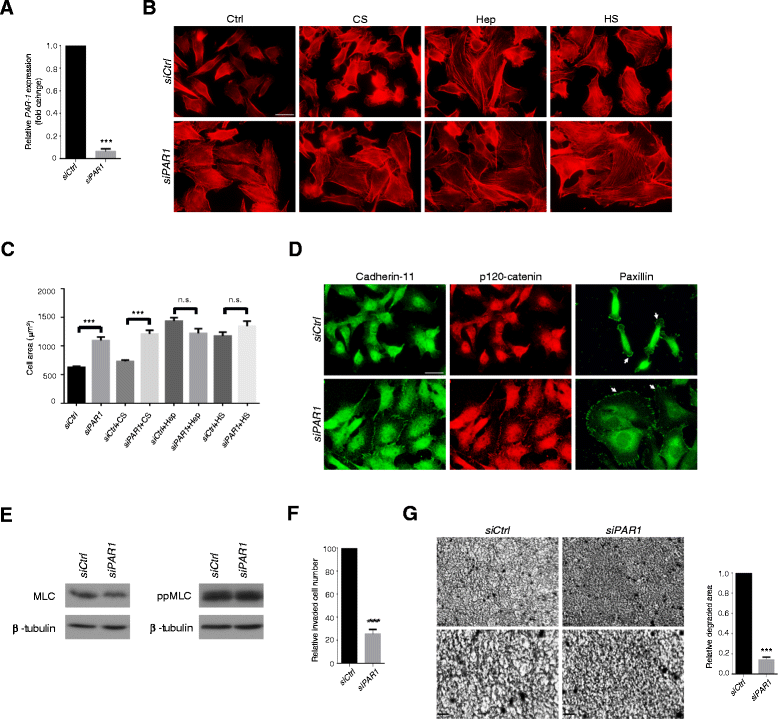
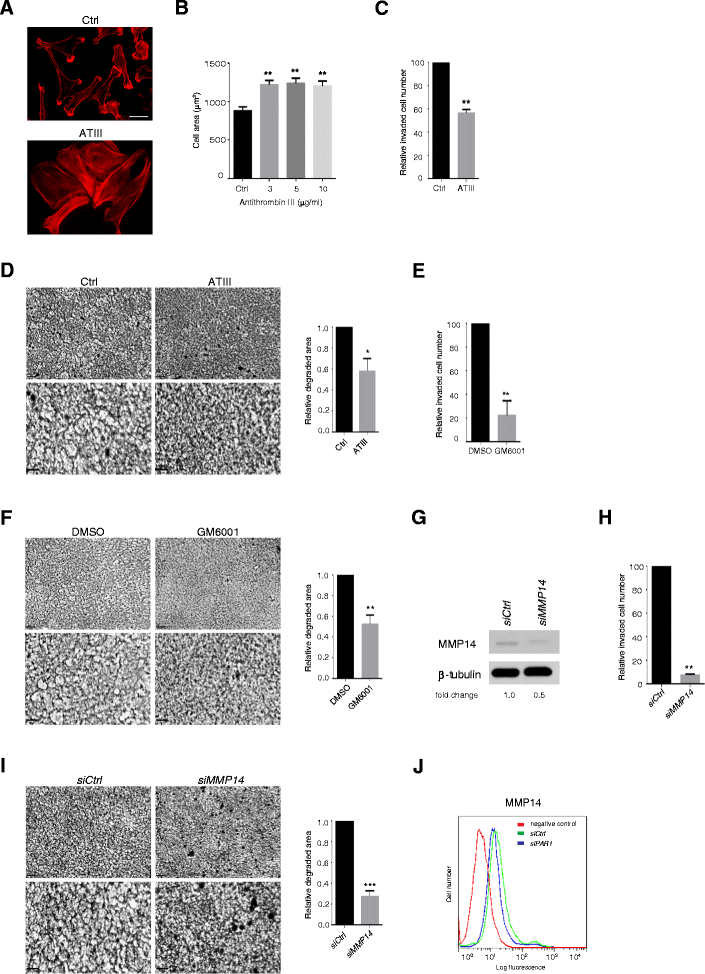
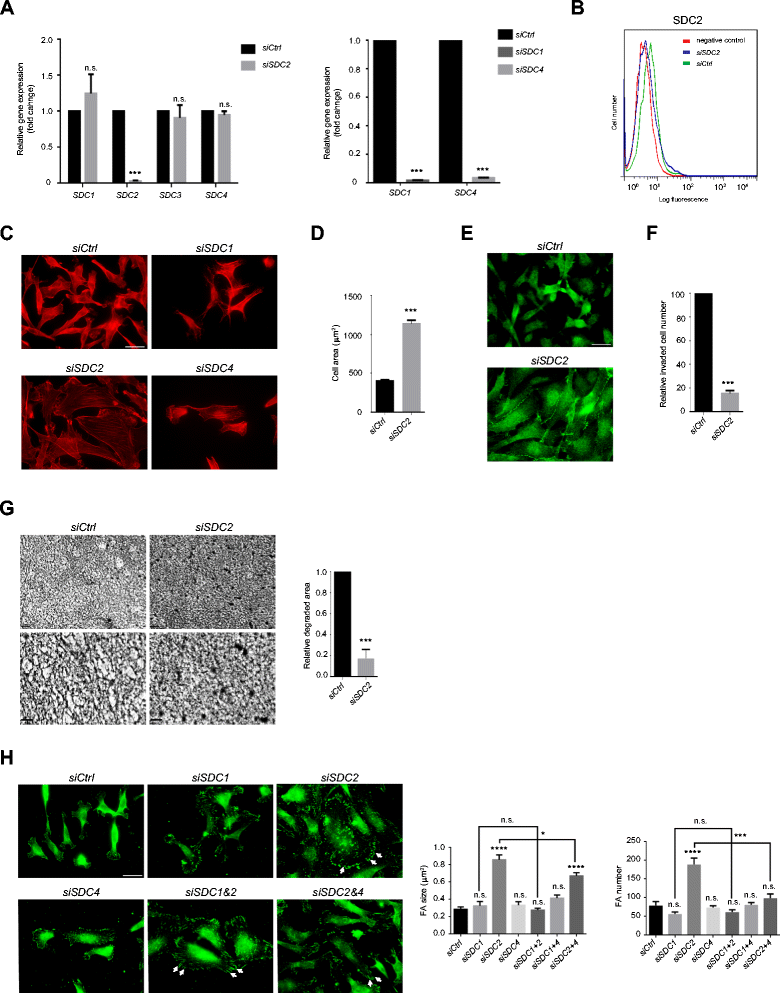
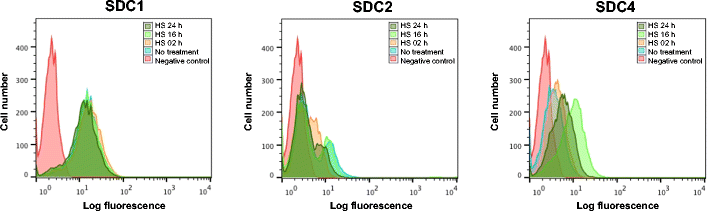
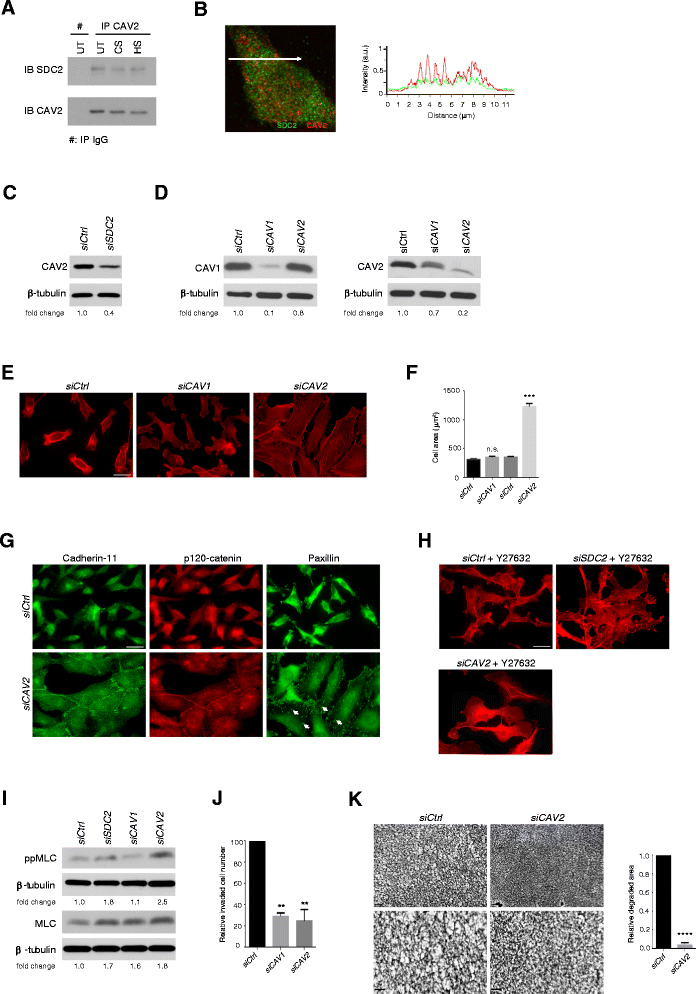
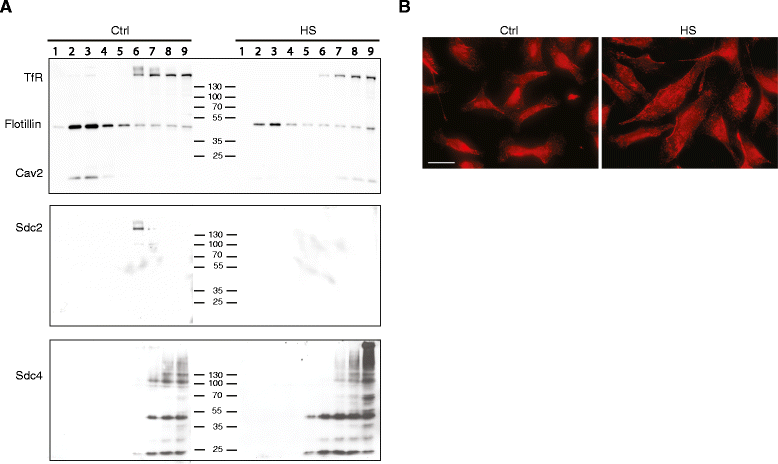
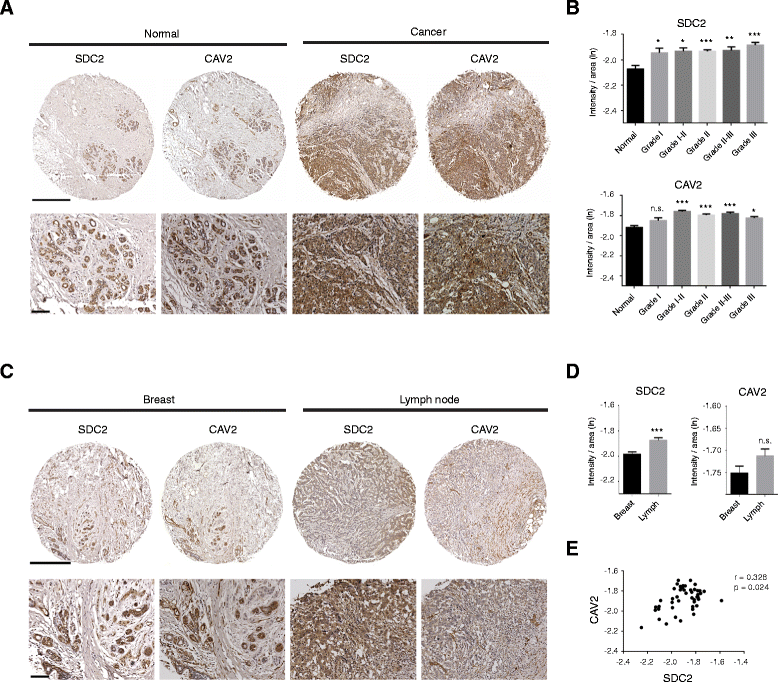
Results: MDA-MB231 cells were shown to be highly sensitive to exogenous heparan sulfate or heparin, promoting increased spreading, focal adhesion and adherens junction formation with concomitantly reduced invasion and matrix degradation. The molecular basis for this effect was revealed to have two components. First, thrombin inhibition contributed to enhanced cell adhesion and reduced invasion. Second, a specific loss of cell surface syndecan-2 was noted. The ensuing junction formation was dependent on syndecan-4, whose role in promoting actin cytoskeletal organization is known. Syndecan-2 interacts with, and may regulate, caveolin-2. Depletion of either molecule had the same adhesion-promoting influence, along with reduced invasion, confirming a role for this complex in maintaining the invasive phenotype of mammary carcinoma cells. Finally, both syndecan-2 and caveolin-2 were upregulated in tissue arrays from breast cancer patients compared to normal mammary tissue. Moreover their expression levels were correlated in triple negative breast cancers.
Conclusion: Cell surface proteoglycans, notably syndecan-2, may be important regulators of breast carcinoma progression through regulation of cytoskeleton, cell adhesion and invasion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Syndecan-2 regulation of morphology in breast carcinoma cells is dependent on RhoGTPases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1840(8):2482-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.01.018. Epub 2014 Jan 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24447566
-
Podocytes require the engagement of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans for adhesion to extracellular matrices.Kidney Int. 2010 Dec;78(11):1088-99. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.136. Epub 2010 May 12. Kidney Int. 2010. PMID: 20463653 Free PMC article.
-
Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans control the response of renal interstitial fibroblasts to fibroblast growth factor-2.Kidney Int. 2001 Jun;59(6):2084-94. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00723.x. Kidney Int. 2001. PMID: 11380810
-
Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in Human Colorectal Cancer.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018 Jun 20;2018:8389595. doi: 10.1155/2018/8389595. eCollection 2018. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018. PMID: 30027065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syndecan proteoglycan contributions to cytoskeletal organization and contractility.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2009 Aug;19(4):479-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2009.00941.x. Epub 2009 Jun 15. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2009. PMID: 19538537 Review.
Cited by
-
Pleiotropic Effects of Heparins: From Clinical Applications to Molecular Mechanisms in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Oct 22;2018:7568742. doi: 10.1155/2018/7568742. eCollection 2018. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30425976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EDIL3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and paclitaxel resistance through its interaction with integrin αVβ3 in cancer cells.Cell Death Discov. 2020 Sep 16;6:86. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-00322-x. eCollection 2020. Cell Death Discov. 2020. PMID: 33014430 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and mechanistic characterization of bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase-N-sulfotransferase 1.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 13;15(1):1326. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45419-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38351061 Free PMC article.
-
The GAG-specific branched peptide NT4 reduces angiogenesis and invasiveness of tumor cells.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 22;13(3):e0194744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194744. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29566097 Free PMC article.
-
The Cardiac Syndecan-2 Interactome.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 28;8:792. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00792. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32984315 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

