Diagnostic Values of Cerebrospinal Fluid T-Tau and Aβ₄₂ using Meso Scale Discovery Assays for Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 25613100
- PMCID: PMC4517668
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-143099
Diagnostic Values of Cerebrospinal Fluid T-Tau and Aβ₄₂ using Meso Scale Discovery Assays for Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) recently established electrochemiluminescence-based assays to measure cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of total tau (t-tau) and amyloid-β 1-42 peptide (Aβ42) that can aid in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The goal of this investigation is to independently evaluate this platform and establish cut-off values of these biomarkers for AD diagnosis.
Objective: To validate the analytical and clinical performance of the MSD t-tau and Aβ42 kits and propose diagnostic cut-off values for the field.
Methods: The analytical performance of the CSF t-tau and Aβ42 assays was determined, followed by assessment of diagnostic performance of CSF t-tau, Aβ42, and t-tau/Aβ42 in three clinically characterized cohorts.
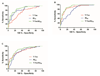
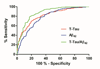
Results: Both MSD assays demonstrated consistent and stable analytical performance, as well as resistance to several important pre-analytic variables. Diagnostically, t-tau/Aβ42 performed the best.
Conclusions: Our results independently confirm the analytical and clinical performance of the MSD CSF t-tau and Aβ42 assays. Based on a large, multi-center, clinically-diagnosed cohort, we propose for the first time candidate diagnostic cut-offs for MSD measured CSF t-tau, Aβ42, and t-tau/Aβ42. However, these values needs to be refined as more subjects are included and the assays are tested by other laboratories.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Aβ$^{42}$; Meso Scale Discovery; cerebrospinal fluid; tau.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein E genotype and the diagnostic accuracy of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer disease.JAMA Psychiatry. 2014 Oct;71(10):1183-91. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1060. JAMA Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25162367
-
Additional use of Aβ₄₂/Aβ₄₀ ratio with cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers P-tau and Aβ₄₂ increases the level of evidence of Alzheimer's disease pathophysiological process in routine practice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;41(2):377-86. doi: 10.3233/JAD-131838. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014. PMID: 24614902
-
CSF biomarkers and incipient Alzheimer disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment.JAMA. 2009 Jul 22;302(4):385-93. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1064. JAMA. 2009. PMID: 19622817
-
Simultaneous analysis of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers using microsphere-based xMAP multiplex technology for early detection of Alzheimer's disease.Methods. 2012 Apr;56(4):484-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.03.023. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Methods. 2012. PMID: 22503777 Review.
-
Alzheimer's disease--Recent biomarker developments in relation to updated diagnostic criteria.Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Sep 20;449:3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.01.041. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 25668231 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantification of CSF biomarkers using an electrochemiluminescence-based detection system in the differential diagnosis of AD and sCJD.J Neurol. 2015 Oct;262(10):2305-11. doi: 10.1007/s00415-015-7837-x. Epub 2015 Jul 11. J Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26162713
-
Approaches to the discovery of non-invasive urinary biomarkers of prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2018 Aug 21;9(65):32534-32550. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25946. eCollection 2018 Aug 21. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30197761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
APOE4 leads to blood-brain barrier dysfunction predicting cognitive decline.Nature. 2020 May;581(7806):71-76. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2247-3. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32376954 Free PMC article.
-
A First Tetraplex Assay for the Simultaneous Quantification of Total α-Synuclein, Tau, β-Amyloid42 and DJ-1 in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 26;11(4):e0153564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153564. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27116005 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association and interaction studies of CSF T-tau/Aβ42 ratio in ADNI cohort.Neurobiol Aging. 2017 Sep;57:247.e1-247.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 15. Neurobiol Aging. 2017. PMID: 28641921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cummings J, Zhong K. Biomarker-driven therapeutic management of Alzheimer's disease: establishing the foundations. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014;95:67–77. - PubMed
-
- McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR, Jr, Kawas CH, Klunk WE, Koroshetz WJ, Manly JJ, Mayeux R, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rossor MN, Scheltens P, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Weintraub S, Phelps CH. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:263–269. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Hampel H, Molinuevo JL, Blennow K, DeKosky ST, Gauthier S, Selkoe D, Bateman R, Cappa S, Crutch S, Engelborghs S, Frisoni GB, Fox NC, Galasko D, Habert MO, Jicha GA, Nordberg A, Pasquier F, Rabinovici G, Robert P, Rowe C, Salloway S, Sarazin M, Epelbaum S, de Souza LC, Vellas B, Visser PJ, Schneider L, Stern Y, Scheltens P, Cummings JL. Advancing research diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer's disease: the IWG-2 criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:614–629. - PubMed
-
- Blennow K, Hampel H. CSF markers for incipient Alzheimer's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2003;2:605–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

