GIV/Girdin transmits signals from multiple receptors by triggering trimeric G protein activation
- PMID: 25605737
- PMCID: PMC4358093
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R114.613414
GIV/Girdin transmits signals from multiple receptors by triggering trimeric G protein activation
Abstract
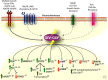
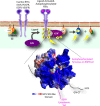
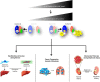
Activation of trimeric G proteins has been traditionally viewed as the exclusive job of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). This view has been challenged by the discovery of non-receptor activators of trimeric G proteins. Among them, GIV (a.k.a. Girdin) is the first for which a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity has been unequivocally associated with a well defined motif. Here we discuss how GIV assembles alternative signaling pathways by sensing cues from various classes of surface receptors and relaying them via G protein activation. We also describe the dysregulation of this mechanism in disease and how its targeting holds promise for novel therapeutics.
Keywords: Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor (GEF); Heterotrimeric G Protein; Liver Fibrosis; Nephrotic Syndrome; Receptor Tyrosine Kinase; Src Homology 2 Domain (SH2 Domain); Tumor Metastasis.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heterotrimeric G protein signaling via GIV/Girdin: Breaking the rules of engagement, space, and time.Bioessays. 2016 Apr;38(4):379-93. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500133. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 26879989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for activation of trimeric Gi proteins by multiple growth factor receptors via GIV/Girdin.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Nov 5;25(22):3654-71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-05-0978. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 25187647 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C-theta (PKCθ) phosphorylates and inhibits the guanine exchange factor, GIV/Girdin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 2;110(14):5510-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303392110. Epub 2013 Mar 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23509302 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects of cell-permeant peptides that activate G proteins downstream of growth factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 19;112(20):E2602-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1505543112. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25926659 Free PMC article.
-
The GAPs, GEFs, GDIs and…now, GEMs: New kids on the heterotrimeric G protein signaling block.Cell Cycle. 2017 Apr 3;16(7):607-612. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1282584. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28287365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heterotrimeric G protein signaling via GIV/Girdin: Breaking the rules of engagement, space, and time.Bioessays. 2016 Apr;38(4):379-93. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500133. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 26879989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GRDN-1/Girdin regulates dendrite morphogenesis and cilium position in two specialized sensory neuron types in C. elegans.Dev Biol. 2021 Apr;472:38-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.12.022. Epub 2021 Jan 16. Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33460640 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary biosensors reveal different G-protein signaling modes triggered by GPCRs and non-receptor activators.Elife. 2021 Mar 31;10:e65620. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65620. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33787494 Free PMC article.
-
Specific inhibition of GPCR-independent G protein signaling by a rationally engineered protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 28;114(48):E10319-E10328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707992114. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29133411 Free PMC article.
-
Girdin (GIV) Expression as a Prognostic Marker of Recurrence in Mismatch Repair-Proficient Stage II Colon Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 15;22(14):3488-98. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2290. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27029492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gilman A. G. (1987) G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 56, 615–649 - PubMed
-
- Morris A. J., Malbon C. C. (1999) Physiological regulation of G protein-linked signaling. Physiol. Rev. 79, 1373–1430 - PubMed
-
- Hopkins A. L., Groom C. R. (2002) The druggable genome. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 1, 727–730 - PubMed
-
- Sato M., Blumer J. B., Simon V., Lanier S. M. (2006) Accessory proteins for G proteins: partners in signaling. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 46, 151–187 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

