Allergen challenge sensitizes TRPA1 in vagal sensory neurons and afferent C-fiber subtypes in guinea pig esophagus
- PMID: 25591867
- PMCID: PMC4360047
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00374.2014
Allergen challenge sensitizes TRPA1 in vagal sensory neurons and afferent C-fiber subtypes in guinea pig esophagus
Abstract
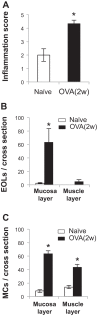
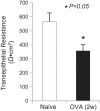
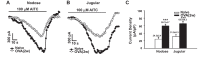
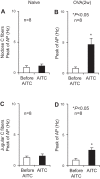
Transient receptor potential A1 (TRPA1) is a newly defined cationic ion channel, which selectively expresses in primary sensory afferent nerve, and is essential in mediating inflammatory nociception. Our previous study demonstrated that TRPA1 plays an important role in tissue mast cell activation-induced increase in the excitability of esophageal vagal nodose C fibers. The present study aims to determine whether prolonged antigen exposure in vivo sensitizes TRPA1 in a guinea pig model of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Antigen challenge-induced responses in esophageal mucosa were first assessed by histological stains and Ussing chamber studies. TRPA1 function in vagal sensory neurons was then studied by calcium imaging and by whole cell patch-clamp recordings in 1,1'-dioctadecyl-3,3,3',3'-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate (DiI)-labeled esophageal vagal nodose and jugular neurons. Extracellular single-unit recordings were performed in vagal nodose and jugular C-fiber neuron subtypes using ex vivo esophageal-vagal preparations with intact nerve endings in the esophagus. Antigen challenge significantly increased infiltrations of eosinophils and mast cells in the esophagus. TRPA1 agonist allyl isothiocyanate (AITC)-induced calcium influx in nodose and jugular neurons was significantly increased, and current densities in esophageal DiI-labeled nodose and jugular neurons were also significantly increased in antigen-challenged animals. Prolonged antigen challenge decreased esophageal epithelial barrier resistance, which allowed intraesophageal-infused AITC-activating nodose and jugular C fibers at their nerve endings. Collectively, these results demonstrated that prolonged antigen challenge sensitized TRPA1 in esophageal sensory neurons and afferent C fibers. This novel finding will help us to better understand the molecular mechanism underlying esophageal sensory and motor dysfunctions in EoE.
Keywords: dysphagia; eosinophilic esophagitis; heartburn; jugular; nodose.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
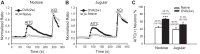
Similar articles
-
TRPA1 in mast cell activation-induced long-lasting mechanical hypersensitivity of vagal afferent C-fibers in guinea pig esophagus.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):G34-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00068.2009. Epub 2009 May 7. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19423751
-
TRPM8 function and expression in vagal sensory neurons and afferent nerves innervating guinea pig esophagus.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Mar 15;308(6):G489-96. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00336.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25591866 Free PMC article.
-
Increased acid responsiveness in vagal sensory neurons in a guinea pig model of eosinophilic esophagitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Jul 15;307(2):G149-57. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00097.2014. Epub 2014 May 29. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24875100 Free PMC article.
-
Capsaicin-Sensitive Vagal Afferent Nerve-Mediated Interoceptive Signals in the Esophagus.Molecules. 2021 Jun 28;26(13):3929. doi: 10.3390/molecules26133929. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34203134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction between TRPA1 and TRPV1: Synergy on pulmonary sensory nerves.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Dec;35:87-93. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26283426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of organophosphorus pesticide toxicity in the context of airway hyperreactivity and asthma.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):L485-L501. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00211.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29952220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models of eosinophilic esophagitis.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Jul 25;116(2):349-356. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae043. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38507307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Pain and Itch by TRP Channels.Neurosci Bull. 2018 Feb;34(1):120-142. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0200-8. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Neurosci Bull. 2018. PMID: 29282613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of inflammatory pain and cough by a novel charged sodium channel blocker.Br J Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;178(19):3905-3923. doi: 10.1111/bph.15531. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33988876 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and Pathological Significance of Esophageal TRP Channels: Special Focus on TRPV4 in Esophageal Epithelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 20;23(9):4550. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094550. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35562940 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdulnour-Nakhoul SM, Al-Tawil Y, Gyftopoulos AA, Brown KL, Hansen M, Butcher KF, Eidelwein AP, Noel RA, Rabon E, Posta A, Nakhoul NL. Alterations in junctional proteins, inflammatory mediators and extracellular matrix molecules in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Immunol 148: 265–278, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Aceves SS. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 35: 145–159, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Aceves SS, Chen D, Newbury RO, Dohil R, Bastian JF, Broide DH. Mast cells infiltrate the esophageal smooth muscle in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis, express TGF-beta1, and increase esophageal smooth muscle contraction. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126: 1198–1204, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Bandell M, Story GM, Hwang SW, Viswanath V, Eid SR, Petrus MJ, Earley TJ, Patapoutian A. Noxious cold ion channel TRPA1 is activated by pungent compounds and bradykinin. Neuron 41: 849–857, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

