The process of installing REDCap, a web based database supporting biomedical research: the first year
- PMID: 25589907
- PMCID: PMC4287671
- DOI: 10.4338/ACI-2014-06-CR-0054
The process of installing REDCap, a web based database supporting biomedical research: the first year
Abstract
Background: Clinical and research data are essential for patient care, research and healthcare system planning. REDCapTM is a web-based tool for research data curatorship developed at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, USA. The Faculty of Health Sciences at the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg South Africa identified the need for a cost effective data management instrument. REDCap was installed as per the user agreement with Vanderbilt University in August 2012.
Objectives: In order to assist other institutions that may lack the in-house Information Technology capacity, this paper describes the installation and support of REDCap and incorporates an analysis of user uptake over the first year of use.
Methods: We reviewed the staffing requirements, costs of installation, process of installation and necessary infrastructure and end-user requests following the introduction of REDCap at Wits. The University Legal Office and Human Research Ethics Committee were consulted regarding the REDCap end-user agreement. Bi-monthly user meetings resulted in a training workshop in August 2013. We compared our REDCap software user numbers and records before and after the first training workshop.
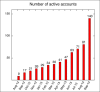
Results: Human resources were recruited from existing staff. Installation costs were limited to servers and security certificates. The total costs to provide a functional REDCap platform was less than $9000. Eighty-one (81) users were registered in the first year. After the first training workshop the user numbers increased by 59 in one month and the total number of active users to 140 by the end of August 2013. Custom software applications for REDCap were created by collaboration between clinicians and software developers.
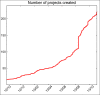
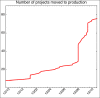
Conclusion: REDCap was installed and maintained at limited cost. A small number of people with defined skills can support multiple REDCap users in two to four hours a week. End user training increased in the number of users, number of projects created and the number of projects moved to production.
Keywords: Database management systems; clinical research; electronic data capture; medical informatics; translational research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in the research
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electronic Data Capture System (REDCap) for Health Care Research and Training in a Resource-Constrained Environment: Technology Adoption Case Study.JMIR Med Inform. 2022 Aug 30;10(8):e33402. doi: 10.2196/33402. JMIR Med Inform. 2022. PMID: 36040763 Free PMC article.
-
A study of user requests regarding the fully electronic health record system at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital: challenges for future electronic health record systems.Int J Med Inform. 2013 May;82(5):387-97. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Int J Med Inform. 2013. PMID: 22959193
-
REDLetr: Workflow and tools to support the migration of legacy clinical data capture systems to REDCap.Int J Med Inform. 2016 Sep;93:103-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2016.06.015. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Int J Med Inform. 2016. PMID: 27396629 Free PMC article.
-
A review of content-based image retrieval systems in medical applications-clinical benefits and future directions.Int J Med Inform. 2004 Feb;73(1):1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2003.11.024. Int J Med Inform. 2004. PMID: 15036075 Review.
-
Workflow based framework for life science informatics.Comput Biol Chem. 2007 Oct;31(5-6):305-19. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2007.08.009. Epub 2007 Aug 19. Comput Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17931570 Review.
Cited by
-
Protocol of an iterative qualitative study to develop a molecular testing decision aid for shared decision-making in patients with lung cancer after surgery.BMJ Open. 2022 Sep 19;12(9):e061367. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-061367. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36123064 Free PMC article.
-
Strengthening ethics committees for health-related research in sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping review.BMJ Open. 2022 Nov 21;12(11):e062847. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-062847. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36410802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diaspora linkages benefit both sides: a single partnership experience.Glob Health Action. 2019;12(1):1645558. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2019.1645558. Glob Health Action. 2019. PMID: 31362603 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Level and Factors Influencing Emergency Department Nurses Fatigue: A Case Study of the Saudi Arabian Context.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jul 13;10(7):1294. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10071294. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885820 Free PMC article.
-
A Protocol for Collecting Human Cardiac Tissue for Research.VAD J. 2016;2(1):10.13023/VAD.2016.12. doi: 10.13023/VAD.2016.12. Epub 2016 Jun 3. VAD J. 2016. PMID: 28042604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coovadia H, Jewkesn R, Barron P, Sanders D, McIntyre D.The health and health system of South Africa: historical roots of current public health challenges. Lancet 2009; 374(9692): 817-834. - PubMed
-
- University of the Witwatersrand. Faculty of health Sciences, Faculty. http://www.wits.ac.za/academic/health/faculty/ (Last accessed 4/21/2014)
-
- University of the Witwatersrand. Library. Database management guidelines. http://libguides.wits.ac.za/DataManagement/ (Last accessed 4/21/2014)
-
- Travis P, Bennett S, Haines A, Pang T, Bhutta Z, Hyder AA, Pielemeier NR, Mills A, Evans T.Overcoming health-systems constraints to achieve the Millennium Development Goals. Lancet 2004; 364(9437): 900-906. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources