Envisioning the dynamics and flexibility of Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex to decipher its roles in DNA replication and repair
- PMID: 25576492
- PMCID: PMC4417436
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.12.004
Envisioning the dynamics and flexibility of Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex to decipher its roles in DNA replication and repair
Abstract
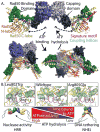
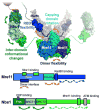
The Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) complex is a dynamic macromolecular machine that acts in the first steps of DNA double strand break repair, and each of its components has intrinsic dynamics and flexibility properties that are directly linked with their functions. As a result, deciphering the functional structural biology of the MRN complex is driving novel and integrated technologies to define the dynamic structural biology of protein machinery interacting with DNA. Rad50 promotes dramatic long-range allostery through its coiled-coil and zinc-hook domains. Its ATPase activity drives dynamic transitions between monomeric and dimeric forms that can be modulated with mutants modifying the ATPase rate to control end joining versus resection activities. The biological functions of Mre11's dual endo- and exonuclease activities in repair pathway choice were enigmatic until recently, when they were unveiled by the development of specific nuclease inhibitors. Mre11 dimer flexibility, which may be regulated in cells to control MRN function, suggests new inhibitor design strategies for cancer intervention. Nbs1 has FHA and BRCT domains to bind multiple interaction partners that further regulate MRN. One of them, CtIP, modulates the Mre11 excision activity for homologous recombination repair. Overall, these combined properties suggest novel therapeutic strategies. Furthermore, they collectively help to explain how MRN regulates DNA repair pathway choice with implications for improving the design and analysis of cancer clinical trials that employ DNA damaging agents or target the DNA damage response.
Keywords: Allostery; Conformational change; CtIP; Double strand break repair; Dynamics; Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 is a keystone complex connecting DNA repair machinery, double-strand break signaling, and the chromatin template.Biochem Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;85(4):509-20. doi: 10.1139/O07-069. Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17713585 Review.
-
NBS1 promotes the endonuclease activity of the MRE11-RAD50 complex by sensing CtIP phosphorylation.EMBO J. 2019 Apr 1;38(7):e101005. doi: 10.15252/embj.2018101005. Epub 2019 Feb 20. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 30787182 Free PMC article.
-
The MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 Complex Conducts the Orchestration of Damage Signaling and Outcomes to Stress in DNA Replication and Repair.Annu Rev Biochem. 2018 Jun 20;87:263-294. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-012415. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Annu Rev Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29709199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast cancer risk is associated with the genes encoding the DNA double-strand break repair Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007 Oct;16(10):2024-32. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0116. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007. PMID: 17932350
-
Nbs1 flexibly tethers Ctp1 and Mre11-Rad50 to coordinate DNA double-strand break processing and repair.Cell. 2009 Oct 2;139(1):87-99. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.033. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19804755 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Knowns Unknowns: Exploring the Homologous Recombination Repair Pathway in Toxoplasma gondii.Front Microbiol. 2016 May 3;7:627. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00627. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27199954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zn(II) to Ag(I) Swap in Rad50 Zinc Hook Domain Leads to Interprotein Complex Disruption through the Formation of Highly Stable Agx(Cys)y Cores.Inorg Chem. 2023 Mar 13;62(10):4076-4087. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c03767. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Inorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 36863010 Free PMC article.
-
Double-strand DNA break repair: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2023 Oct 5;4(5):e388. doi: 10.1002/mco2.388. eCollection 2023 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37808268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rad51 recombinase prevents Mre11 nuclease-dependent degradation and excessive PrimPol-mediated elongation of nascent DNA after UV irradiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Dec 1;112(48):E6624-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508543112. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26627254 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic Rad50 functions as a rod-shaped dimer.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017 Mar;24(3):248-257. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3369. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28134932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Ahmadie H, Iyer G, Hohl M, Asthana S, Inagaki A, Schultz N, Hanrahan AJ, Scott SN, Brannon AR, McDermott GC, Pirun M, Ostrovnaya I, Kim P, Socci ND, Viale A, Schwartz GK, Reuter V, Bochner BH, Rosenberg JE, Bajorin DF, Berger MF, Petrini JHJ, Solit DB, Taylor BS. Synthetic Lethality in ATM-Deficient RAD50-Mutant Tumors Underlies Outlier Response to Cancer Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:1014–1021. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0380. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

