Oxidized phospholipids protect against lung injury and endothelial barrier dysfunction caused by heat-inactivated Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 25575515
- PMCID: PMC4360062
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00248.2014
Oxidized phospholipids protect against lung injury and endothelial barrier dysfunction caused by heat-inactivated Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
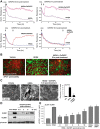
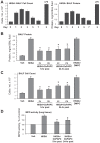
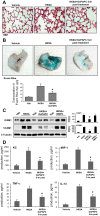
Increased endothelial cell (EC) permeability and vascular inflammation along with alveolar epithelial damage are key features of acute lung injury (ALI). Products of 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine oxidation (OxPAPC) showed protective effects against inflammatory signaling and vascular EC barrier dysfunction induced by gram-negative bacterial wall lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We explored the more general protective effects of OxPAPC and investigated whether delayed posttreatment with OxPAPC boosts the recovery of lung inflammatory injury and EC barrier dysfunction triggered by intratracheal injection of heat-killed gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (HKSA) bacteria. HKSA-induced pulmonary EC permeability, activation of p38 MAP kinase and NF-κB inflammatory cascades, secretion of IL-8 and soluble ICAM1, fibronectin deposition, and expression of adhesion molecules ICAM1 and VCAM1 by activated EC were significantly attenuated by cotreatment as well as posttreatment with OxPAPC up to 16 h after HKSA addition. Remarkably, posttreatment with OxPAPC up to 24 h post-HKSA challenge dramatically accelerated lung recovery by restoring lung barrier properties monitored by Evans blue extravasation and protein content in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid and reducing inflammation reflected by decreased MIP-1, KC, TNF-α, IL-13 levels and neutrophil count in BAL samples. These studies demonstrate potent in vivo and in vitro protective effects of posttreatment with anti-inflammatory oxidized phospholipids in the model of ALI caused by HKSA. These results warrant further investigations into the potential use of OxPAPC compounds combined with antibiotic therapies as a treatment of sepsis and ALI induced by gram-positive bacterial pathogens.
Keywords: cytoskeleton; inflammation; oxidized phospholipids; pulmonary endothelium; vascular leak.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidized Phospholipids in Healthy and Diseased Lung Endothelium.Cells. 2020 Apr 15;9(4):981. doi: 10.3390/cells9040981. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32326516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized Phospholipids in Control of Endothelial Barrier Function: Mechanisms and Implication in Lung Injury.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 23;12:794437. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.794437. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34887839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostacyclin post-treatment improves LPS-induced acute lung injury and endothelial barrier recovery via Rap1.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1852(5):778-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.12.016. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25545047 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized phospholipids reduce vascular leak and inflammation in rat model of acute lung injury.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006 May 15;173(10):1130-8. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200511-1737OC. Epub 2006 Mar 2. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 16514111 Free PMC article.
-
Thermodynamic and kinetic investigations of the release of oxidized phospholipids from lipid membranes and its effect on vascular integrity.Chem Phys Lipids. 2013 Oct-Nov;175-176:9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Chem Phys Lipids. 2013. PMID: 23911706 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of prostaglandin lipid mediators on agonist-induced lung endothelial permeability and inflammation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Oct 1;313(4):L710-L721. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00519.2016. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28663336 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2/PHB2 alleviates mitochondrial damage and protects against Staphylococcus aureus-induced acute lung injury.MedComm (2020). 2023 Dec 7;4(6):e448. doi: 10.1002/mco2.448. eCollection 2023 Dec. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 38077250 Free PMC article.
-
6-Gingerol via overexpression of miR-322-5p impede lipopolysaccharide-caused inflammatory response in RAW264.7 cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Dec;396(12):3797-3807. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02543-0. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37347266
-
MRSA-induced endothelial permeability and acute lung injury are attenuated by FTY720 S-phosphonate.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022 Jan 1;322(1):L149-L161. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00100.2021. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35015568 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized Phospholipids in Healthy and Diseased Lung Endothelium.Cells. 2020 Apr 15;9(4):981. doi: 10.3390/cells9040981. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32326516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arbibe L, Mira JP, Teusch N, Kline L, Guha M, Mackman N, Godowski PJ, Ulevitch RJ, Knaus UG. Toll-like receptor 2-mediated NF-kappa B activation requires a Rac1-dependent pathway. Nat Immunol 1: 533–540, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Beckers CM, van Hinsbergh VW, van Nieuw Amerongen GP. Driving Rho GTPase activity in endothelial cells regulates barrier integrity. Thromb Haemost 103: 40–55, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Birukov KG, Bochkov VN, Birukova AA, Kawkitinarong K, Rios A, Leitner A, Verin AD, Bokoch GM, Leitinger N, Garcia JG. Epoxycyclopentenone-containing oxidized phospholipids restore endothelial barrier function via Cdc42 and Rac. Circ Res 95: 892–901, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Birukov KG, Jacobson JR, Flores AA, Ye SQ, Birukova AA, Verin AD, Garcia JG. Magnitude-dependent regulation of pulmonary endothelial cell barrier function by cyclic stretch. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285: L785–L797, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Birukova AA, Adyshev D, Gorshkov B, Bokoch GM, Birukov KG, Verin AA. GEF-H1 is involved in agonist-induced human pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290: L540–L548, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

