Comprehensive review of human sapoviruses
- PMID: 25567221
- PMCID: PMC4284302
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00011-14
Comprehensive review of human sapoviruses
Abstract
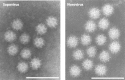
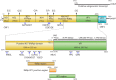
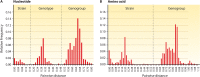
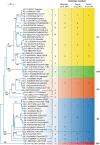
Sapoviruses cause acute gastroenteritis in humans and animals. They belong to the genus Sapovirus within the family Caliciviridae. They infect and cause disease in humans of all ages, in both sporadic cases and outbreaks. The clinical symptoms of sapovirus gastroenteritis are indistinguishable from those caused by noroviruses, so laboratory diagnosis is essential to identify the pathogen. Sapoviruses are highly diverse genetically and antigenically. Currently, reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) assays are widely used for sapovirus detection from clinical specimens due to their high sensitivity and broad reactivity as well as the lack of sensitive assays for antigen detection or cell culture systems for the detection of infectious viruses. Sapoviruses were first discovered in 1976 by electron microscopy in diarrheic samples of humans. To date, sapoviruses have also been detected from several animals: pigs, mink, dogs, sea lions, and bats. In this review, we focus on genomic and antigenic features, molecular typing/classification, detection methods, and clinical and epidemiological profiles of human sapoviruses.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Genetic diversity of human caliciviruses detected in schoolchildren with gastroenteritis in Nizhni Novgorod].Vopr Virusol. 2009 Nov-Dec;54(6):24-8. Vopr Virusol. 2009. PMID: 20030278 Russian.
-
Polymerase chain reaction primer sets for the detection of genetically diverse human sapoviruses.Arch Virol. 2020 Oct;165(10):2335-2340. doi: 10.1007/s00705-020-04746-9. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Arch Virol. 2020. PMID: 32719956 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and Genetic Variability of Sapoviruses in Africa.Viruses. 2020 Apr 27;12(5):490. doi: 10.3390/v12050490. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32349380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and molecular characterization of human noroviruses and sapoviruses in Ethiopia.Arch Virol. 2016 Aug;161(8):2169-82. doi: 10.1007/s00705-016-2887-7. Epub 2016 May 19. Arch Virol. 2016. PMID: 27193022
-
Porcine sapoviruses: Pathogenesis, epidemiology, genetic diversity, and diagnosis.Virus Res. 2020 Sep;286:198025. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198025. Epub 2020 May 26. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32470356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A dual typing system establishment and global diversity analysis for sapoviruses.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 22;25(1):1131. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11048-w. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39578768 Free PMC article.
-
Propagating and banking genetically diverse human sapovirus strains using a human duodenal cell line: investigating antigenic differences between strains.J Virol. 2024 Sep 17;98(9):e0063924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00639-24. Epub 2024 Aug 12. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39132992
-
Genetic diversity of enteric viruses responsible of gastroenteritis in urban and rural Burkina Faso.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Jul 8;18(7):e0012228. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012228. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38976836 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Genomics Investigation of Neboviruses Reveals Distinct Codon Usage Patterns and Host Specificity.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 29;12(4):696. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040696. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674640 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Severity of Enteric Viruses Detected Using a Quantitative Molecular Assay Compared With Conventional Assays in the Global Enteric Multicenter Study.J Infect Dis. 2024 Nov 15;230(5):1157-1166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae201. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38637321
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

