Microbiology of diabetic foot infections: from Louis Pasteur to 'crime scene investigation'
- PMID: 25564342
- PMCID: PMC4286146
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-014-0232-0
Microbiology of diabetic foot infections: from Louis Pasteur to 'crime scene investigation'
Abstract
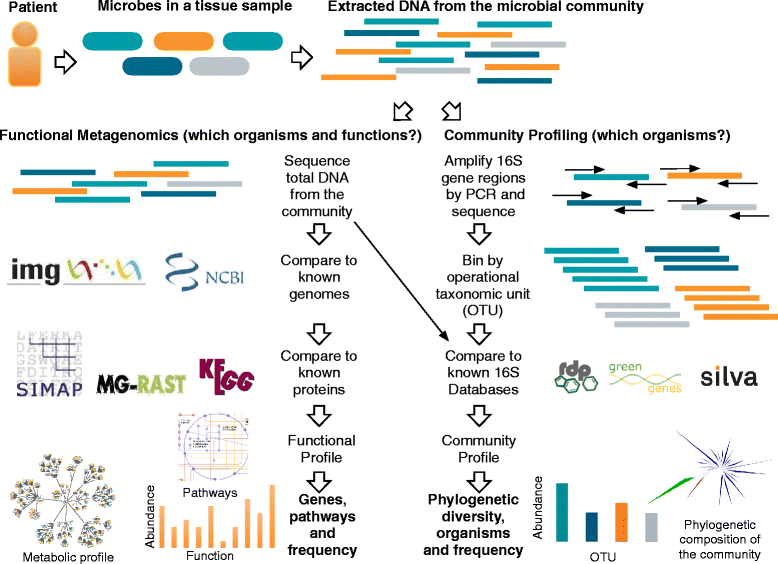
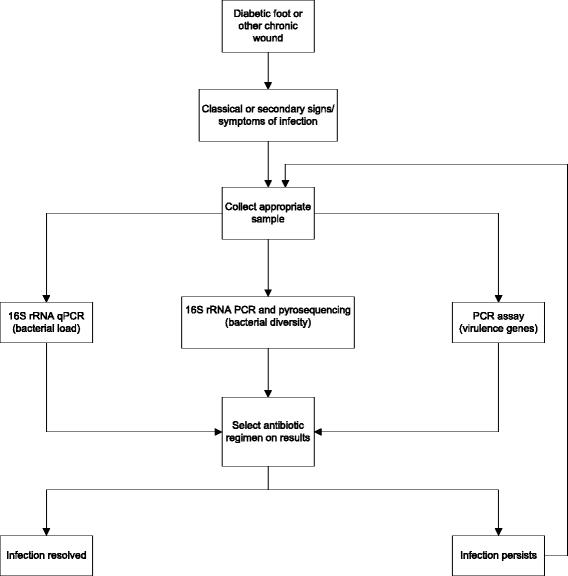
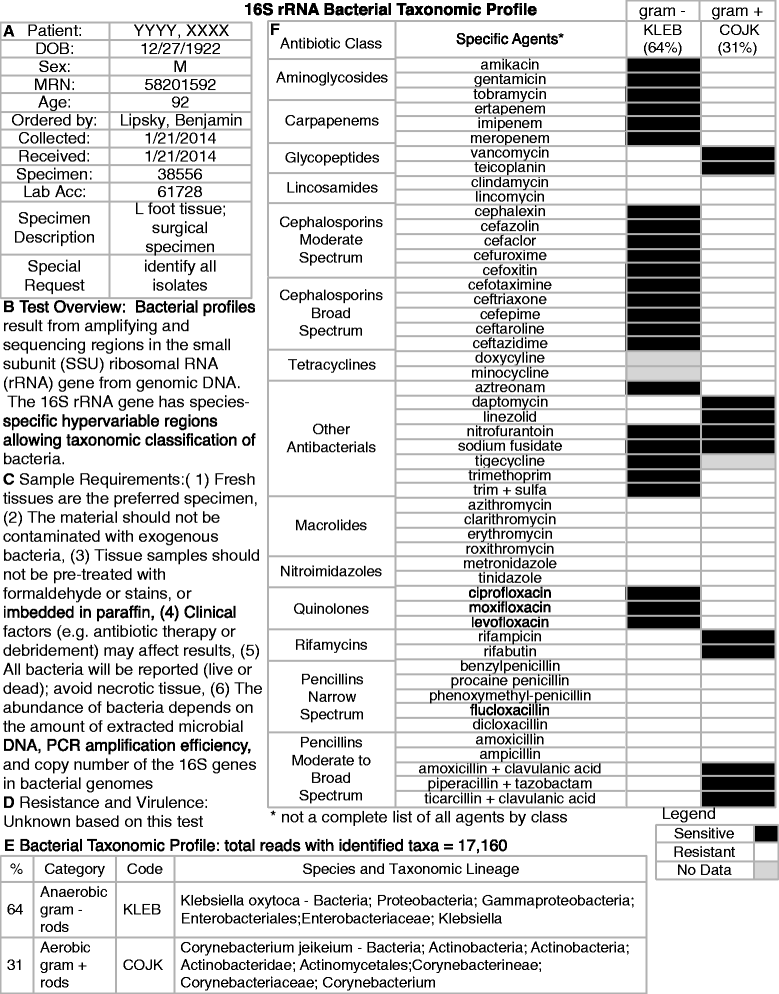
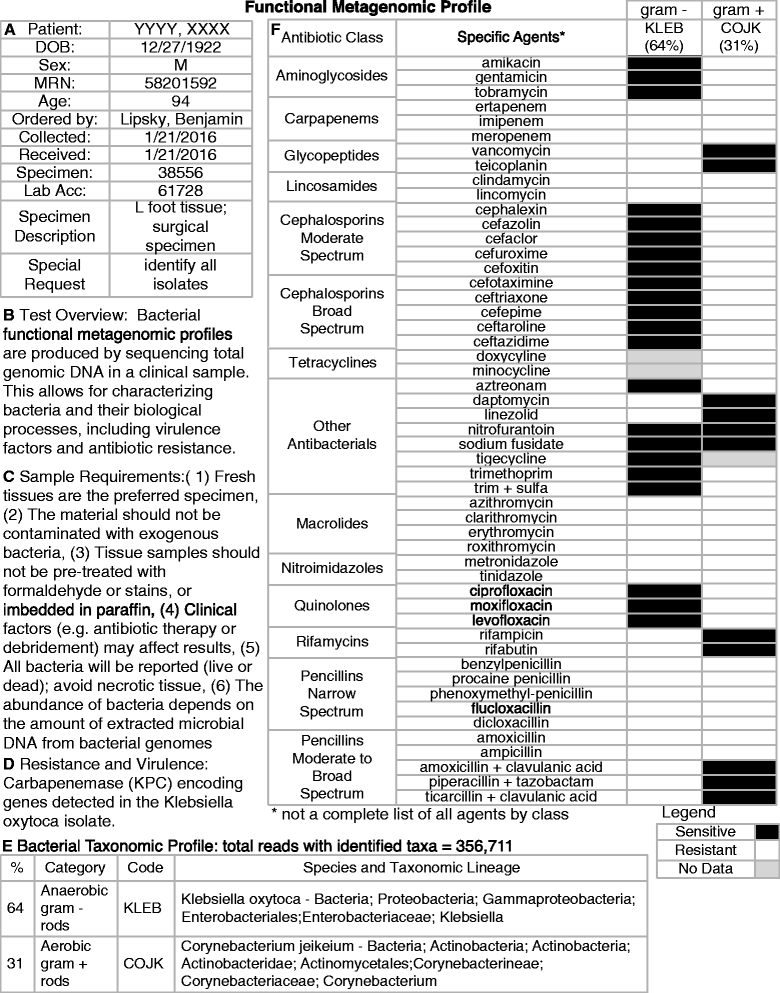
Were he alive today, would Louis Pasteur still champion culture methods he pioneered over 150 years ago for identifying bacterial pathogens? Or, might he suggest that new molecular techniques may prove a better way forward for quickly detecting the true microbial diversity of wounds? As modern clinicians faced with treating complex patients with diabetic foot infections (DFI), should we still request venerated and familiar culture and sensitivity methods, or is it time to ask for newer molecular tests, such as 16S rRNA gene sequencing? Or, are molecular techniques as yet too experimental, non-specific and expensive for current clinical use? While molecular techniques help us to identify more microorganisms from a DFI, can they tell us 'who done it?', that is, which are the causative pathogens and which are merely colonizers? Furthermore, can molecular techniques provide clinically relevant, rapid information on the virulence of wound isolates and their antibiotic sensitivities? We herein review current knowledge on the microbiology of DFI, from standard culture methods to the current era of rapid and comprehensive 'crime scene investigation' (CSI) techniques.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can molecular DNA-based techniques unravel the truth about diabetic foot infections?Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017 Jan;33(1). doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2834. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 27291330 Review.
-
Quantitation and composition of cutaneous microbiota in diabetic and nondiabetic men.J Infect Dis. 2013 Apr;207(7):1105-14. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit005. Epub 2013 Jan 8. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23300163 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from inpatients with infected diabetic foot ulcers in an Algerian University Hospital.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013 Sep;19(9):E398-404. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12199. Epub 2013 Mar 23. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013. PMID: 23521557
-
Susceptibility patterns of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in diabetic foot infections.BMC Microbiol. 2016 Jun 23;16(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0737-0. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27339028 Free PMC article.
-
The role of anaerobes in diabetic foot infections.Anaerobe. 2015 Aug;34:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Anaerobe. 2015. PMID: 25841893 Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus Toxins and Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Role in Pathogenesis and Interest in Diagnosis.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jul 7;8(7):209. doi: 10.3390/toxins8070209. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27399775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utility of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Nares Screening for Patients with a Diabetic Foot Infection.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Mar 24;64(4):e02213-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02213-19. Print 2020 Mar 24. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 31988097 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Genetic Analysis of Multidrug Resistant Bacteria from Diabetic Foot Ulcers.Front Microbiol. 2016 Jan 5;6:1464. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01464. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26779134 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic wound microbiome.BMC Med. 2020 Nov 24;18(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01820-6. BMC Med. 2020. PMID: 33228639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiotic Treatment Practices and Microbial Profile in Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Cureus. 2024 Aug 17;16(8):e67084. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67084. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39286701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vallery-Radot R: The Life of Pasteur, vol. II. In Translation from the French by Mrs RL Devonshire. 1902.
-
- Prompers L, Schaper N, Apelqvist J, Edmonds M, Jude E, Mauricio D, Uccioli L, Urbancic V, Bakker K, Holstein P, Jirkovska A, Piaggesi A, Ragnarson-Tennvall G, Reike H, Spraul M, Van Acker K, Van Baal J, Van Merode F, Ferreira I, Huijberts M. Prediction of outcome in individuals with diabetic foot ulcers: focus on the differences between individuals with and without peripheral arterial disease: The EURODIALE Study. Diabetologia. 2008;51:747–755. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-0940-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

