Clinical efficacy of oral ganciclovir for prophylaxis and treatment of recurrent herpes simplex keratitis
- PMID: 25563312
- PMCID: PMC4837818
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.147808
Clinical efficacy of oral ganciclovir for prophylaxis and treatment of recurrent herpes simplex keratitis
Erratum in
-
Clinical efficacy of oral ganciclovir for prophylaxis and treatment of recurrent herpes simplex keratitis: corrigendum.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015 Feb 5;128(3):426. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.150128. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015. PMID: 25635450 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Corrigendum: Clinical Efficacy of Oral Ganciclovir for Prophylaxis and Treatment of Recurrent Herpes Simplex Keratitis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Jan 5;129(1):115. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.172610. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 26712448 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Herpes simplex keratitis (HSK) caused by herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1), which has high recurrent rate and incidence of severe vision loss, is the leading cause of infectious blindness in the world. The aim was to explore the clinical efficacy of oral ganciclovir (GCV) in the prevention of recurrent HSK.
Methods: A multicenter, prospective, randomized, single-blind, and controlled clinical trial was conducted from April 2010 to June 2013. One hundred seventy-three patients (173 eyes involved) who were diagnosed as recurrent HSK definitely, including stromal keratitis and corneal endotheliitis, were divided into three groups randomly: negative control (placebo) group was topically administered with 0.15% GCV ophthalmic gel, 4 times per day and 0.1% fluorometholone eye drops, 3 times per day until resolution of HSK; positive control acyclovir (ACV) group was topically adopted the same ophthalmic gel and eye drops and additionally received oral ACV 400 mg 5 times a day for 10 weeks and followed by 400 mg 2 times per day for 6 months; test GCV group was topically adopted the same treatment as negative control group and additionally received oral GCV 1000 mg 3 times per day for 8 weeks. The symptoms and signs were evaluated before and after the therapy 1 st week, 2 nd week and then followed up every 2 weeks until recovery. Furthermore, we followed up recurrence of HSK for every 3 months after recovery and then assessed the cure time, recurrent rate and adverse reactions.
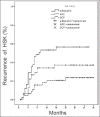
Results: One hundred and seventy-three patients were followed up 7-48 months (mean 32.1 ± 12.3 months), but 34 patients were failed to follow-up. The cure time was 12.1 ± 4.3, 11.9 ± 4.0 weeks in negative control (placebo) group and positive control ACV group respectively (P = 0.991), which was longer than that in test GCV group (8.6 ± 2.8 weeks) and there was a significant difference between test GCV group and negative control (placebo) group or positive control ACV group (P = 0.000). Furthermore, the recurrent rate was higher in negative control (placebo) group (47.3%) than that in positive control group ACV (26.7%) and test GCV group (17.2%), and there was a great significant difference among the three groups (P = 0.007), but there was no significant difference between positive control ACV group and test GCV group (P = 0.358). In addition, there was no obvious adverse reaction expect neutropenia (only one patient in test GCV group).
Conclusion: Short-term oral GCV could cure recurrent HSK and endotheliitis, shorten the course, reduce recurrent rate of HSK and have confirmed safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Clinical assessment of oral ganciclovir capsules on the treatment of herpes simplex keratitis].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Nov;46(11):994-9. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21211295 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Effectiveness and safety of 0.15% ganciclovir in situ ophthalmic gel for herpes simplex keratitis - a multicenter, randomized, investigator-masked, parallel group study in Chinese patients.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013 Apr 29;7:361-8. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S42624. Print 2013. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013. PMID: 23761964 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
6-Thioguanine Inhibits Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection of Eyes.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0064621. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00646-21. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34730435 Free PMC article.
-
[Herpes simplex virus latency, reactivation, and a new antiviral therapy for herpetic keratitis].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2008 Mar;112(3):247-64; discussion 265. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 18411713 Review. Japanese.
-
Ganciclovir ophthalmic gel 0.15%: safety and efficacy of a new treatment for herpes simplex keratitis.Curr Eye Res. 2012 Jul;37(7):654-60. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2012.692846. Epub 2012 May 18. Curr Eye Res. 2012. PMID: 22607463 Review.
Cited by
-
Successful Management of Herpes Simplex Keratitis With Oral Valganciclovir in Patients Unresponsive or Allergic to Conventional Antiviral Therapy.Cornea. 2019 Jun;38(6):663-667. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000001917. Cornea. 2019. PMID: 30882539 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy of oral ganciclovir for prophylaxis and treatment of recurrent herpes simplex keratitis: corrigendum.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015 Feb 5;128(3):426. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.150128. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015. PMID: 25635450 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Corrigendum: Clinical Efficacy of Oral Ganciclovir for Prophylaxis and Treatment of Recurrent Herpes Simplex Keratitis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Jan 5;129(1):115. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.172610. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 26712448 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Synthesis and pharmacophore modelling of 2,6,9-trisubstituted purine derivatives and their potential role as apoptosis-inducing agents in cancer cell lines.Molecules. 2015 Apr 15;20(4):6808-26. doi: 10.3390/molecules20046808. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25884555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biser SA, Perry HD. Corneal and Anterior Segment Diseases – Herpes Simplex Keratitis. Ophthal Hyperguide: Corneal and Anterior Segment Diseases. c2006. [Last cited 2007 Jan 10]. Availabe from: http://ophthalmic.hyperguides.com .
-
- Remeijer L, Maertzdorf J, Doornenbal P, Verjans GM, Osterhaus AD. Herpes simplex virus 1 transmission through corneal transplantation. Lancet. 2001;357:442. - PubMed
-
- Remeijer L, Maertzdorf J, Buitenwerf J, Osterhaus AD, Verjans GM. Corneal herpes simplex virus type 1 superinfection in patients with recrudescent herpetic keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43:358–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous