HDL from apoA1 transgenic mice expressing the 4WF isoform is resistant to oxidative loss of function
- PMID: 25561462
- PMCID: PMC4340312
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M056754
HDL from apoA1 transgenic mice expressing the 4WF isoform is resistant to oxidative loss of function
Abstract
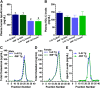
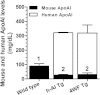
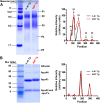
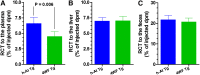
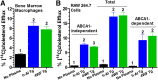
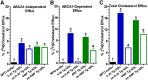
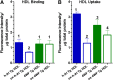
HDL functions are impaired by myeloperoxidase (MPO), which selectively targets and oxidizes human apoA1. We previously found that the 4WF isoform of human apoA1, in which the four tryptophan residues are substituted with phenylalanine, is resistant to MPO-mediated loss of function. The purpose of this study was to generate 4WF apoA1 transgenic mice and compare functional properties of the 4WF and wild-type human apoA1 isoforms in vivo. Male mice had significantly higher plasma apoA1 levels than females for both isoforms of human apoA1, attributed to different production rates. With matched plasma apoA1 levels, 4WF transgenics had a trend for slightly less HDL-cholesterol versus human apoA1 transgenics. While 4WF transgenics had 31% less reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) to the plasma compartment, equivalent RCT to the liver and feces was observed. Plasma from both strains had similar ability to accept cholesterol and facilitate ex vivo cholesterol efflux from macrophages. Furthermore, we observed that 4WF transgenic HDL was partially (∼50%) protected from MPO-mediated loss of function while human apoA1 transgenic HDL lost all ABCA1-dependent cholesterol acceptor activity. In conclusion, the structure and function of HDL from 4WF transgenic mice was not different than HDL derived from human apoA1 transgenic mice.
Keywords: ATP binding cassette transporter A1; apolipoprotein A1; cholesterol efflux; dysfunctional high density lipoprotein; myeloperoxidase; reverse cholesterol transport.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PI(4,5)P2 Is Translocated by ABCA1 to the Cell Surface Where It Mediates Apolipoprotein A1 Binding and Nascent HDL Assembly.Circ Res. 2016 Sep 16;119(7):827-38. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308856. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 27514935 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidant resistant human apolipoprotein A-I functions similarly to the unmodified human isoform in delaying atherosclerosis progression and promoting atherosclerosis regression in hyperlipidemic mice.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 4;17(2):e0259751. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259751. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35120132 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of high density lipoprotein by myeloperoxidase generates a pro-inflammatory particle.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 6;284(45):30825-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.047605. Epub 2009 Sep 2. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19726691 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo macrophage-specific RCT and antioxidant and antiinflammatory HDL activity measurements: New tools for predicting HDL atheroprotection.Atherosclerosis. 2009 Oct;206(2):321-7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.12.044. Epub 2009 Mar 21. Atherosclerosis. 2009. PMID: 19362310 Review.
-
Dysfunctional HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016 Jan;13(1):48-60. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.124. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26323267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imbalance of APOB Lipoproteins and Large HDL in Type 1 Diabetes Drives Atherosclerosis.Circ Res. 2024 Jul 5;135(2):335-349. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.323100. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Circ Res. 2024. PMID: 38828596 Free PMC article.
-
PI(4,5)P2 Is Translocated by ABCA1 to the Cell Surface Where It Mediates Apolipoprotein A1 Binding and Nascent HDL Assembly.Circ Res. 2016 Sep 16;119(7):827-38. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308856. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 27514935 Free PMC article.
-
Carbamylated lipoproteins in diabetes.World J Diabetes. 2023 Mar 15;14(3):159-169. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i3.159. World J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37035232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDL Function and Atherosclerosis: Reactive Dicarbonyls as Promising Targets of Therapy.Circ Res. 2023 May 26;132(11):1521-1545. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.321563. Epub 2023 May 25. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 37228232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methionine oxidized apolipoprotein A-I at the crossroads of HDL biogenesis and amyloid formation.FASEB J. 2018 Jun;32(6):3149-3165. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701127R. Epub 2018 Jan 17. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29401604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gordon D. J., Probstfield J. L., Garrison R. J., Neaton J. D., Castelli W. P., Knoke J. D., Jacobs D. R., Jr, Bangdiwala S., Tyroler H. A. 1989. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Four prospective American studies. Circulation. 79: 8–15. - PubMed
-
- Barter P. J., Caulfield M., Eriksson M., Grundy S. M., Kastelein J. J., Komajda M., Lopez-Sendon J., Mosca L., Tardif J. C., Waters D. D., et al. 2007. Effects of torcetrapib in patients at high risk for coronary events. N. Engl. J. Med. 357: 2109–2122. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz G. G., Olsson A. G., Abt M., et al. dal-OUTCOMES Investigators. 2012. Effects of dalcetrapib in patients with a recent acute coronary syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 367: 2089–2099. - PubMed
-
- Michos E. D., Sibley C. T., Baer J. T., Blaha M. J., Blumenthal R. S. 2012. Niacin and statin combination therapy for atherosclerosis regression and prevention of cardiovascular disease events: reconciling the AIM-HIGH (Atherothrombosis Intervention in Metabolic Syndrome with Low HDL/High Triglycerides: Impact on Global Health Outcomes) trial with previous surrogate endpoint trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 59: 2058–2064. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

