The protective effect of FGF21 on diabetes-induced male germ cell apoptosis is associated with up-regulated testicular AKT and AMPK/Sirt1/PGC-1α signaling
- PMID: 25560828
- PMCID: PMC6285187
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2014-1619
The protective effect of FGF21 on diabetes-induced male germ cell apoptosis is associated with up-regulated testicular AKT and AMPK/Sirt1/PGC-1α signaling
Abstract
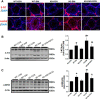
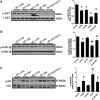
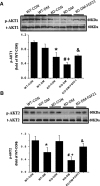
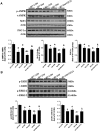
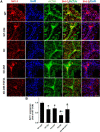
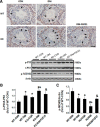
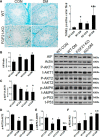
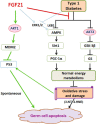
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a metabolic regulator that is required for normal spermatogenesis and protects against diabetes-induced germ cell apoptosis. Here, we tried to define whether diabetes-induced germ cell apoptosis that is predominantly due to increased oxidative stress was associated with impaired glucose and fatty acid metabolism, by examining the effects of Fgf21 gene knockout (FGF21-KO) or FGF21 treatment on the glucose and fatty acid metabolic pathways in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Western blottings revealed that protein kinase B (AKT)-mediated glucose signaling was down-regulated in diabetic testes and further decreased in FGF21-KO diabetic group both 10 days and 2 months after diabetes onset, reflected by reduced glycogen synthase (GS) kinase (GSK)-3β phosphorylation and increased GS phosphorylation. Deletion of the Fgf21 gene also inactivated fatty acid metabolism-related factors, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), sirtuin 1 (Sirt1), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), along with exacerbating diabetes-induced testicular oxidative stress and damage. Treatment with recombinant FGF21 partially prevented these diabetic effects. In FGF21-KO nondiabetic mice, testicular AMPK/Sirt1/PGC-1α signaling was down-regulated and AKT1 and murine double minute 2 were inactivated along with the increased p53 expression but not AKT2, GSK-3β, and GS. These results suggest that the role of FGF21 in maintaining spermatogenesis is associated with its activation of AKT1 and inhibition of p53. Deletion of the Fgf21gene significantly exacerbates diabetes-induced down-regulation of testicular AKT/GSK-3β/GS and AMPK/Sirt1/PGC-1α pathways and testicular oxidative stress and cell apoptosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibroblast growth factor-21 prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy via AMPK-mediated antioxidation and lipid-lowering effects in the heart.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Feb 14;9(2):227. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0307-5. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29445083 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned media ameliorate diabetic endothelial dysfunction by improving mitochondrial bioenergetics via the Sirt1/AMPK/PGC-1α pathway.Clin Sci (Lond). 2016 Dec 1;130(23):2181-2198. doi: 10.1042/CS20160235. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016. PMID: 27613156
-
Neohesperidin Exerts Lipid-Regulating Effects in vitro and in vivo via Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and AMP-Activated Protein Kinase/Sirtuin Type 1/Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Coactivator 1α Signaling Axis.Pharmacology. 2017;100(3-4):115-126. doi: 10.1159/000452492. Epub 2017 May 30. Pharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28554169
-
Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):1939-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770291 Review.
-
[Recent advances in the study of AMPK and inflammatory pulmonary disease].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2014 Aug;49(8):1089-96. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 25322548 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Activation of the sweet taste receptor, T1R3, by the artificial sweetener sucralose regulates the pulmonary endothelium.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Jan 1;314(1):L165-L176. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00490.2016. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28971978 Free PMC article.
-
Metallothionein Is Downstream of Nrf2 and Partially Mediates Sulforaphane Prevention of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Diabetes. 2017 Feb;66(2):529-542. doi: 10.2337/db15-1274. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 27903744 Free PMC article.
-
Rifaximin Protects against Malathion-Induced Rat Testicular Toxicity: A Possible Clue on Modulating Gut Microbiome and Inhibition of Oxidative Stress by Mitophagy.Molecules. 2022 Jun 24;27(13):4069. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134069. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807317 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Akt2 in the Protective Effect of Fenofibrate against Diabetic Nephropathy.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Jan 1;16(4):553-567. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.40643. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32025205 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-34a targets sirtuin 1 and leads to diabetes-induced testicular apoptotic cell death.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Sep;96(9):939-949. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1667-0. Epub 2018 Jul 21. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30030567
References
-
- Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, Koukos G, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARα and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 2007;5:426–437. - PubMed
-
- Gälman C, Lundåsen T, Kharitonenkov A, et al. . The circulating metabolic regulator FGF21 is induced by prolonged fasting and PPARα activation in man. Cell Metab. 2008;8:169–174. - PubMed
-
- Planavila A, Redondo I, Hondares E, et al. . Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against cardiac hypertrophy in mice. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

