Mice lacking the SLAM family member CD84 display unaltered platelet function in hemostasis and thrombosis
- PMID: 25551754
- PMCID: PMC4281120
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115306
Mice lacking the SLAM family member CD84 display unaltered platelet function in hemostasis and thrombosis
Abstract
Background: Platelets are anuclear cell fragments derived from bone marrow megakaryocytes that safeguard vascular integrity by forming thrombi at sites of vascular injury. Although the early events of thrombus formation--platelet adhesion and aggregation--have been intensively studied, less is known about the mechanisms and receptors that stabilize platelet-platelet interactions once a thrombus has formed. One receptor that has been implicated in this process is the signaling lymphocyte activation molecule (SLAM) family member CD84, which can undergo homophilic interactions and becomes phosphorylated upon platelet aggregation.
Objective: The role of CD84 in platelet physiology and thrombus formation was investigated in CD84-deficient mice.
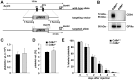
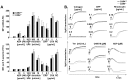
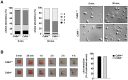
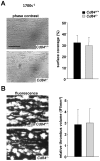
Methods and results: We generated CD84-deficient mice and analyzed their platelets in vitro and in vivo. Cd84(-/-) platelets exhibited normal activation and aggregation responses to classical platelet agonists. Furthermore, CD84 deficiency did not affect integrin-mediated clot retraction and spreading of activated platelets on fibrinogen. Notably, also the formation of stable three-dimensional thrombi on collagen-coated surfaces under flow ex vivo was unaltered in the blood of Cd84(-/-) mice. In vivo, Cd84(-/-) mice exhibited unaltered hemostatic function and arterial thrombus formation.
Conclusion: These results show that CD84 is dispensable for thrombus formation and stabilization, indicating that its deficiency may be functionally compensated by other receptors or that it may be important for platelet functions different from platelet-platelet interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of platelet and endothelial GARP in thrombosis and hemostasis.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 9;12(3):e0173329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173329. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28278197 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet aggregation induces platelet aggregate stability via SLAM family receptor signaling.Blood. 2005 Nov 1;106(9):3028-34. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0333. Epub 2005 Jul 21. Blood. 2005. PMID: 16037392
-
The SLAM family member CD84 is regulated by ADAM10 and calpain in platelets.J Thromb Haemost. 2012 Dec;10(12):2581-92. doi: 10.1111/jth.12013. J Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 23025437
-
Novel targets for antithrombotic drug discovery.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2006 Mar-Apr;36(2):228-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.12.026. Epub 2006 Feb 13. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2006. PMID: 16473533 Review.
-
Role of platelets in thrombosis and hemostasis.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;72(3):278-84. doi: 10.1139/y94-043. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 8069774 Review.
Cited by
-
The homophilic CD84 receptor is upregulated on platelets in COVID-19 and sepsis.Thromb Res. 2022 Dec;220:121-124. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2022.10.011. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Thromb Res. 2022. PMID: 36334399 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The role of platelet and endothelial GARP in thrombosis and hemostasis.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 9;12(3):e0173329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173329. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28278197 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Rap1/Talin1 interaction regulates platelet and neutrophil integrin activity in mice.Blood. 2018 Dec 27;132(26):2754-2762. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-04-846766. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Blood. 2018. PMID: 30442677 Free PMC article.
-
One immune cell to bind them all: platelet contribution to neurodegenerative disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Sep 27;19(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00754-4. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39334369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Immune Responses by Platelet-Derived ADAM10.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 5;11:44. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00044. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32117229 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nieswandt B, Aktas B, Moers A, Sachs UJ (2005) Platelets in atherothrombosis: lessons from mouse models. Journal of thrombosis and haemostasis: JTH 3:1725–1736. - PubMed
-
- Jackson SP (2011) Arterial thrombosis–insidious, unpredictable and deadly. Nat Med 17:1423–1436. - PubMed
-
- Nieswandt B, Pleines I, Bender M (2011) Platelet adhesion and activation mechanisms in arterial thrombosis and ischaemic stroke. J Thromb Haemost 9 Suppl 1 92–104. - PubMed
-
- Watson SP, Auger JM, McCarty OJ, Pearce AC (2005) GPVI and integrin alphaIIb beta3 signaling in platelets. J Thromb Haemost 3:1752–1762. - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg MH, Partridge A, Shattil SJ (2005) Integrin regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:509–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

