Setd1a regulates progenitor B-cell-to-precursor B-cell development through histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation and Ig heavy-chain rearrangement
- PMID: 25550471
- PMCID: PMC4396605
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.14-263061
Setd1a regulates progenitor B-cell-to-precursor B-cell development through histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation and Ig heavy-chain rearrangement
Abstract
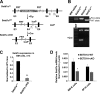
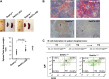
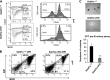
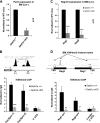
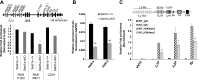
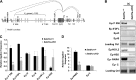
SETD1A is a member of trithorax-related histone methyltransferases that methylate lysine 4 at histone H3 (H3K4). We showed previously that Setd1a is required for mesoderm specification and hematopoietic lineage differentiation in vitro. However, it remains unknown whether or not Setd1a controls specific hematopoietic lineage commitment and differentiation during animal development. Here, we reported that homozygous Setd1a knockout (KO) mice are embryonic lethal. Loss of the Setd1a gene in the hematopoietic compartment resulted in a blockage of the progenitor B-cell-to-precursor B-cell development in bone marrow (BM) and B-cell maturation in spleen. The Setd1a-cKO (conditional knockout) mice exhibited an enlarged spleen with disrupted spleen architecture and leukocytopenia. Mechanistically, Setd1a deficiency in BM reduced the levels of H3K4me3 at critical B-cell gene loci, including Pax5 and Rag1/2, which are critical for the IgH (Ig heavy-chain) locus contractions and rearrangement. Subsequently, the differential long-range looped interactions of the enhancer Eμ with proximal 5' DH region and 3' regulatory regions as well as with Pax5-activated intergenic repeat elements and 5' distal VH genes were compromised by the Setd1a-cKO. Together, our findings revealed a critical role of Setd1a and its mediated epigenetic modifications in regulating the IgH rearrangement and B-cell development.
Keywords: B-cell differentiation; Setd1a KO mice; long-range chromatin loops; promoter H3K4me3; transcriptional regulation.
© FASEB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Setd1a and NURF mediate chromatin dynamics and gene regulation during erythroid lineage commitment and differentiation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 6;44(15):7173-88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw327. Epub 2016 May 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27141965 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modifications of the VH region after DJH recombination in Pro-B cells.Immunology. 2017 Oct;152(2):218-231. doi: 10.1111/imm.12758. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 28502113 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal patterns of methylation of H3K36 and H3K27 on proximal vs. distal IgVH genes are modulated by IL-7 and Pax5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jun 24;105(25):8685-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711758105. Epub 2008 Jun 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18562282 Free PMC article.
-
The role of SETD1A and SETD1B in development and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020 Aug;1863(8):194578. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194578. Epub 2020 May 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020. PMID: 32389824 Review.
-
Distinct functions of histone H3, lysine 4 methyltransferases in normal and malignant hematopoiesis.Curr Opin Hematol. 2017 Jul;24(4):322-328. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000346. Curr Opin Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28375985 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Setd1a and NURF mediate chromatin dynamics and gene regulation during erythroid lineage commitment and differentiation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 6;44(15):7173-88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw327. Epub 2016 May 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27141965 Free PMC article.
-
COMPASS and SWI/SNF complexes in development and disease.Nat Rev Genet. 2021 Jan;22(1):38-58. doi: 10.1038/s41576-020-0278-0. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Nat Rev Genet. 2021. PMID: 32958894 Review.
-
Epigenetic maintenance of adult neural stem cell quiescence in the mouse hippocampus via Setd1a.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 6;15(1):5674. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50010-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38971831 Free PMC article.
-
Histone lysine methyltransferases in biology and disease.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019 Oct;26(10):880-889. doi: 10.1038/s41594-019-0298-7. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31582846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic control in skin development, homeostasis and injury repair.Exp Dermatol. 2019 Apr;28(4):453-463. doi: 10.1111/exd.13872. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Exp Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30624812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wysocka J., Swigut T., Milne T. A., Dou Y., Zhang X., Burlingame A. L., Roeder R. G., Brivanlou A. H., Allis C. D. (2005) WDR5 associates with histone H3 methylated at K4 and is essential for H3 K4 methylation and vertebrate development. Cell 121, 859–872 - PubMed
-
- Dou Y., Milne T. A., Ruthenburg A. J., Lee S., Lee J. W., Verdine G. L., Allis C. D., Roeder R. G. (2006) Regulation of MLL1 H3K4 methyltransferase activity by its core components. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 713–719 - PubMed
-
- Mohan M., Lin C., Guest E., Shilatifard A. (2010) Licensed to elongate: a molecular mechanism for MLL-based leukaemogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10, 721–728 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

