Oxamflatin treatment enhances cloned porcine embryo development and nuclear reprogramming
- PMID: 25548976
- PMCID: PMC4312790
- DOI: 10.1089/cell.2014.0075
Oxamflatin treatment enhances cloned porcine embryo development and nuclear reprogramming
Abstract
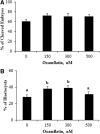
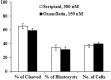
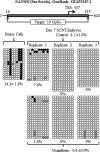
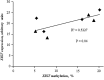
Faulty epigenetic reprogramming of somatic nuclei is thought to be the main reason for low cloning efficiency by somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT). Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi), such as Scriptaid, improve developmental competence of SCNT embryos in several species. Another HDACi, Oxamflatin, is about 100 times more potent than Scriptaid in the ability to inhibit nuclear-specific HDACs. The present study determined the effects of Oxamflatin treatment on embryo development, DNA methylation, and gene expression. Oxamflatin treatment enhanced blastocyst formation of SCNT embryos in vitro. Embryo transfer produced more pigs born and fewer mummies from the Oxamflatin-treated group compared to the Scriptaid-treated positive control. Oxamflatin also decreased DNA methylation of POU5F1 regulatory elements and centromeric repeat elements in day-7 blastocysts. When compared to in vitro-fertilized (IVF) embryos, the methylation status of POU5F1, NANOG, and centromeric repeat was similar in the cloned embryos, indicating these genes were successfully reprogrammed. However, compared to the lack of methylation of XIST in day-7 IVF embryos, a higher methylation level in day-7 cloned embryos was observed, implying that X chromosomes were activated in day-7 IVF blastocysts, but were not fully activated in cloned embryos, i.e., reprogramming of XIST was delayed. A time-course analysis of XIST DNA methylation on day-13, -15, -17, and -19 in vivo embryos revealed that XIST methylation initiated at about day 13 and was not completed by day 19. The methylation of the XIST gene in day-19 control cloned embryos was delayed again when compared to in vivo embryos. However, methylation of XIST in Oxamflatin-treated embryos was comparable with in vivo embryos, which further demonstrated that Oxamflatin could accelerate the delayed reprogramming of XIST gene and thus might improve cloning efficiency.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Oxamflatin improves developmental competence of porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos.Cell Reprogram. 2012 Oct;14(5):398-406. doi: 10.1089/cell.2012.0007. Cell Reprogram. 2012. PMID: 23013534
-
BIX-01294 increases pig cloning efficiency by improving epigenetic reprogramming of somatic cell nuclei.Reproduction. 2016 Jan;151(1):39-49. doi: 10.1530/REP-15-0460. Reproduction. 2016. PMID: 26604326
-
Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitor oxamflatin on in vitro porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos.Cell Reprogram. 2014 Aug;16(4):253-65. doi: 10.1089/cell.2013.0058. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Cell Reprogram. 2014. PMID: 24960409 Free PMC article.
-
[Advances in epigenetic reprogramming of somatic cells nuclear transfer in mammals].Yi Chuan. 2019 Dec 20;41(12):1099-1109. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-193. Yi Chuan. 2019. PMID: 31857281 Review. Chinese.
-
Effects of trichostatin A on pig SCNT blastocyst formation rate and cell number: A meta-analysis.Res Vet Sci. 2018 Apr;117:161-166. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2017.12.011. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Res Vet Sci. 2018. PMID: 29277014 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial cloning of domestic animals.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 21;112(29):8874-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1501718112. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26195770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of omics and nanotechnology to improve pig embryo production in vitro.Mol Reprod Dev. 2019 Nov;86(11):1531-1547. doi: 10.1002/mrd.23260. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Mol Reprod Dev. 2019. PMID: 31478591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
XIST Derepression in Active X Chromosome Hinders Pig Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer.Stem Cell Reports. 2018 Feb 13;10(2):494-508. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.12.015. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Stem Cell Reports. 2018. PMID: 29337117 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1-dependent modulation of methylation and acetylation of histone H3 on lysine 9 (H3K9) in the zygotic pronuclei improves porcine embryo development.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 1;8:83. doi: 10.1186/s40104-017-0214-0. eCollection 2017. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29118980 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Crotonylation on Reprogramming of Cashmere Goat Somatic Cells with Different Differentiation Degrees.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 19;12(20):2848. doi: 10.3390/ani12202848. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong L., Lako M., Dean W., and Stojkovic M. (2006). Epigenetic modification is central to genome reprogramming in somatic cell nuclear transfer. Stem Cells 24, 805–814 - PubMed
-
- Bauer B.K., Spate L.D., Murphy C.N., and Prather R.S. (2010). Arginine supplementation in vitro increases porcine embryo development and affects mRNA transcript expression. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 23, 107–107
-
- Cervoni N., and Szyf M. (2001). Demethylase activity is directed by histone acetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 40778–40787 - PubMed
-
- Do J.T., Han D.W., Gentile L., Sobek-Klocke I., Stehling M., and Scholer H.R. (2008). Enhanced reprogramming of Xist by induced upregulation of Tsix and Dnmt3a. Stem Cells 26, 2821–2831 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

