Two-component regulators control hilA expression by controlling fimZ and hilE expression within Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 25547794
- PMCID: PMC4333451
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.02506-14
Two-component regulators control hilA expression by controlling fimZ and hilE expression within Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
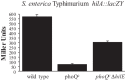
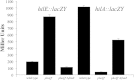
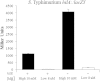
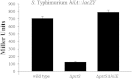
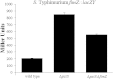
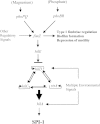
Salmonellae initiate disease through the invasion of host cells within the intestine. This ability to invade requires the coordinated action of numerous genes, many of which are found within Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1). The key to this process is the ability of the bacteria to respond to the environment, thereby upregulating the necessary genes under optimal conditions. Central to the control of SPI-1 is the transcriptional activator hilA. Work has identified at least 10 different activators and 8 different repressors responsible for the control of hilA. We have previously shown that hilE is a Salmonella-specific negative regulator that is able to repress hilA expression and invasion. Additionally, fimZ, a transcriptional activator responsible for the expression of type I fimbriae as well as flagellar genes, has also been implicated in this process. fimZ is homologous to response regulators from other two-component regulatory systems, although a sensor for the system has not been identified. The phoPQ and phoBR regulons are both two-component systems that negatively affect hilA expression, although the mechanism of action has not been determined. Our results show that PhoBR is capable of inducing fimZ expression, whereas PhoPQ does not affect fimZ expression but does upregulate hilE in an FimZ-dependent manner. Therefore, phosphate (sensed by PhoBR) and magnesium (sensed by PhoPQ) levels are important in controlling hilA expression levels when Salmonella is in the intestinal environment.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The fimYZ genes regulate Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium invasion in addition to type 1 fimbrial expression and bacterial motility.Infect Immun. 2005 Mar;73(3):1377-85. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.3.1377-1385.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15731035 Free PMC article.
-
Delineation of the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium HilA regulon through genome-wide location and transcript analysis.J Bacteriol. 2007 Jul;189(13):4587-96. doi: 10.1128/JB.00178-07. Epub 2007 May 4. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17483226 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinate regulation of Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI1) and SPI4 in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2008 Mar;76(3):1024-35. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01224-07. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18160484 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella invasion gene regulation: a story of environmental awareness.J Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43 Spec No:110-7. J Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15765064 Review.
-
Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;10(1):24-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17208038 Review.
Cited by
-
Three tandem promoters, together with IHF, regulate growth phase dependent expression of the Escherichia coli kps capsule gene cluster.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 20;7(1):17924. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17891-0. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29263430 Free PMC article.
-
PhoP-Mediated Repression of the SPI1 Type 3 Secretion System in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jul 24;201(16):e00264-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00264-19. Print 2019 Aug 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31182495 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction pathway mediated by the novel regulator LoiA for low oxygen tension induced Salmonella Typhimurium invasion.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jun 2;13(6):e1006429. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006429. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28575106 Free PMC article.
-
HilE is required for synergistic activation of SPI-1 gene expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Feb 16;21(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02110-8. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33593291 Free PMC article.
-
HilE Regulates HilD by Blocking DNA Binding in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2018 Mar 26;200(8):e00750-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00750-17. Print 2018 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29378886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CDC. 2010. Salmonella. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA: http://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/index.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

