Signalling Through Retinoic Acid Receptors is Required for Reprogramming of Both Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast Cells and Epiblast Stem Cells to Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 25546009
- PMCID: PMC4863141
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.1926
Signalling Through Retinoic Acid Receptors is Required for Reprogramming of Both Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast Cells and Epiblast Stem Cells to Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
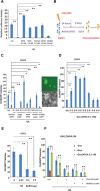
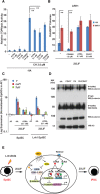
We previously demonstrated that coexpressing retinoic acid (RA) receptor gamma and liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH1 or NR5A2) with OCT4, MYC, KLF4, and SOX2 (4F) rapidly reprograms mouse embryonic fibroblast cells (MEFs) into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Here, we further explore the role of RA in reprogramming and report that the six factors (6F) efficiently and directly reprogram MEFs into integration-free iPSCs in defined medium (N2B27) in the absence of feeder cells. Through genetic and chemical approaches, we find that RA signalling is essential, in a highly dose-sensitive manner, for MEF reprogramming. The removal of exogenous RA from N2B27, the inhibition of endogenous RA synthesis or the expression of a dominant-negative form of RARA severely impedes reprogramming. By contrast, supplementing N2B27 with various retinoids substantially boosts reprogramming. In addition, when coexpressed with LRH1, RA receptors (RARs) can promote reprogramming in the absence of both exogenous and endogenously synthesized RA. Remarkably, the reprogramming of epiblast stem cells into embryonic stem cell-like cells also requires low levels of RA, which can modulate Wnt signalling through physical interactions of RARs with β-catenin. These results highlight the important functions of RA signalling in reprogramming somatic cells and primed stem cells to naïve pluripotency. Stem Cells 2015;33:1390-1404.
Keywords: Epiblast stem cells; Induced pluripotent stem cells; Liver receptor homolog-1; Reprogramming; Retinoic acid receptor gamma; Retinoic acid receptors; β-Catenin.
© 2014 AlphaMed Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid and efficient reprogramming of somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells by retinoic acid receptor gamma and liver receptor homolog 1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Nov 8;108(45):18283-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100893108. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21990348 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous expression of reprogramming factors induces and maintains mouse pluripotency without specific growth factors and signaling inhibitors.Cell Prolif. 2021 Aug;54(8):e13090. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13090. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Cell Prolif. 2021. PMID: 34197016 Free PMC article.
-
Derivation of novel human ground state naive pluripotent stem cells.Nature. 2013 Dec 12;504(7479):282-6. doi: 10.1038/nature12745. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24172903
-
Accessing naïve human pluripotency.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012 Jun;22(3):272-82. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.03.001. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012. PMID: 22463982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoic acid signaling and mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation: Cross talk between genomic and non-genomic effects of RA.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jan;1851(1):66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 24768681 Review.
Cited by
-
Capturing Human Naïve Pluripotency in the Embryo and in the Dish.Stem Cells Dev. 2017 Aug 15;26(16):1141-1161. doi: 10.1089/scd.2017.0055. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Stem Cells Dev. 2017. PMID: 28537488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of vitamins in stem cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 May;77(9):1771-1791. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03352-6. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31676963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Positive feedback between retinoic acid and 2-phospho-L-ascorbic acid trisodium salt during somatic cell reprogramming.Cell Regen. 2020 Oct 1;9(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13619-020-00057-1. Cell Regen. 2020. PMID: 33000315 Free PMC article.
-
RXRα provokes tumor suppression through p53/p21/p16 and PI3K-AKT signaling pathways during stem cell differentiation and in cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2018 May 1;9(5):532. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0610-1. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29748541 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal activation of LRH-1 and RAR-γ in human pluripotent stem cells induces a functional naïve-like state.EMBO Rep. 2020 Oct 5;21(10):e47533. doi: 10.15252/embr.201847533. Epub 2020 Aug 16. EMBO Rep. 2020. PMID: 33252195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga‐Otto K et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 2007;318:1917–1920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

