The homeostatic role of neuropeptide Y in immune function and its impact on mood and behaviour
- PMID: 25545642
- PMCID: PMC4353849
- DOI: 10.1111/apha.12445
The homeostatic role of neuropeptide Y in immune function and its impact on mood and behaviour
Abstract
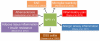
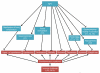
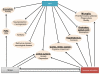
Neuropeptide Y (NPY), one of the most abundant peptides in the nervous system, exerts its effects via five receptor types, termed Y1, Y2, Y4, Y5 and Y6. NPY's pleiotropic functions comprise the regulation of brain activity, mood, stress coping, ingestion, digestion, metabolism, vascular and immune function. Nerve-derived NPY directly affects immune cells while NPY also acts as a paracrine and autocrine immune mediator, because immune cells themselves are capable of producing and releasing NPY. NPY is able to induce immune activation or suppression, depending on a myriad of factors such as the Y receptors activated and cell types involved. There is an intricate relationship between psychological stress, mood disorders and the immune system. While stress represents a risk factor for the development of mood disorders, it exhibits diverse actions on the immune system as well. Conversely, inflammation is regarded as an internal stressor and is increasingly recognized to contribute to the pathogenesis of mood and metabolic disorders. Intriguingly, the cerebral NPY system has been found to protect against distinct disturbances in response to immune challenge, attenuating the sickness response and preventing the development of depression. Thus, NPY plays an important homeostatic role in balancing disturbances of physiological systems caused by peripheral immune challenge. This implication is particularly evident in the brain in which NPY counteracts the negative impact of immune challenge on mood, emotional processing and stress resilience. NPY thus acts as a unique signalling molecule in the interaction of the immune system with the brain in health and disease.
Keywords: brain; immune system; neuropeptide Y.
© 2014 Scandinavian Physiological Society. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide in the gut-brain axis.Neuropeptides. 2012 Dec;46(6):261-74. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Neuropeptides. 2012. PMID: 22979996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intriguing mission of neuropeptide Y in the immune system.Amino Acids. 2013 Jul;45(1):41-53. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-1185-7. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Amino Acids. 2013. PMID: 22143431 Review.
-
Neuropeptide Y: A stressful review.Neuropeptides. 2016 Feb;55:99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2015.09.008. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Neuropeptides. 2016. PMID: 26441327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NPY and receptors in immune and inflammatory diseases.Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(17):1743-52. doi: 10.2174/156802607782341046. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17979783 Review.
-
Neuropeptide Y: a new mediator linking sympathetic nerves, blood vessels and immune system?Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003 Feb;81(2):89-94. doi: 10.1139/y03-006. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12710520 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of varying intensities of heat stress on neuropeptide Y and proopiomelanocortin mRNA expression in rats.Biomed Rep. 2020 Nov;13(5):39. doi: 10.3892/br.2020.1346. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Biomed Rep. 2020. PMID: 32934812 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertension and Low Body Weight Are Associated with Depressive Symptoms Only in Females: Findings from the Shika Study.Behav Sci (Basel). 2022 Oct 27;12(11):413. doi: 10.3390/bs12110413. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354390 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptides in gut-brain axis and their influence on host immunity and stress.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Mar 4;18:843-851. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.02.018. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32322366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota and the Neuroendocrine System.Neurotherapeutics. 2018 Jan;15(1):5-22. doi: 10.1007/s13311-017-0600-5. Neurotherapeutics. 2018. PMID: 29380303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Label-Free and 10-Plex DiLeu Isobaric Tag Quantitative Methods for Profiling Changes in the Mouse Hypothalamic Neuropeptidome and Proteome: Assessment of the Impact of the Gut Microbiome.Anal Chem. 2020 Oct 20;92(20):14021-14030. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02939. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32926775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abid K, Rochat B, Lassahn PG, Stocklin R, Michalet S, Brakch N, Aubert JF, Vatansever B, Tella P, De Meester I, Grouzmann E. Kinetic study of neuropeptide Y (NPY) proteolysis in blood and identification of NPY3-35: a new peptide generated by plasma kallikrein. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:24715–24724. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adrian TE, Savage AP, Bacarese-Hamilton AJ, Wolfe K, Besterman HS, Bloom SR. Peptide YY abnormalities in gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterology. 1986;90:379–384. - PubMed
-
- Ahlborg G, Weitzberg E, Sollevi A, Lundberg JM. Splanchnic and renal vasoconstrictor and metabolic responses to neuropeptide Y in resting and exercising man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992;145:139–149. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed AA, Wahbi A, Nordlind K, Kharazmi A, Sundqvist KG, Mutt V, Liden S. In vitro Leishmania major promastigote-induced macrophage migration is modulated by sensory and autonomic neuropeptides. Scand J Immunol. 1998;48:79–85. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed AA, Wahbi AH, Nordlin K. Neuropeptides modulate a murine monocyte/macrophage cell line capacity for phagocytosis and killing of Leishmania major parasites. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2001;23:397–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

