HSP90 inhibition enhances antimitotic drug-induced mitotic arrest and cell death in preclinical models of non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 25542032
- PMCID: PMC4277299
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115228
HSP90 inhibition enhances antimitotic drug-induced mitotic arrest and cell death in preclinical models of non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
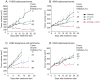
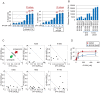
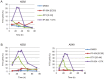
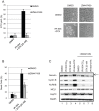
HSP90 inhibitors are currently undergoing clinical evaluation in combination with antimitotic drugs in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but little is known about the cellular effects of this novel drug combination. Therefore, we investigated the molecular mechanism of action of IPI-504 (retaspimycin HCl), a potent and selective inhibitor of HSP90, in combination with the microtubule targeting agent (MTA) docetaxel, in preclinical models of NSCLC. We identified a subset of NSCLC cell lines in which these drugs act in synergy to enhance cell death. Xenograft models of NSCLC demonstrated tumor growth inhibition, and in some cases, regression in response to combination treatment. Treatment with IPI-504 enhanced the antimitotic effects of docetaxel leading to the hypothesis that the mitotic checkpoint is required for the response to drug combination. Supporting this hypothesis, overriding the checkpoint with an Aurora kinase inhibitor diminished the cell death synergy of IPI-504 and docetaxel. To investigate the molecular basis of synergy, an unbiased stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) proteomic approach was employed. Several mitotic regulators, including components of the ubiquitin ligase, anaphase promoting complex (APC/C), were specifically down-regulated in response to combination treatment. Loss of APC/C by RNAi sensitized cells to docetaxel and enhanced its antimitotic effects. Treatment with a PLK1 inhibitor (BI2536) also sensitized cells to IPI-504, indicating that combination effects may be broadly applicable to other classes of mitotic inhibitors. Our data provide a preclinical rationale for testing the combination of IPI-504 and docetaxel in NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Hsp90 inhibitor IPI-504 rapidly lowers EML4-ALK levels and induces tumor regression in ALK-driven NSCLC models.Oncogene. 2011 Jun 2;30(22):2581-6. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.625. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21258415
-
Inhibition of Hsp90 down-regulates mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression and sensitizes EGFR mutant tumors to paclitaxel.Cancer Res. 2008 Jan 15;68(2):589-96. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1570. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18199556 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-drug loaded micelles delivering chemotherapy and targeted therapies directed against HSP90 and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in prostate cancer.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 28;12(3):e0174658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174658. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28350865 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer.Curr Opin Oncol. 2014 Mar;26(2):159-64. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000047. Curr Opin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24463348 Review.
-
Retaspimycin hydrochloride (IPI-504): a novel heat shock protein inhibitor as an anticancer agent.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 Sep;18(9):1375-83. doi: 10.1517/13543780903158934. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19642950 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting HSP90 as a Novel Therapy for Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Translational Relevance.Cells. 2022 Sep 6;11(18):2778. doi: 10.3390/cells11182778. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36139353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined HSP90 and kinase inhibitor therapy: Insights from The Cancer Genome Atlas.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015 Sep;20(5):729-41. doi: 10.1007/s12192-015-0604-1. Epub 2015 Jun 13. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015. PMID: 26070366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative T1 brain mapping in early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: longitudinal changes, lesion heterogeneity and disability.Eur Radiol. 2024 Jun;34(6):3826-3839. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10351-6. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37943312 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Dual HDAC6 and Tubulin Inhibitor, MPT0B451, Displays Anti-tumor Ability in Human Cancer Cells in Vitro and in Vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Mar 13;9:205. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00205. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29593536 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting polo-like kinase 1 suppresses essential functions of alloreactive T cells.Immunol Res. 2016 Jun;64(3):687-98. doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8778-2. Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 26724940
References
-
- Topham CH, Taylor SS (2013) Mitosis and apoptosis: how is the balance set? Curr Opin Cell Biol 25:780–785. - PubMed
-
- Jordan MA, Wilson L (2004) Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 4:253–265. - PubMed
-
- Rowinsky EK, Eisenhauer EA, Chaudhry V, Arbuck SG, Donehower RC (1993) Clinical toxicities encountered with paclitaxel (Taxol). Semin Oncol 20:1–15. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

