Silencing BMI1 eliminates tumor formation of pediatric glioma CD133+ cells not by affecting known targets but by down-regulating a novel set of core genes
- PMID: 25526772
- PMCID: PMC4289398
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-014-0160-4
Silencing BMI1 eliminates tumor formation of pediatric glioma CD133+ cells not by affecting known targets but by down-regulating a novel set of core genes
Abstract
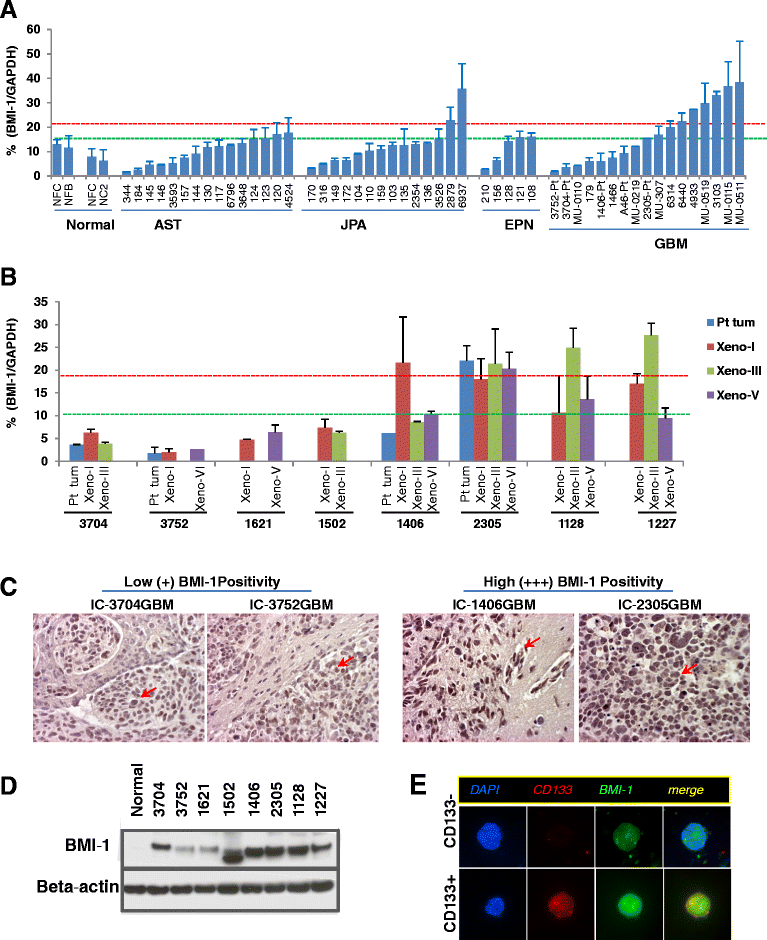
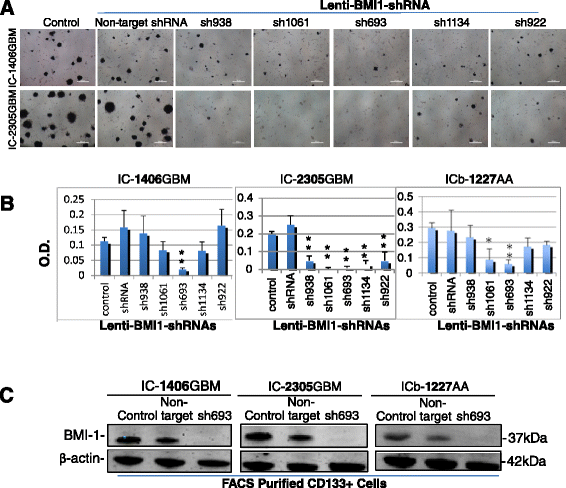
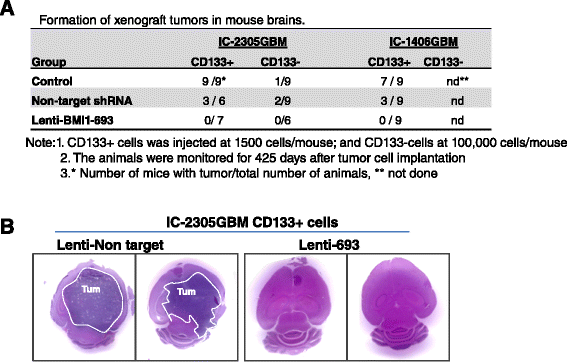
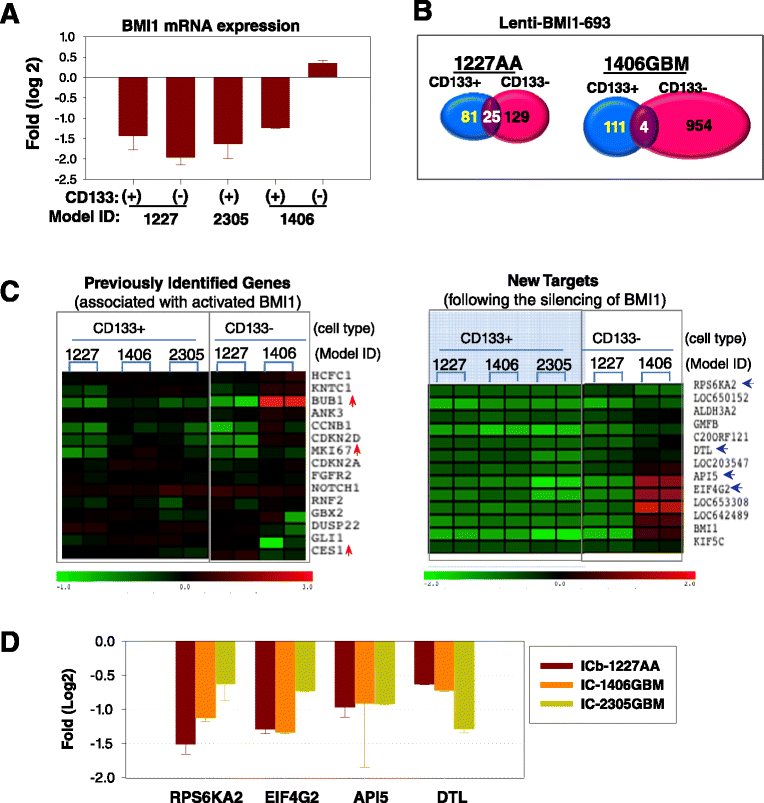
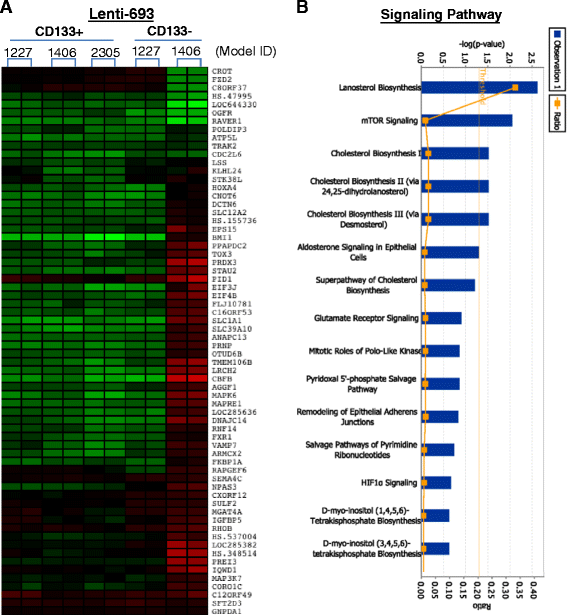
Clinical outcome of children with malignant glioma remains dismal. Here, we examined the role of over-expressed BMI1, a regulator of stem cell self-renewal, in sustaining tumor formation in pediatric glioma stem cells. Our investigation revealed BMI1 over-expression in 29 of 54 (53.7%) pediatric gliomas, 8 of 8 (100%) patient derived orthotopic xenograft (PDOX) mouse models, and in both CD133+ and CD133- glioma cells. We demonstrated that lentiviral-shRNA mediated silencing of suppressed cell proliferation in vitro in cells derived from 3 independent PDOX models and eliminated tumor-forming capacity of CD133+ and CD133- cells derived from 2 PDOX models in mouse brains. Gene expression profiling showed that most of the molecular targets of BMI1 ablation in CD133+ cells were different from that in CD133- cells. Importantly, we found that silencing BMI1 in CD133+ cells derived from 3 PDOX models did not affect most of the known genes previously associated with the activated BMI1, but modulated a novel set of core genes, including RPS6KA2, ALDH3A2, FMFB, DTL, API5, EIF4G2, KIF5c, LOC650152, C20ORF121, LOC203547, LOC653308, and LOC642489, to mediate the elimination of tumor formation. In summary, we identified the over-expressed BMI1 as a promising therapeutic target for glioma stem cells, and suggest that the signaling pathways associated with activated BMI1 in promoting tumor growth may be different from those induced by silencing BMI1 in blocking tumor formation. These findings highlighted the importance of careful re-analysis of the affected genes following the inhibition of abnormally activated oncogenic pathways to identify determinants that can potentially predict therapeutic efficacy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bmi1 marks intermediate precursors during differentiation of human brain tumor initiating cells.Stem Cell Res. 2012 Mar;8(2):141-53. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2011.09.008. Epub 2011 Oct 8. Stem Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22265735
-
Bmi1 regulates human glioblastoma stem cells through activation of differential gene networks in CD133+ brain tumor initiating cells.J Neurooncol. 2019 Jul;143(3):417-428. doi: 10.1007/s11060-019-03192-1. Epub 2019 May 21. J Neurooncol. 2019. PMID: 31115870
-
Cathepsin B and uPAR regulate self-renewal of glioma-initiating cells through GLI-regulated Sox2 and Bmi1 expression.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Mar;34(3):550-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs375. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23222817 Free PMC article.
-
Role of stemness-related molecules in neuroblastoma.Pediatr Res. 2012 Apr;71(4 Pt 2):511-5. doi: 10.1038/pr.2011.54. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Pediatr Res. 2012. PMID: 22430387 Review.
-
Insight into the complex regulation of CD133 in glioma.Int J Cancer. 2011 Feb 1;128(3):501-10. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25687. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 20853315 Review.
Cited by
-
Patient-Derived Models of Cancer in the NCI PDMC Consortium: Selection, Pitfalls, and Practical Recommendations.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 29;16(3):565. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030565. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD57 defines a novel cancer stem cell that drive invasion of diffuse pediatric-type high grade gliomas.Br J Cancer. 2024 Jul;131(2):258-270. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02724-5. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38834745
-
Circ_0060055 Promotes the Growth, Invasion, and Radioresistance of Glioblastoma by Targeting MiR-197-3p/API5 Axis.Neurotox Res. 2022 Oct;40(5):1292-1303. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00548-w. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 35849320
-
Glioma Stem Cells in Pediatric High-Grade Gliomas: From Current Knowledge to Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 4;14(9):2296. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092296. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Off-target effect of the BMI1 inhibitor PTC596 drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma multiforme.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2020 Jan 6;4:1. doi: 10.1038/s41698-019-0106-1. eCollection 2020. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31934644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolff JE, Driever PH, Erdlenbruch B, Kortmann RD, Rutkowski S, Pietsch T, Parker C, Metz MW, Gnekow A, Kramm CM. Intensive chemotherapy improves survival in pediatric high-grade glioma after gross total resection: results of the HIT-GBM-C protocol. Cancer. 2010;116(3):705–712. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24730. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

