The scaffold protein WRAP53β orchestrates the ubiquitin response critical for DNA double-strand break repair
- PMID: 25512560
- PMCID: PMC4265676
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.246546.114
The scaffold protein WRAP53β orchestrates the ubiquitin response critical for DNA double-strand break repair
Abstract
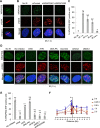
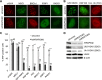
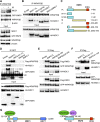
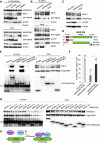
The WD40 domain-containing protein WRAP53β (WD40 encoding RNA antisense to p53; also referred to as WDR79/TCAB1) controls trafficking of splicing factors and the telomerase enzyme to Cajal bodies, and its functional loss has been linked to carcinogenesis, premature aging, and neurodegeneration. Here, we identify WRAP53β as an essential regulator of DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair. WRAP53β rapidly localizes to DSBs in an ATM-, H2AX-, and MDC1-dependent manner. We show that WRAP53β targets the E3 ligase RNF8 to DNA lesions by facilitating the interaction between RNF8 and its upstream partner, MDC1, in response to DNA damage. Simultaneous binding of MDC1 and RNF8 to the highly conserved WD40 scaffold domain of WRAP53β facilitates their interaction and accumulation of RNF8 at DSBs. In this manner, WRAP53β controls proper ubiquitylation at DNA damage sites and the downstream assembly of 53BP1, BRCA1, and RAD51. Furthermore, we reveal that knockdown of WRAP53β impairs DSB repair by both homologous recombination (HR) and nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ), causes accumulation of spontaneous DNA breaks, and delays recovery from radiation-induced cell cycle arrest. Our findings establish WRAP53β as a novel regulator of DSB repair by providing a scaffold for DNA repair factors.
Keywords: DNA repair; MDC1; RNF8 E3 ligase; WD40 scaffold; WRAP53β; ubiquitin.
© 2014 Henriksson et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The proximity ligation assay reveals that at DNA double-strand breaks WRAP53β associates with γH2AX and controls interactions between RNF8 and MDC1.Nucleus. 2015;6(5):417-24. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2015.1106675. Nucleus. 2015. PMID: 26734725 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the scaffold WD40 protein WRAP53β enhances the repair of and cell survival from DNA double-strand breaks.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Jun 16;7(6):e2267. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.172. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27310875 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the Cajal body protein WRAP53β by ATM promotes its involvement in the DNA damage response.RNA Biol. 2017 Jun 3;14(6):804-813. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1243647. Epub 2016 Oct 7. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27715493 Free PMC article.
-
The Cajal Body Protein WRAP53β Prepares the Scene for Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks by Regulating Local Ubiquitination.Front Mol Biosci. 2019 Jul 4;6:51. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00051. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31334247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of heterochromatin on DNA double strand break repair: Getting the strong, silent type to relax.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Dec 10;9(12):1273-82. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Oct 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 21036673 Review.
Cited by
-
[Effect of WRAP53 β Targeted Co-Inhibitory Pathways Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis in Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 May;53(3):457-465. doi: 10.12182/20220560208. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35642155 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Selenomethionine suppresses head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression through TopBP1/ATR and TCAB1 signaling.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Jul;39(7):877-887. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-665. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 37750664
-
RNF8 ubiquitinates RecQL4 and promotes its dissociation from DNA double strand breaks.Oncogenesis. 2021 Mar 5;10(3):24. doi: 10.1038/s41389-021-00315-0. Oncogenesis. 2021. PMID: 33674555 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing controls the ubiquitin response during DNA double-strand break repair.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Oct;23(10):1648-57. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.58. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 27315300 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate-Early, Early, and Late Responses to DNA Double Stranded Breaks.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 31;13:793884. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.793884. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35173769 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- d’Adda di Fagagna F, Teo SH, Jackson SP. 2004. Functional links between telomeres and proteins of the DNA-damage response. Genes Dev 18: 1781–1799. - PubMed
-
- Doil C, Mailand N, Bekker-Jensen S, Menard P, Larsen DH, Pepperkok R, Ellenberg J, Panier S, Durocher D, Bartek J, et al. . 2009. RNF168 binds and amplifies ubiquitin conjugates on damaged chromosomes to allow accumulation of repair proteins. Cell 136: 435–446. - PubMed
-
- Falck J, Coates J, Jackson SP. 2005. Conserved modes of recruitment of ATM, ATR and DNA-PKcs to sites of DNA damage. Nature 434: 605–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
