Small RNAs meet their targets: when methylation defends miRNAs from uridylation
- PMID: 25483033
- PMCID: PMC4615765
- DOI: 10.4161/rna.36243
Small RNAs meet their targets: when methylation defends miRNAs from uridylation
Abstract
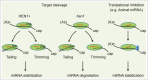
Small RNAs are incorporated into Argonaute protein-containing complexes to guide the silencing of target RNAs in both animals and plants. The abundance of endogenous small RNAs is precisely controlled at multiple levels including transcription, processing and Argonaute loading. In addition to these processes, 3' end modification of small RNAs, the topic of a research area that has rapidly evolved over the last several years, adds another layer of regulation of their abundance, diversity and function. Here, we review our recent understanding of small RNA 3' end methylation and tailing.
Keywords: argonaute; methylation; small RNA; uridylation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methylation protects miRNAs and siRNAs from a 3'-end uridylation activity in Arabidopsis.Curr Biol. 2005 Aug 23;15(16):1501-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.029. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16111943 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila RNA methyltransferase, DmHen1, modifies germline piRNAs and single-stranded siRNAs in RISC.Curr Biol. 2007 Jul 17;17(14):1265-72. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.06.030. Epub 2007 Jun 28. Curr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17604629
-
Analysis of the Uridylation of Both ARGONAUTE-Bound MiRNAs and 5' Cleavage Products of Their Target RNAs in Plants.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1640:23-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7165-7_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28608332
-
Assembly and function of small RNA - argonaute protein complexes.Biol Chem. 2014 Jun;395(6):611-29. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2014-0116. Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24603840 Review.
-
The 3' end formation in small RNAs.Gene Expr. 2002;10(1-2):59-78. Gene Expr. 2002. PMID: 11868988 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of novel and conserved microRNAs in several tissues of the Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) based on illumina deep sequencing technology.BMC Genomics. 2016 Apr 12;17:283. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2606-5. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27066897 Free PMC article.
-
PBOX-sRNA-seq uncovers novel features of miRNA modification and identifies selected 5'-tRNA fragments bearing 2'-O-modification.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 12;52(14):e65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae537. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38908023 Free PMC article.
-
3'-Terminal 2'-O-methylation of lung cancer miR-21-5p enhances its stability and association with Argonaute 2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jul 27;48(13):7027-7040. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa504. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32542340 Free PMC article.
-
Internal RNA 2'-O-methylation on the HIV-1 genome impairs reverse transcription.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 9;52(3):1359-1373. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1134. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38015463 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread 3'-end uridylation in eukaryotic RNA viruses.Sci Rep. 2016 May 6;6:25454. doi: 10.1038/srep25454. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27151171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Axtell MJ. Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 2013; 64:137-59; PMID: 23330790; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120043 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10:126-39; PMID:19165215; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm2632 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vagin VV, Sigova A, Li C, Seitz H, Gvozdev V, Zamore PD. A distinct small RNA pathway silences selfish genetic elements in the germline. Science 2006; 313:320-4; PMID:16809489; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1129333 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Luteijn MJ, Ketting RF. PIWI-interacting RNAs: from generation to transgenerational epigenetics. Nat Rev Genet 2013; 14:523-34; PMID:23797853; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrg3495 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yu B, Yang Z, Li J, Minakhina S, Yang M, Padgett RW, Steward R, Chen X. Methylation as a crucial step in plant microRNA biogenesis. Science 2005; 307:932-5; PMID:15705854; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1107130 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
