Domain I and II from newly emerging goose tembusu virus envelope protein functions as a dominant-negative inhibitor of virus infectivity
- PMID: 25481678
- PMCID: PMC7172782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2014.11.003
Domain I and II from newly emerging goose tembusu virus envelope protein functions as a dominant-negative inhibitor of virus infectivity
Abstract
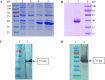
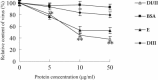
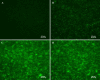
Flavivirus envelope protein locates at the outermost surface of viral particle and mediates virus entry and fusion infection, and domains I and II of E protein play an important role in this process. In this study, we have expressed and purified goose tembusu virus (GTV) E protein domains I and II (DI/II) from E. coli, and tested conceptual approach that purified protein serves as anti-viral reagent. We found that DI/II inhibited GTV JS804 infection in BHK-21 cells in a dose-dependent manner, and this inhibition activity was achieved by binding to cell membrane specifically. Moreover, JS804 treated with DI/II specific anti-serum decreased its infectivity to BHK-21 cells. Taken together, this is first to show that the purified DI/II domain of tembusu virus expressed in E. coli was able to interfere with virus infection, which opens an avenue to develop novel anti-viral regents to prevent and eventually eradicate GTV infection.
Keywords: Domain I and II; Envelope protein; Goose tembusu virus; Inhibition.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Screening and identification of B-cell epitopes within envelope protein of tembusu virus.Virol J. 2018 Sep 17;15(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12985-018-1052-1. Virol J. 2018. PMID: 30223850 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody That Recognizes a Unique Epitope on Domain III of the Envelope Protein of Tembusu Virus.Viruses. 2020 Jun 15;12(6):647. doi: 10.3390/v12060647. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32549221 Free PMC article.
-
Protective immune response against newly emerging goose tembusu virus infection induced by immunization with a recombinant envelope protein.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2015 Oct;61(4):318-24. doi: 10.1111/lam.12459. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26108865
-
Duck egg drop syndrome virus: an emerging Tembusu-related flavivirus in China.Sci China Life Sci. 2013 Aug;56(8):701-10. doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4515-z. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Sci China Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23917842 Review.
-
An updated review of avian-origin Tembusu virus: a newly emerging avian Flavivirus.J Gen Virol. 2017 Oct;98(10):2413-2420. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000908. Epub 2017 Sep 6. J Gen Virol. 2017. PMID: 28874226 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Immune-Related Gene Expression in Duck Embryo Fibroblasts Following Duck Tembusu Virus Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 8;19(8):2328. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082328. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30096804 Free PMC article.
-
A Single Mutation at Position 156 in the Envelope Protein of Tembusu Virus Is Responsible for Virus Tissue Tropism and Transmissibility in Ducks.J Virol. 2018 Aug 16;92(17):e00427-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00427-18. Print 2018 Sep 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29899104 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and identification of B-cell epitopes within envelope protein of tembusu virus.Virol J. 2018 Sep 17;15(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12985-018-1052-1. Virol J. 2018. PMID: 30223850 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide inhibitors of tembusu virus infection derived from the envelope protein.Vet Microbiol. 2020 Jun;245:108708. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108708. Epub 2020 May 7. Vet Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32456819 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody That Recognizes a Unique Epitope on Domain III of the Envelope Protein of Tembusu Virus.Viruses. 2020 Jun 15;12(6):647. doi: 10.3390/v12060647. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32549221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brault J.B., Kudelko M., Vidalain P.O., Tangy F., Desprès P., Pardigon N. The interaction of flavivirus M protein with light chain Tctex-1 of human dynein plays a role in late stages of virus replication. Virology. 2011;417:369–378. - PubMed
-
- Chu J., Rajamanonmani R., Li J., Bhuvanakantham R., Lescar J., Ng M.L. Inhibition of West Nile virus entry by using a recombinant domain III from the envelope glycoprotein. Journal of General Virology. 2005;86:405–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

