Wnt and FGF mediated epithelial-mesenchymal crosstalk during lung development
- PMID: 25470458
- PMCID: PMC4344844
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.24234
Wnt and FGF mediated epithelial-mesenchymal crosstalk during lung development
Abstract
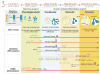
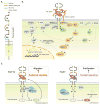
Background: The adaptation to terrestrial life required the development of an organ capable of efficient air-blood gas exchange. To meet the metabolic load of cellular respiration, the mammalian respiratory system has evolved from a relatively simple structure, similar to the two-tube amphibian lung, to a highly complex tree-like system of branched epithelial airways connected to a vast network of gas exchanging units called alveoli. The development of such an elaborate organ in a relatively short time window is therefore an extraordinary feat and involves an intimate crosstalk between mesodermal and endodermal cell lineages.
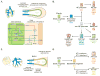
Results: This review describes the molecular processes governing lung development with an emphasis on the current knowledge on the role of Wnt and FGF signaling in lung epithelial differentiation.
Conclusions: The Wnt and FGF signaling pathways are crucial for the dynamic and reciprocal communication between epithelium and mesenchyme during lung development. In addition, some of this developmental crosstalk is reemployed in the adult lung after injury to drive regeneration, and may, when aberrantly or chronically activated, result in chronic lung diseases. Novel insights into how the Wnt and FGF pathways interact and are integrated into a complex gene regulatory network will not only provide us with essential information about how the lung regenerates itself, but also enhance our understanding of the pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases, as well as improve the controlled differentiation of lung epithelium from pluripotent stem cells.
Keywords: Fgf10; Hippo; Wnt; differentiation; epithelium; progenitor.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tissue crosstalk in lung development.J Cell Biochem. 2014 Sep;115(9):1469-77. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24811. J Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24644090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Canonical Wnt signaling activity in early stages of chick lung development.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 2;9(12):e112388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112388. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25460002 Free PMC article.
-
FGF, TGFβ and Wnt crosstalk: embryonic to in vitro cartilage development from mesenchymal stem cells.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015 Apr;9(4):332-42. doi: 10.1002/term.1744. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015. PMID: 23576364 Review.
-
Coordination of epithelial branching and salivary gland lumen formation by Wnt and FGF signals.Dev Biol. 2011 Oct 1;358(1):156-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.07.023. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21806977
-
Fgf10 Signaling in Lung Development, Homeostasis, Disease, and Repair After Injury.Front Genet. 2018 Sep 25;9:418. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00418. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30319693 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex-Specific Alterations of the Lung Transcriptome at Birth in Mouse Offspring Prenatally Exposed to Vanilla-Flavored E-Cigarette Aerosols and Enhanced Susceptibility to Asthma.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 20;20(4):3710. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043710. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36834405 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic activation of Wnt, Fgf, and Hh signaling during soft palate development.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 15;14(10):e0223879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223879. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31613912 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Orchestrates Human Lung Branching Morphogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 9;23(9):5265. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095265. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563656 Free PMC article.
-
The Extracellular Matrix in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Target and Source.Front Med (Lausanne). 2015 Dec 23;2:91. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2015.00091. eCollection 2015. Front Med (Lausanne). 2015. PMID: 26779482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of Hippo Signaling Pathway in Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017 Sep 20;20(9):629-634. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.09.07. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28935017 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Alescio T, Cassini A. Induction in vitro of tracheal buds by pulmonary mesenchyme grafted on tracheal epithelium. J Exp Zool. 1962;150:83–94. - PubMed
-
- Ameri J, Stahlberg A, Pedersen J, Johansson JK, Johannesson MM, Artner I, Semb H. FGF2 specifies hESC-derived definitive endoderm into foregut/midgut cell lineages in a concentration-dependent manner. Stem Cells. 2010;28:45–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

