Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors
- PMID: 25470051
- PMCID: PMC5997177
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13989
Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors
Abstract
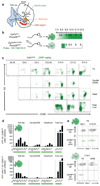
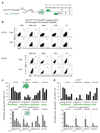
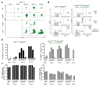
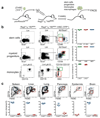
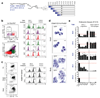
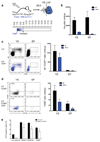
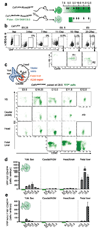
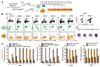
Most haematopoietic cells renew from adult haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), however, macrophages in adult tissues can self-maintain independently of HSCs. Progenitors with macrophage potential in vitro have been described in the yolk sac before emergence of HSCs, and fetal macrophages can develop independently of Myb, a transcription factor required for HSC, and can persist in adult tissues. Nevertheless, the origin of adult macrophages and the qualitative and quantitative contributions of HSC and putative non-HSC-derived progenitors are still unclear. Here we show in mice that the vast majority of adult tissue-resident macrophages in liver (Kupffer cells), brain (microglia), epidermis (Langerhans cells) and lung (alveolar macrophages) originate from a Tie2(+) (also known as Tek) cellular pathway generating Csf1r(+) erythro-myeloid progenitors (EMPs) distinct from HSCs. EMPs develop in the yolk sac at embryonic day (E) 8.5, migrate and colonize the nascent fetal liver before E10.5, and give rise to fetal erythrocytes, macrophages, granulocytes and monocytes until at least E16.5. Subsequently, HSC-derived cells replace erythrocytes, granulocytes and monocytes. Kupffer cells, microglia and Langerhans cells are only marginally replaced in one-year-old mice, whereas alveolar macrophages may be progressively replaced in ageing mice. Our fate-mapping experiments identify, in the fetal liver, a sequence of yolk sac EMP-derived and HSC-derived haematopoiesis, and identify yolk sac EMPs as a common origin for tissue macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Fetal monocytes and the origins of tissue-resident macrophages.Cell Immunol. 2018 Aug;330:5-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Cell Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29475558 Review.
-
Identification Of Erythromyeloid Progenitors And Their Progeny In The Mouse Embryo By Flow Cytometry.J Vis Exp. 2017 Jul 17;(125):55305. doi: 10.3791/55305. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28745620 Free PMC article.
-
Megakaryocyte production is sustained by direct differentiation from erythromyeloid progenitors in the yolk sac until midgestation.Immunity. 2021 Jul 13;54(7):1433-1446.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.04.026. Epub 2021 May 31. Immunity. 2021. PMID: 34062116 Free PMC article.
-
C-Myb(+) erythro-myeloid progenitor-derived fetal monocytes give rise to adult tissue-resident macrophages.Immunity. 2015 Apr 21;42(4):665-78. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.03.011. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 25902481 Free PMC article.
-
Early hematopoiesis and macrophage development.Semin Immunol. 2015 Dec;27(6):379-87. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.03.013. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Semin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 27021646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fetal-Derived Immune Cells at the Roots of Lifelong Pathophysiology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 23;9:648313. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.648313. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33708774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role and Regulation of Transcription Factors in Osteoclastogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 10;24(22):16175. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216175. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monocytes and macrophages in tissue repair: Implications for immunoregenerative biomaterial design.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016 May;241(10):1084-97. doi: 10.1177/1535370216650293. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016. PMID: 27229903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of neuroimmune processes by damage- and resolution-associated molecular patterns.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Mar;16(3):423-429. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.293134. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 32985460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global Transcriptomic and Characteristics Comparisons between Mouse Fetal Liver and Bone Marrow Definitive Erythropoiesis.Cells. 2024 Jul 5;13(13):1149. doi: 10.3390/cells13131149. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38995000 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

