CD4+ T-lymphocytes are activated by surgical stress following colorectal resection in cancer patients
- PMID: 25469274
- PMCID: PMC4251095
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2014.442
CD4+ T-lymphocytes are activated by surgical stress following colorectal resection in cancer patients
Abstract
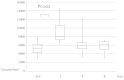
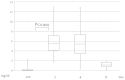
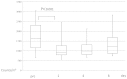
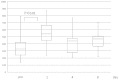
The aim of the present study was to measure adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels in CD4+ T cells as a marker of T-cell activity following surgery for colorectal cancer using the ImmuKnow assay kit. A total of 16 consecutive patients who underwent surgical resection for colorectal cancer between August and December, 2012 were enrolled in this study, of whom 7 underwent laparoscopic resection and 9 underwent open abdominal surgery. The intracellular ATP levels in CD4+ T-lymphocytes were measured using the ImmuKnow assay kit preoperatively and on the 1st, 4th and 8th postoperative days, as were the white blood cell (WBC) count, lymphocyte count and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. The ATP level of the CD4+ T-cells was significantly elevated on the 1st day following surgery compared to the preoperative level (P<0.01) and gradually returned to preoperative levels; the lymphocyte count was significantly decreased on the 1st postoperative day (P<0.001). In addition, the ImmuKnow assay demonstrated that only the ATP level, but not the WBC count, lymphocyte count or CRP level, exhibited a significant difference on the 1st (P=0.080) and 8th (P=0.042) postoperative days between the laparoscopic and open abdominal surgery groups. In conclusion, the ATP level of CD4+ T-lymphocytes was increased in response to surgical stress, in tandem with a decrease in the lymphocyte count. Therefore, the ImmuKnow assay kit may be clinically applicable for monitoring the immune response following surgery, as it exhibits a higher sensitivity compared to other assays.
Keywords: CD4+ T cells; ImmuKnow assay; colorectal cancer; laparoscopic surgery; surgical stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune cell functional assay in monitoring of adult liver transplantation recipients with infection.Transplantation. 2010 Mar 15;89(5):620-6. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181c690fa. Transplantation. 2010. Retraction in: Transplantation. 2019 Aug;103(8):1737. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002824 PMID: 20010326 Retracted.
-
Surgical stress response after colorectal resection: a comparison of robotic, laparoscopic, and open surgery.Tech Coloproctol. 2015 May;19(5):275-80. doi: 10.1007/s10151-014-1263-4. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Tech Coloproctol. 2015. PMID: 25762242
-
Assessment of CD4 T-lymphocyte reactivity by the Cylex ImmuKnow assay in patients following allogeneic hematopoietic SCT.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010 Mar;45(3):527-33. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2009.182. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010. PMID: 19718067
-
Assessing immunologic function through CD4 T-lymphocyte ahenosine triphosphate levels by ImmuKnow assay in Chinese patients following renal transplantation.Transplant Proc. 2011 Sep;43(7):2574-8. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2011.04.012. Transplant Proc. 2011. PMID: 21911125
-
The usefulness of intracellular adenosine-5'-triphosphate measurement in CD4+ cells in renal transplant.Nefrologia. 2013;33(3):381-8. doi: 10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2012.Oct.11540. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Nefrologia. 2013. PMID: 23640115 Review. English, Spanish.
References
-
- Kowalski R, Post D, Schneider MC, et al. Immune cell function testing: an adjunct to therapeutic drug monitoring in transplant patient management. Clin Transplant. 2003;17:77–88. - PubMed
-
- Kowalski RJ, Post DR, Mannon RB, et al. Assessing relative risks of infection and rejection: a meta-analysis using an immune function assay. Transplantation. 2006;82:663–668. - PubMed
-
- Husain S, Raza K, Pilewski JM, et al. Experience with immune monitoring in lung transplant recipients: correlation of low immune function with infection. Transplantation. 2009;87:1852–1857. - PubMed
-
- Xue F, Zhang J, Han L, Li Q, Xu N, Zhou T, Xi Z, Wu Y, Xia Q. Immune cell functional assay in monitoring of adult liver transplantation recipients with infection. Transplantation. 2010;89:620–626. - PubMed
-
- Hooper E, Hawkins DM, Kowalski RJ, Post DR, Britz JA, Brooks KC, Turman MA. Establishing pediatric immune response zones using the Cylex ImmuKnow assay. Clin Transplant. 2005;19:834–839. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
