Effect of rosuvastatin on atrial structural remodeling in rabbits with myocardial infarction
- PMID: 25469252
- PMCID: PMC4251138
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2014.366
Effect of rosuvastatin on atrial structural remodeling in rabbits with myocardial infarction
Abstract
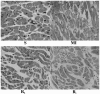
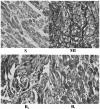
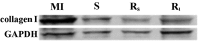
The present study aimed to investigate the effect of rosuvastatin on atrial structural remodeling in rabbits with myocardial infarction (MI). The rabbits were randomly divided into 4 groups: The sham operation group (S; n=8), the MI group (MI; n=7), the group with low-dose rosuvastatin [Rs; 2.5 mg/(kg/d), n=7] and the group with high-dose rosuvastatin [Rl, 5 mg/(kg/d), n=8]. A rabbit MI model was established via ligation of the anterior descending coronary artery. After 8 weeks of intervention, the left atrial diameter (LAD), atrial collagen content, expression level of type I collagen and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) were measured. LAD in the MI group was significantly larger than the S, Rs and Rl groups after 8 weeks. The left atrial collagen content of the MI group was also significantly greater than those observed in the other 3 groups. The expression of type I collagen in the MI group was significantly increased compared to the other 3 groups. However, LVEF of the MI group was lower compared to the other 3 groups. There were no significant differences between the Rs and Rl groups in the above indexes. In conclusion, rosuvastatin can improve post-MI atrial structural remodeling.
Keywords: atrial structural remodeling; myocardial infarction; rabbit; rosuvastatin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of rosuvastatin on atrial nerve sprouting and electrical remodeling in rabbits with myocardial infarction.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 May 15;8(5):7553-60. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26221299 Free PMC article.
-
Rosuvastatin attenuates atrial structural remodelling in rats with myocardial infarction through the inhibition of the p38 MAPK signalling pathway.Heart Lung Circ. 2015 Apr;24(4):386-94. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2014.11.012. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Heart Lung Circ. 2015. PMID: 25613240
-
[Change of short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase in heart failure after myocardial infarction in rats and the intervention of aerobic exercise].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Feb;31(2):172-177. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.02.010. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 30827304 Chinese.
-
[Effects of perindopril on left ventricular remodeling and myocardial osteopontin expression in rats with myocardial infarction].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Nov;26(11):1584-8. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 17121705 Chinese.
-
Atrial Infarction and Ischemic Mitral Regurgitation Contribute to Post-MI Remodeling of the Left Atrium.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Dec 12;70(23):2878-2889. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.10.013. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 29216983
Cited by
-
Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil mitigates high-cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and vascular damage.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017 Apr;390(4):409-422. doi: 10.1007/s00210-017-1343-x. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28101628
-
Effects of rosuvastatin on atrial nerve sprouting and electrical remodeling in rabbits with myocardial infarction.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 May 15;8(5):7553-60. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26221299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ma YX, Li WH, Xie Q. Rosuvastatin inhibits TGF-beta1 expression and alleviates myocardial fibrosis in diabetic rats. Pharmazie. 2013;68:355–358. - PubMed
-
- Paraskevaidis IA, Iliodromitis EK, Ikonomidis I, et al. The effect of acute administration of statins on coronary microcirculation during the pre-revascularization period in patients with myocardial infraction. Atherosclerosis. 2012;223:184–189. - PubMed
-
- Hayashidani S, Tsutsui H, Shiomi T, et al. Fluvastatin, a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitor, attenuates left ventricular remodeling and failure after experimental myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2002;105:868–873. - PubMed
-
- Jiang BH, Tardif JC, Sauvageau S, et al. Beneficial effects of atorvastatin on lung structural remodeling and function in ischemic heart failure. J Card Fail. 2010;16:679–688. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
