BMP4 increases the expression of TRPC and basal [Ca2+]i via the p38MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways independent of BMPRII in PASMCs
- PMID: 25461595
- PMCID: PMC4251900
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112695
BMP4 increases the expression of TRPC and basal [Ca2+]i via the p38MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways independent of BMPRII in PASMCs
Abstract
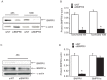
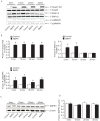
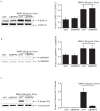
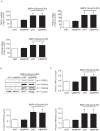
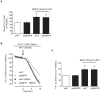
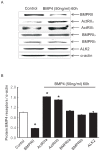
Multiple abnormalities of bone morphogenetic protein (BMPs) signaling are implicated in the process of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). BMP4 plays an important role during the process of pulmonary arterial remodeling and mutant of the principle BMP4 receptor, BMP receptors II (BMPRII), is found to associate with the development of PAH. However, the likely mechanism defining the contribution of BMPRII to BMP4 mediated signaling in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) remains comprehensively unclear. We previously found that enhanced store operated calcium entry (SOCE) and basal intracellular calcium concentration [Ca2+]i were induced by BMP4 via upregulation of TRPC1, 4 and 6 expression in PASMCs, and that BMP4 modulated TRPC channel expression through activating p38MAPK and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. In this study, BMPRII siRNA was used to knockdown BMPRII expression to investigate whether BMP4 upregulates the expression of TRPC and activating Smad1/5/8, ERK1/2 and p38MAPK pathway via BMPRII in distal PASMCs. Our results showed that knockdown of BMPRII: 1) attenuated BMP4 induced activation of P-Smad1/5/8, without altering BMP4 induced P-p38MAPK and P-ERK1/2 activation in PASMCs; 2) did not attenuate the BMP4-induced TRPC1, 4 and 6 expression; 3) did not affect BMP4-enhanced SOCE and basal [Ca2+]i. Thus, we concluded that BMP4 activated Smad1/5/8 pathway is BMPRII-dependent, while the BMP4 - ERK/p-P38 - TRPC - SOCE signaling axis are likely mediated through other receptor rather than BMPRII.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
BMP4 increases canonical transient receptor potential protein expression by activating p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Aug;49(2):212-20. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0051OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23526217 Free PMC article.
-
NOX4 mediates BMP4-induced upregulation of TRPC1 and 6 protein expressions in distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 9;9(9):e107135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107135. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25203114 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-1-dependent up-regulation of BMP4 mediates hypoxia-induced increase of TRPC expression in PASMCs.Cardiovasc Res. 2015 Jul 1;107(1):108-18. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv122. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Cardiovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25824146 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 decreases TRPC expression, store-operated Ca(2+) entry, and basal [Ca(2+)]i in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 May 1;304(9):C833-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00036.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23447035 Free PMC article.
-
BMP type II receptor as a therapeutic target in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Aug;74(16):2979-2995. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2510-4. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28447104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Roles and mechanisms of TRPC3 and the PLCγ/PKC/CPI-17 signaling pathway in regulating parturition.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jan;17(1):898-910. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7998. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29115500 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperplastic Growth of Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cells from Subjects with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Is Activated through JNK and p38 MAPK.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 23;10(4):e0123662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123662. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25905460 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological activation of PPARγ inhibits hypoxia-induced proliferation through a caveolin-1-targeted and -dependent mechanism in PASMCs.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Apr 1;314(4):C428-C438. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00143.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29351409 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical Transient Receptor Potential Channels and Their Link with Cardio/Cerebro-Vascular Diseases.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2017 Sep 1;25(5):471-481. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2016.096. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2017. PMID: 28274093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome Analysis and Gene Identification in the Pulmonary Artery of Broilers with Ascites Syndrome.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 8;11(6):e0156045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156045. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27275925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eickelberg O, Morty RE (2007) Transforming growth factor beta/bone morphogenic protein signaling in pulmonary arterial hypertension: remodeling revisited. Trends Cardiovasc Med 17:263–269. - PubMed
-
- Young KA, Ivester C, West J, Carr M, Rodman DM (2006) BMP signaling controls PASMC KV channel expression in vitro and in vivo. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290:L841–848. - PubMed
-
- Takeda M, Otsuka F, Nakamura K, Inagaki K, Suzuki J, et al. (2004) Characterization of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) system in human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells isolated from a sporadic case of primary pulmonary hypertension: roles of BMP type IB receptor (activin receptor-like kinase-6) in the mitotic action. Endocrinology 145:4344–4354. - PubMed
-
- Hruska KA, Mathew S, Saab G (2005) Bone morphogenetic proteins in vascular calcification. Circ Res 97:105–114. - PubMed
-
- Gutierrez FR, Moran CJ, Ludbrook PA, McKnight RC, Weldon CS (1980) Pulmonary arterial calcification with reversible pulmonary hypertension. AJR Am J Roentgenol 135:177–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

