Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 induces HDAC4 degradation in hypertrophic chondrocytes
- PMID: 25447540
- PMCID: PMC4289442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.11.003
Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 induces HDAC4 degradation in hypertrophic chondrocytes
Abstract
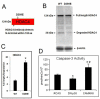
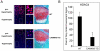
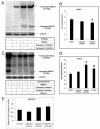
Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) is a critical negative regulator for chondrocyte hypertrophy by binding to and inhibiting Runx2, a critical transcription factor for chondrocyte hypertrophy. It is unclear how HDAC4 expression and stability are regulated during growth plate development. We report here that inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) p38 by dominant negative p38 or p38 inhibitor prevents HDAC4 degradation. Mutation of a potential caspase-2 and 3 cleavage site Asp289 stabilizes HDAC4 in chondrocytes. In contrast, constitutively active MAPK kinase 6 (constitutive activator of p38) transgenic mice exhibit decreased HDAC4 content in vivo. We also observed that p38 stimulates caspase-3 activity in chondrocytes. Inhibition of p38 or caspases reduced HDAC4 degradation. HDAC4 inhibited Runx2 promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner and caspase inhibitors further enhanced this inhibition by preventing HDAC4 degradation. Overall, these results demonstrate that p38 promotes HDAC4 degradation by increasing caspase-mediated cleavage, which releases Runx2 from a repressive influence of HDAC4 and promotes the chondrocyte hypertrophy and bone formation.
Keywords: Caspase; Degradation; HDAC4; Inhibition; p38.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
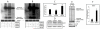
Similar articles
-
The role of histone deacetylase 4 during chondrocyte hypertrophy and endochondral bone development.Bone Joint Res. 2020 May 16;9(2):82-89. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.92.BJR-2019-0172.R1. eCollection 2020 Feb. Bone Joint Res. 2020. PMID: 32435460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-1 regulates chondrocyte phenotype by repressing histone deacetylase 4 during growth plate development.FASEB J. 2014 Sep;28(9):3930-41. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-249318. Epub 2014 May 23. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24858276 Free PMC article.
-
Parathyroid hormone-related peptide represses chondrocyte hypertrophy through a protein phosphatase 2A/histone deacetylase 4/MEF2 pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Nov;29(21):5751-62. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00415-09. Epub 2009 Aug 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19704004 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-381 Regulates Chondrocyte Hypertrophy by Inhibiting Histone Deacetylase 4 Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 23;17(9):1377. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091377. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27563877 Free PMC article.
-
Smad-Runx interactions during chondrocyte maturation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 1(Pt 1):S15-22. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11263661 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone deacetylase 4 deletion results in abnormal chondrocyte hypertrophy and premature ossification from collagen type 2α1‑expressing cells.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Nov;22(5):4031-4040. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11465. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33000215 Free PMC article.
-
The role of histone deacetylase 4 during chondrocyte hypertrophy and endochondral bone development.Bone Joint Res. 2020 May 16;9(2):82-89. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.92.BJR-2019-0172.R1. eCollection 2020 Feb. Bone Joint Res. 2020. PMID: 32435460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Etanercept on Experimental Osteoarthritis in Rats: Role of Histone Deacetylases.Cartilage. 2024 Jul 26:19476035241264012. doi: 10.1177/19476035241264012. Online ahead of print. Cartilage. 2024. PMID: 39057748 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Role of IL-1β Signaling in Chondrocytes Associated with Retinoid Signaling during Fracture Healing.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 29;21(7):2365. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072365. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32235405 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional, epigenetic and microRNA regulation of growth plate.Bone. 2020 Aug;137:115434. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115434. Epub 2020 May 16. Bone. 2020. PMID: 32422296 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnold MA, Kim Y, Czubryt MP, Phan D, McAnally J, Qi X, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN. MEF2C transcription factor controls chondrocyte hypertrophy and bone development. Developmental Cell. 2007;12:377–389. - PubMed
-
- Chen Q, Johnson DM, Haudenschild DR, Goetinck PF. Progression and recapitulation of the chondrocyte differentiation program: cartilage matrix protein is a marker for cartilage maturation. Dev Biol. 1995;172:293–306. - PubMed
-
- Chrysis D, Nilsson O, Ritzen EM, Savendahl L. Apoptosis is developmentally regulated in rat growth plate. Endocrine. 2002;18:271–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

