Interferon regulatory factors: critical mediators of human lupus
- PMID: 25445206
- PMCID: PMC4306637
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.10.002
Interferon regulatory factors: critical mediators of human lupus
Abstract
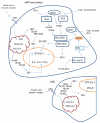
The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is multifactorial, and the interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) play an important role. Autoantibodies formed in SLE target nuclear antigens, and immune complexes formed by these antibodies contain nucleic acid. These immune complexes can activate antiviral pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), resulting in the downstream activation of IRFs, which can induce type I interferon (IFN-I) and other inflammatory mediators. Genetic variations in IRFs have been associated with susceptibility to SLE, and current evidence supports the idea that these polymorphisms are gain of function in humans. Recent studies suggest that these genetic variations contribute to the break in humoral tolerance that allows for nucleic acid binding autoantibodies, and that the same polymorphisms also augment IFN-I production in the presence of these autoantibody immune complexes, forming a feed-forward loop. In this review, we will outline major features of the PRR/IRF systems and describe the role of the IRFs in human SLE pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon regulatory factors in human lupus pathogenesis.Transl Res. 2011 Jun;157(6):326-31. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.01.006. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 21575916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A compass that points to lupus: genetic studies on type I interferon pathway.Genes Immun. 2007 Sep;8(6):445-55. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6364409. Epub 2007 Jun 21. Genes Immun. 2007. PMID: 17581625 Review.
-
Interferon regulatory factor 5 in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:780436. doi: 10.1155/2012/780436. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23251221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Murine dendritic cell type I IFN production induced by human IgG-RNA immune complexes is IFN regulatory factor (IRF)5 and IRF7 dependent and is required for IL-6 production.J Immunol. 2007 Jun 1;178(11):6876-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.11.6876. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17513736
-
[Interleukin-2 signaling pathway regulating molecules in systemic lupus erythematosus].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Dec 18;48(6):1100-1104. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 27987522 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effects of IRF1 and IFN-β interaction on the M1 polarization of macrophages and its antitumor function.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Jul;38(1):148-60. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2583. Epub 2016 May 10. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27176664 Free PMC article.
-
The type I interferons: Basic concepts and clinical relevance in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.Gene. 2016 Jan 15;576(1 Pt 1):14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.09.058. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26410416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type I interferon in rheumatic diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018 Mar 21;14(4):214-228. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2018.31. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29559718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drugs in early clinical development for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2016;25(5):573-83. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2016.1162291. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26950689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-106b-5p Inhibits IRF1/IFN-β Signaling to Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization of Glioblastoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jul 30;13:7479-7492. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S238975. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32801770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldblatt F, O’Neill SG. Clinical aspects of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Lancet. 2013;382:797–808. - PubMed
-
- Perniok A, Wedekind F, Herrmann M, Specker C, Schneider M. High levels of circulating early apoptic peripheral blood mononuclear cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 1998;7:113–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

