NEDD4-2 (NEDD4L): the ubiquitin ligase for multiple membrane proteins
- PMID: 25433090
- PMCID: PMC6636357
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.11.051
NEDD4-2 (NEDD4L): the ubiquitin ligase for multiple membrane proteins
Abstract
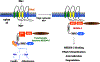
NEDD4-2 (also known as NEDD4L, neural precursor cell expressed developmentally down-regulated 4-like) is a ubiquitin protein ligase of the Nedd4 family which is known to bind and regulate a number of membrane proteins to aid in their internalization and turnover. Several of the NEDD4-2 substrates include ion channels, such as the epithelial and voltage-gated sodium channels. Given the critical function of NEDD4-2 in regulating membrane proteins, this ligase is essential for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis. In this article we review the biology and function of this important ubiquitin-protein ligase and discuss its pathophysiological significance.
Keywords: Epithelial sodium channel (ENaC); Hypertension; NEDD4 family; Ubiquitin; Ubiquitin protein ligases; Voltage-gated sodium channels (Na(v)s).
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ubiquitylation of voltage-gated sodium channels.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;221:231-50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41588-3_11. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24737239 Review.
-
Dysregulation of voltage-gated sodium channels by ubiquitin ligase NEDD4-2 in neuropathic pain.J Clin Invest. 2013 Jul;123(7):3002-13. doi: 10.1172/JCI68996. Epub 2013 Jun 17. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23778145 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitin Ligase Nedd4L Regulates the Na/K/2Cl Co-transporter NKCC1/SLC12A2 in the Colon.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 24;292(8):3137-3145. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.770065. Epub 2017 Jan 13. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28087701 Free PMC article.
-
Hrs controls sorting of the epithelial Na+ channel between endosomal degradation and recycling pathways.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 1;285(40):30523-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.150755. Epub 2010 Jul 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20675381 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of voltage-gated ion channels in excitable cells by the ubiquitin ligases Nedd4 and Nedd4-2.Channels (Austin). 2011 Jan-Feb;5(1):79-88. doi: 10.4161/chan.5.1.13967. Epub 2011 Jan 1. Channels (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21057195 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the Ubiquitin System in Chronic Pain.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 May 28;14:674914. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.674914. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34122010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Nedd4-2/Ndfip1 axis is a negative regulator of IgE-mediated mast cell activation.Nat Commun. 2016 Oct 27;7:13198. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13198. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27786273 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK phosphorylation of the β1Pix exchange factor regulates the assembly and function of an ENaC inhibitory complex in kidney epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Dec 1;317(6):F1513-F1525. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00592.2018. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31566435 Free PMC article.
-
Insights Into the Biological Role of NEDD4L E3 Ubiquitin Ligase in Human Cancers.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 15;11:774648. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.774648. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34869021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine-tuning of ULK1 mRNA and protein levels is required for autophagy oscillation.J Cell Biol. 2016 Dec 19;215(6):841-856. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201605089. Epub 2016 Dec 8. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27932573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albesa M, Grilo LS, Gavillet B and Abriel H (2011). Nedd4–2-dependent ubiquitylation and regulation of the cardiac potassium channel hERG1. J Mol Cell Cardiol 51(1): 90–98. - PubMed
-
- Andre B and Springael JY (1994). WWP, a new amino acid motif present in single or multiple copies in various proteins including dystrophin and the SH3-binding Yes-associated protein YAP65. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 205(2): 1201–1205. - PubMed
-
- Araki N, Umemura M, Miyagi Y, Yabana M, Miki Y, Tamura K, Uchino K, Aoki R, Goshima Y, Umemura S and Ishigami T (2008). Expression, transcription, and possible antagonistic interaction of the human Nedd4L gene variant: implications for essential hypertension. Hypertension 51(3): 773–777. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

