CD147 promotes Src-dependent activation of Rac1 signaling through STAT3/DOCK8 during the motility of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 25428919
- PMCID: PMC4381592
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2801
CD147 promotes Src-dependent activation of Rac1 signaling through STAT3/DOCK8 during the motility of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
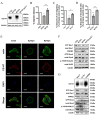
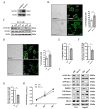
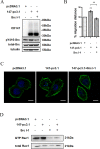
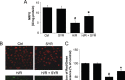
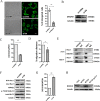
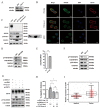
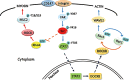
Metastasis is considered a dynamic process in tumor development that is related to abnormal migration and invasion. Tumor cells can move as individual cells in two interconvertible modes: mesenchymal-type and amoeboid. Previously, we reported that the interaction between CD147 and Annexin II can inhibit the amoeboid movement in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. However, the mechanism of CD147 involved in mesenchymal movement is still unclear. Notably, our results show overexpression of CD147 led to mesenchymal-type movement in HCC cells. Evidence indicated that the mesenchymal-type cell movement induced by CD147 was Src dependent, as observed by confocal microscopy and Rac1 activity assay. The phosphorylation of Src (pY416-Src) can be up-regulated by CD147, and this regulation is mediated by focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Next, we identified DOCK8 as a GEF for Rac1, a key molecule driving mesenchymal-type movement. We also found that Src promotes STAT3 phosphorylation and STAT3 facilitates DOCK8 transcription, thus enhancing DOCK8 expression and Rac1 activation. This study provides a novel mechanism of CD147 regulating mesenchymal-type movement in HCC cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HAb18G/CD147 promotes cell motility by regulating annexin II-activated RhoA and Rac1 signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Hepatology. 2011 Dec;54(6):2012-24. doi: 10.1002/hep.24592. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21809360
-
CD147 regulates cancer migration via direct interaction with Annexin A2 and DOCK3-β-catenin-WAVE2 signaling.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 2;7(5):5613-29. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6723. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26716413 Free PMC article.
-
Hypo-phosphorylated CD147 promotes migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and predicts a poor prognosis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2019 Aug;42(4):537-554. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00444-0. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2019. PMID: 31016558
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
-
DOCK8 deficiency: Insights into pathophysiology, clinical features and management.Clin Immunol. 2017 Aug;181:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28625885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the role of DOCK8 in tumorigenesis by regulating immunity and the application of nanotechnology in DOCK8 deficiency therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 1;13:1065029. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1065029. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36386145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Status of Dedicator of Cytokinesis-Associated Immunodeficiency: DOCK8 and DOCK2.Dermatol Clin. 2017 Jan;35(1):11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2016.07.002. Dermatol Clin. 2017. PMID: 27890234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD147 promotes collective invasion through cathepsin B in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jul 29;39(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01647-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32727598 Free PMC article.
-
CD147 promotes cell motility via upregulation of p190-B RhoGAP in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2016 Sep 6;16(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12935-016-0344-z. eCollection 2016. Cancer Cell Int. 2016. PMID: 27601938 Free PMC article.
-
"Stealth dissemination" of macrophage-tumor cell fusions cultured from blood of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 28;12(9):e0184451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184451. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28957348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kohn EC. Invasion and metastasis: biology and clinical potential. Pharmacology & therapeutics. 1991;52(2):235–244. - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz M, Christofori G. Mechanisms of motility in metastasizing cells. Molecular cancer research : MCR. 2010;8(5):629–642. - PubMed
-
- Price JT, Thompson EW. Mechanisms of tumour invasion and metastasis: emerging targets for therapy. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets. 2002;6(2):217–233. - PubMed
-
- Vignjevic D, Montagnac G. Reorganisation of the dendritic actin network during cancer cell migration and invasion. Seminars in cancer biology. 2008;18(1):12–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

