A vertebrate-conserved cis-regulatory module for targeted expression in the main hypothalamic regulatory region for the stress response
- PMID: 25427861
- PMCID: PMC4248439
- DOI: 10.1186/s12861-014-0041-x
A vertebrate-conserved cis-regulatory module for targeted expression in the main hypothalamic regulatory region for the stress response
Abstract
Background: The homeodomain transcription factor orthopedia (Otp) is an evolutionarily conserved regulator of neuronal fates. In vertebrates, Otp is necessary for the proper development of different regions of the brain and is required in the diencephalon to specify several hypothalamic cell types, including the cells that control the stress response. To understand how this widely expressed transcription factor accomplishes hypothalamus-specific functions, we performed a comprehensive screening of otp cis-regulatory regions in zebrafish.
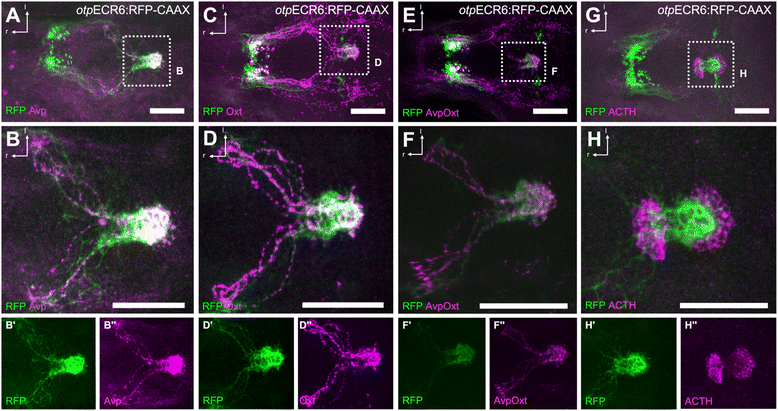
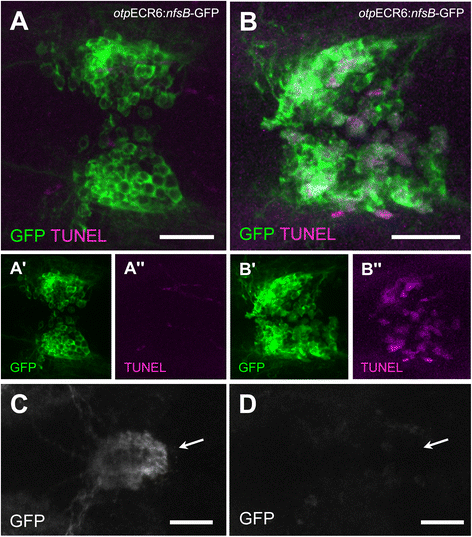
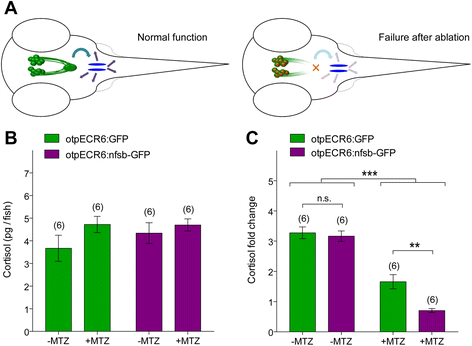
Results: Here, we report the identification of an evolutionarily conserved vertebrate enhancer module with activity in a restricted area of the forebrain, which includes the region of the hypothalamus that controls the stress response. This region includes neurosecretory cells producing Corticotropin-releasing hormone (Crh), Oxytocin (Oxt) and Arginine vasopressin (Avp), which are key components of the stress axis. Lastly, expression of the bacterial nitroreductase gene under this specific enhancer allowed pharmacological attenuation of the stress response in zebrafish larvae.
Conclusion: Vertebrates share many cellular and molecular components of the stress response and our work identified a striking conservation at the cis-regulatory level of a key hypothalamic developmental gene. In addition, this enhancer provides a useful tool to manipulate and visualize stress-regulatory hypothalamic cells in vivo with the long-term goal of understanding the ontogeny of the stress axis in vertebrates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia-1 is essential for normal hypothalamic-pituitary-interrenal (HPI) axis function.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Jun 1;26(11):1992-2005. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx076. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28334933 Free PMC article.
-
Orthopedia transcription factor otpa and otpb paralogous genes function during dopaminergic and neuroendocrine cell specification in larval zebrafish.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 20;8(9):e75002. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075002. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24073233 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular neuroanatomy and chemoarchitecture of the neurosecretory preoptic-hypothalamic area in zebrafish larvae.J Comp Neurol. 2014 May 1;522(7):1542-64. doi: 10.1002/cne.23480. J Comp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24127437
-
The stress system in depression and neurodegeneration: focus on the human hypothalamus.Brain Res Rev. 2008 Mar;57(2):531-53. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2007.04.005. Epub 2007 Apr 27. Brain Res Rev. 2008. PMID: 17524488 Review.
-
Molecular genetics of the developing neuroendocrine hypothalamus.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Jul 8;323(1):115-23. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.04.002. Epub 2010 Apr 10. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20385202 Review.
Cited by
-
The Severity of Acute Stress Is Represented by Increased Synchronous Activity and Recruitment of Hypothalamic CRH Neurons.J Neurosci. 2016 Mar 16;36(11):3350-62. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3390-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26985042 Free PMC article.
-
Role of developmental factors in hypothalamic function.Front Neuroanat. 2015 Apr 21;9:47. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2015.00047. eCollection 2015. Front Neuroanat. 2015. PMID: 25954163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Motivated state control in larval zebrafish: behavioral paradigms and anatomical substrates.J Neurogenet. 2016 Jun;30(2):122-32. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2016.1177048. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Neurogenet. 2016. PMID: 27293113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optogenetically enhanced pituitary corticotroph cell activity post-stress onset causes rapid organizing effects on behaviour.Nat Commun. 2016 Sep 20;7:12620. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12620. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27646867 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Reconstruction of Oxytocinergic Neurons Reveals Separate Hypophysiotropic and Encephalotropic Subtypes in Larval Zebrafish.eNeuro. 2017 Feb 8;4(1):ENEURO.0278-16.2016. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0278-16.2016. eCollection 2017 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2017. PMID: 28317020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acampora D, Postiglione MP, Avantaggiato V, Di Bonito M, Simeone A. The role of Otx and Otp genes in brain development. Int J Dev Biol. 2000;44(6):669–677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

