Glia and neurodevelopment: focus on fetal alcohol spectrum disorders
- PMID: 25426477
- PMCID: PMC4227495
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2014.00123
Glia and neurodevelopment: focus on fetal alcohol spectrum disorders
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: "glia and neurodevelopment: focus on fetal alcohol spectrum disorders".Front Pediatr. 2015 Apr 21;3:27. doi: 10.3389/fped.2015.00027. eCollection 2015. Front Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25954735 Free PMC article.
Abstract
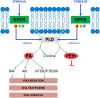
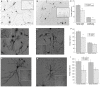
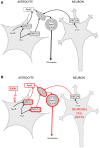
During the last 20 years, new and exciting roles for glial cells in brain development have been described. Moreover, several recent studies implicated glial cells in the pathogenesis of neurodevelopmental disorders including Down syndrome, Fragile X syndrome, Rett Syndrome, Autism Spectrum Disorders, and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD). Abnormalities in glial cell development and proliferation and increased glial cell apoptosis contribute to the adverse effects of ethanol on the developing brain and it is becoming apparent that the effects of fetal alcohol are due, at least in part, to effects on glial cells affecting their ability to modulate neuronal development and function. The three major classes of glial cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia as well as their precursors are affected by ethanol during brain development. Alterations in glial cell functions by ethanol dramatically affect neuronal development, survival, and function and ultimately impair the development of the proper brain architecture and connectivity. For instance, ethanol inhibits astrocyte-mediated neuritogenesis and oligodendrocyte development, survival and myelination; furthermore, ethanol induces microglia activation and oxidative stress leading to the exacerbation of ethanol-induced neuronal cell death. This review article describes the most significant recent findings pertaining the effects of ethanol on glial cells and their significance in the pathophysiology of FASD and other neurodevelopmental disorders.
Keywords: astrocytes; fetal alcohol spectrum disorders; glia; microglia; neurodevelopment; oligodendrocytes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: An Overview from the Glia Perspective.Front Integr Neurosci. 2016 Jan 11;9:65. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2015.00065. eCollection 2015. Front Integr Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26793073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol-Induced Neurodegeneration and Glial Activation in the Developing Brain.Brain Sci. 2016 Aug 16;6(3):31. doi: 10.3390/brainsci6030031. Brain Sci. 2016. PMID: 27537918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroinflammatory contribution of microglia and astrocytes in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.J Neurosci Res. 2021 Aug;99(8):1973-1985. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24735. Epub 2020 Sep 22. J Neurosci Res. 2021. PMID: 32959429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glia and fetal alcohol syndrome.Neurotoxicology. 2001 Oct;22(5):593-9. doi: 10.1016/s0161-813x(01)00037-7. Neurotoxicology. 2001. PMID: 11770880 Review.
-
Ethanol modulation of hippocampal neuroinflammation, myelination, and neurodevelopment in a postnatal mouse model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2021 Sep-Oct;87:107015. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2021.107015. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2021. PMID: 34256161 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Roles of microglia in brain development, tissue maintenance and repair.Brain. 2015 May;138(Pt 5):1138-59. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv066. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25823474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TTB Protects Astrocytes Against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced Injury via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 16;10:792. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00792. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31379570 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: An Overview from the Glia Perspective.Front Integr Neurosci. 2016 Jan 11;9:65. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2015.00065. eCollection 2015. Front Integr Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26793073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligodendrocyte pathology in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Mar;17(3):497-502. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.314294. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 34380877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of ethanol-and choline-treated astrocytes on hippocampal neuron neurite outgrowth in vitro.Sci Prog. 2021 Apr-Jun;104(2):368504211018943. doi: 10.1177/00368504211018943. Sci Prog. 2021. PMID: 34019432 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

