Sphingolipid metabolism and its role in the skeletal tissues
- PMID: 25424644
- PMCID: PMC11114007
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-014-1778-x
Sphingolipid metabolism and its role in the skeletal tissues
Abstract
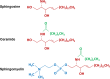
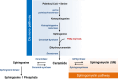
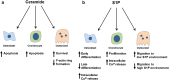
The regulators affecting skeletal tissue formation and its maintenance include a wide array of molecules with very diverse functions. More recently, sphingolipids have been added to this growing list of regulatory molecules in the skeletal tissues. Sphingolipids are integral parts of various lipid membranes present in the cells and organelles. For a long time, these macromolecules were considered as inert structural elements. This view, however, has radically changed in recent years as sphingolipids are now recognized as important second messengers for signal-transduction pathways that affect cell growth, differentiation, stress responses and programmed death. In the current review, we discuss the available data showing the roles of various sphingolipids in three different skeletal cell types-chondrocytes in cartilage and osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone. We provide an overview of the biology of sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 3 (SMPD3), an important regulator of sphingolipid metabolism in the skeleton. SMPD3 is localized in the plasma membrane and has been shown to cleave sphingomyelin to generate ceramide, a bioactive lipid second messenger, and phosphocholine, an essential nutrient. SMPD3 deficiency in mice impairs the mineralization in both cartilage and bone extracellular matrices leading to severe skeletal deformities. A detailed understanding of SMPD3 function may provide a novel insight on the role of sphingolipids in the skeletal tissues.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ceramide/sphingosine/sphingosine 1-phosphate metabolism on the cell surface and in the extracellular space.Cell Signal. 2007 Feb;19(2):229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.07.001. Epub 2006 Sep 11. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 16963225 Review.
-
Sphingosine kinase signalling in immune cells: potential as novel therapeutic targets.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jan;1784(1):66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.07.013. Epub 2007 Aug 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 17913601 Review.
-
Sphingolipids metabolism in the salivary glands of rats with obesity and streptozotocin induced diabetes.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Oct;232(10):2766-2775. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25939. Epub 2017 Apr 27. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28369933 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression of sphingolipid metabolism pathways is altered in hidradenitis suppurativa.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77(2):268-273.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.016. Epub 2017 May 24. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28551069
-
Effect of high fat diet enriched with unsaturated and diet rich in saturated fatty acids on sphingolipid metabolism in rat skeletal muscle.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Nov;225(3):786-91. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22283. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20568228
Cited by
-
Effects of aging on serum levels of lipid molecular species as determined by lipidomics analysis in Japanese men and women.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jun 6;17(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0785-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29875018 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of Enpp6 Results in Transient Bone Hypomineralization.JBMR Plus. 2020 Dec 8;5(2):e10439. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10439. eCollection 2021 Feb. JBMR Plus. 2020. PMID: 33615108 Free PMC article.
-
Trabecular Bone Parameters, TIMP-2, MMP-8, MMP-13, VEGF Expression and Immunolocalization in Bone and Cartilage in Newborn Offspring Prenatally Exposed to Fumonisins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 20;22(22):12528. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212528. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830409 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosphingolipids in Osteoarthritis and Cartilage-Regeneration Therapy: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Prospects Based on a Narrative Review of the Literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 30;25(9):4890. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094890. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial Lipidomic Profiling of Mouse Joint Tissue Demonstrates the Essential Role of PHOSPHO1 in Growth Plate Homeostasis.J Bone Miner Res. 2023 May;38(5):792-807. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4796. Epub 2023 Mar 14. J Bone Miner Res. 2023. PMID: 36824055 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

