Nanoscale stiffness topography reveals structure and mechanics of the transport barrier in intact nuclear pore complexes
- PMID: 25420031
- PMCID: PMC4286247
- DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2014.262
Nanoscale stiffness topography reveals structure and mechanics of the transport barrier in intact nuclear pore complexes
Abstract
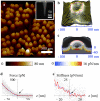
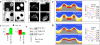
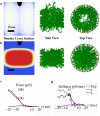
The nuclear pore complex (NPC) is the gate for transport between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm. Small molecules cross the NPC by passive diffusion, but molecules larger than ∼5 nm must bind to nuclear transport receptors to overcome a selective barrier within the NPC. Although the structure and shape of the cytoplasmic ring of the NPC are relatively well characterized, the selective barrier is situated deep within the central channel of the NPC and depends critically on unstructured nuclear pore proteins, and is therefore not well understood. Here, we show that stiffness topography with sharp atomic force microscopy tips can generate nanoscale cross-sections of the NPC. The cross-sections reveal two distinct structures, a cytoplasmic ring and a central plug structure, which are consistent with the three-dimensional NPC structure derived from electron microscopy. The central plug persists after reactivation of the transport cycle and resultant cargo release, indicating that the plug is an intrinsic part of the NPC barrier. Added nuclear transport receptors accumulate on the intact transport barrier and lead to a homogenization of the barrier stiffness. The observed nanomechanical properties in the NPC indicate the presence of a cohesive barrier to transport and are quantitatively consistent with the presence of a central condensate of nuclear pore proteins in the NPC channel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cryo-electron tomography provides novel insights into nuclear pore architecture: implications for nucleocytoplasmic transport.J Mol Biol. 2003 Apr 18;328(1):119-30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00266-3. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12684002
-
Atomic force microscopy visualises a hydrophobic meshwork in the central channel of the nuclear pore.Pflugers Arch. 2008 Apr;456(1):155-62. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0396-y. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Pflugers Arch. 2008. PMID: 18060562
-
Activation of ryanodine receptors in the nuclear envelope alters the conformation of the nuclear pore complex.Biophys Chem. 2004 Dec 1;112(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2004.06.010. Biophys Chem. 2004. PMID: 15501570
-
Biomechanics of the transport barrier in the nuclear pore complex.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Aug;68:42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 12. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28506890 Review.
-
Structural dynamics of the nuclear pore complex.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Aug;68:27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.05.021. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28579449 Review.
Cited by
-
How to operate a nuclear pore complex by Kap-centric control.Nucleus. 2015;6(5):366-72. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2015.1090061. Nucleus. 2015. PMID: 26338152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visualization of Au Nanoparticles Buried in a Polymer Matrix by Scanning Thermal Noise Microscopy.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 17;7:42718. doi: 10.1038/srep42718. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28210001 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic Force Microscopy for Structural and Biophysical Investigations on Nuclear Pore Complexes.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2502:299-310. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2337-4_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35412247
-
The mechanical stability of proteins regulates their translocation rate into the cell nucleus.Nat Phys. 2019 Sep;15(9):973-981. doi: 10.1038/s41567-019-0551-3. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Nat Phys. 2019. PMID: 37484710 Free PMC article.
-
Probing High Permeability of Nuclear Pore Complexes by Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy: Ca2+ Effects on Transport Barriers.Anal Chem. 2019 Apr 16;91(8):5446-5454. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00796. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30907572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fahrenkrog B, Aebi U. The nuclear pore complex: nucleocytoplasmic transport and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:757–766. - PubMed
-
- Alber F, et al. The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex. Nature. 2007;450:695–701. - PubMed
-
- Beck M, Lucic V, Forster F, Baumeister W, Medalia O. Snapshots of nuclear pore complexes in action taken by cryoelectron tomography. Nature. 2007;449:611–615. - PubMed
-
- Hoelz A, Debler EW, Blobel G. Structure of the nuclear pore complex. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011;80:613–643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

