Hypo-anxious phenotype of adolescent offspring prenatally exposed to LPS is associated with reduced mGluR5 expression in hippocampus
- PMID: 25419490
- PMCID: PMC4240012
- DOI: 10.4236/ojmp.2014.33022
Hypo-anxious phenotype of adolescent offspring prenatally exposed to LPS is associated with reduced mGluR5 expression in hippocampus
Abstract
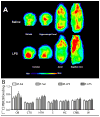
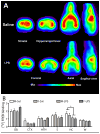
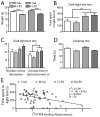
Many studies have reported long-term modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) by inflammatory processes and a pharmacological modulation of mGluR5 is known to regulate anxiety level. However, it is not known if non-pharmacological modulation of mGluR5 by inflammation impaired the unconditional level of anxiety. In this study, we investigated this relation in LPS prenatal immune challenge (120μg/kg, 3x i.p. injection in late gestation), a developmental model of neuroinflammation in which some studies have reported hypo-anxious phenotype. Using positron emission tomographic imaging (PET) approaches, we have demonstrated a decrease in the binding potential of [18F]fluoro-5-(2-pyridinylethynyl)benzonitrile ([18F]FPEB, a radioligand for mGluR5) in hippocampus of adolescent offspring prenatally exposed to LPS, without significant change in the binding of [11C]peripheral benzodiazepine receptor 28 ([11C]PBR28), an inflammatory marker. In addition, dark-light box emergence test revealed a lower level of anxiety in LPS-exposed offspring and this behavioural phenotype was associated with the binding potential of [18F]FPEB in hippocampus. These results confirm that neuroinflammation during developmental phase modulates the physiology of mGluR5 and this alteration can be associated with behavioural phenotype related to anxiety. In addition, this study supports a hypotheses that mGluR5 could be used as a diagnostic target in anxiety.
Keywords: Behavior; anxiety; immune response; inflammation; mGluR5.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loss of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Function on Peripheral Benzodiazepine Receptor in Mice Prenatally Exposed to LPS.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 4;10(11):e0142093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142093. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26536027 Free PMC article.
-
PET imaging studies show enhanced expression of mGluR5 and inflammatory response during progressive degeneration in ALS mouse model expressing SOD1-G93A gene.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Nov 24;12:217. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0439-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26597638 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and preliminary biological evaluation of 3-[(18)F]fluoro-5-(2-pyridinylethynyl)benzonitrile as a PET radiotracer for imaging metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5.Synapse. 2007 Dec;61(12):951-61. doi: 10.1002/syn.20445. Synapse. 2007. PMID: 17787003
-
Recent developments of the PET imaging agents for metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5.Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(18):1800-5. doi: 10.2174/156802607782507394. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17979788 Review.
-
The role of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in the pathogenesis of mood disorders and addiction: combining preclinical evidence with human Positron Emission Tomography (PET) studies.Front Neurosci. 2015 Mar 18;9:86. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00086. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25852460 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Precision Medicine in Multiple Sclerosis: Future of PET Imaging of Inflammation and Reactive Astrocytes.Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Sep 15;9:85. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00085. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27695400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Dietary n-3 LCPUFA Supplementation on the Hippocampus of Aging Female Mice: Impact on Memory, Lipid Raft-Associated Glutamatergic Receptors and Neuroinflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 4;23(13):7430. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137430. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806435 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Function on Peripheral Benzodiazepine Receptor in Mice Prenatally Exposed to LPS.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 4;10(11):e0142093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142093. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26536027 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of brain mGluR5 binding in a pilot study of late-life major depressive disorder using positron emission tomography and [¹¹C]ABP688.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Dec 8;5(12):e693. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.189. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26645628 Free PMC article.
-
Study of influence of the glutamatergic concentration of [18F]FPEB binding to metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 with N-acetylcysteine challenge in rats and SRM/PET study in human healthy volunteers.Transl Psychiatry. 2021 Jan 20;11(1):66. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-01152-2. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33473111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swanson CJ, Bures M, Johnson MP, et al. Metabotropic glutamate receptors as novel targets for anxiety and stress disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:131–144. - PubMed
-
- Brodkin J, Busse C, Sukoff SJ, Varney MA. Anxiolytic-like activity of the mGluR5 antagonist MPEP: a comparison with diazepam and buspirone. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2002;73:359–366. - PubMed
-
- Mikulecka A, Mares P. Effects of mGluR5 and mGluR1 antagonists on anxiety-like behavior and learning in developing rats. Behav Brain Res. 2009;204:133–139. - PubMed
-
- Klodzinska A, Tatarczynska E, Chojnacka-Wojcik E, et al. Anxiolytic-like effects of MTEP, a potent and selective mGlu5 receptor agonist does not involve GABA(A) signaling. Neuropharmacology. 2004;47:342–350. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
