Exome sequencing identifies three novel candidate genes implicated in intellectual disability
- PMID: 25405613
- PMCID: PMC4236113
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112687
Exome sequencing identifies three novel candidate genes implicated in intellectual disability
Abstract
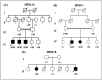
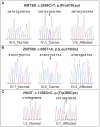
Intellectual disability (ID) is a major health problem mostly with an unknown etiology. Recently exome sequencing of individuals with ID identified novel genes implicated in the disease. Therefore the purpose of the present study was to identify the genetic cause of ID in one syndromic and two non-syndromic Pakistani families. Whole exome of three ID probands was sequenced. Missense variations in two plausible novel genes implicated in autosomal recessive ID were identified: lysine (K)-specific methyltransferase 2B (KMT2B), zinc finger protein 589 (ZNF589), as well as hedgehog acyltransferase (HHAT) with a de novo mutation with autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. The KMT2B recessive variant is the first report of recessive Kleefstra syndrome-like phenotype. Identification of plausible causative mutations for two recessive and a dominant type of ID, in genes not previously implicated in disease, underscores the large genetic heterogeneity of ID. These results also support the viewpoint that large number of ID genes converge on limited number of common networks i.e. ZNF589 belongs to KRAB-domain zinc-finger proteins previously implicated in ID, HHAT is predicted to affect sonic hedgehog, which is involved in several disorders with ID, KMT2B associated with syndromic ID fits the epigenetic module underlying the Kleefstra syndromic spectrum. The association of these novel genes in three different Pakistani ID families highlights the importance of screening these genes in more families with similar phenotypes from different populations to confirm the involvement of these genes in pathogenesis of ID.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genotype-phenotype evaluation of MED13L defects in the light of a novel truncating and a recurrent missense mutation.Eur J Med Genet. 2017 Sep;60(9):451-464. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2017.06.004. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Eur J Med Genet. 2017. PMID: 28645799
-
Kleefstra-variant syndrome with heterozygous mutations in EHMT1 and KCNQ2 genes: a case report.Neurol Sci. 2016 May;37(5):829-31. doi: 10.1007/s10072-016-2482-4. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Neurol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26792009 No abstract available.
-
Targeted next generation sequencing of a panel of autism-related genes identifies an EHMT1 mutation in a Kleefstra syndrome patient with autism and normal intellectual performance.Gene. 2016 Dec 31;595(2):131-141. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.09.027. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Gene. 2016. PMID: 27651234
-
Exome sequencing identifies a de novo SCN2A mutation in a patient with intractable seizures, severe intellectual disability, optic atrophy, muscular hypotonia, and brain abnormalities.Epilepsia. 2014 Apr;55(4):e25-9. doi: 10.1111/epi.12554. Epub 2014 Mar 1. Epilepsia. 2014. PMID: 24579881 Review.
-
Advances in identification of genes involved in autosomal recessive intellectual disability: a brief review.J Med Genet. 2019 Sep;56(9):567-573. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2018-105821. Epub 2019 Mar 6. J Med Genet. 2019. PMID: 30842223 Review.
Cited by
-
KnockoffTrio: A knockoff framework for the identification of putative causal variants in genome-wide association studies with trio design.Am J Hum Genet. 2022 Oct 6;109(10):1761-1776. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.08.013. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Am J Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 36150388 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a ceRNA immunoregulatory network related to the development of vascular dementia through a weighted gene coexpression network analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2021 May;9(10):858. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-1717. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34164492 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Lysine Methylation and Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 30;18(7):1404. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071404. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28665350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatic analysis of the expression and prognosis of ZNF589 in human breast cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 May;10(5):2286-2304. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-3166. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116546 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Genome Sequencing of a Vietnamese Family from a Dioxin Contamination Hotspot Reveals Novel Variants in the Son with Undiagnosed Intellectual Disability.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Nov 23;15(12):2629. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122629. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30477169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gecz J, Shoubridge C, Corbett M (2009) The genetic landscape of intellectual disability arising from chromosome X. Trends Genet 25: 308–316. - PubMed
-
- Stein Z, Belmont L, Durkin M (1987) Mild mental retardation and severe mental retardation compared: Experiences in eight less developed countries. Ups J Med Sci Suppl 44: 89–96. - PubMed
-
- Iqbal Z, van Bokhoven H (2014) Identifying genes responsible for intellectual disability in consanguineous families. Hum Hered 77: 150–160. - PubMed
-
- Najmabadi H, Hu H, Garshasbi M, Zemojtel T, Abedini SS, et al. (2011) Deep sequencing reveals 50 novel genes for recessive cognitive disorders. Nature 478: 57–63. - PubMed
-
- van Bokhoven H (2011) Genetic and epigenetic networks in intellectual disabilities. Annu Rev Genet 45: 81–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

