Host response profile of human brain proteome in toxoplasma encephalitis co-infected with HIV
- PMID: 25404878
- PMCID: PMC4232683
- DOI: 10.1186/1559-0275-11-39
Host response profile of human brain proteome in toxoplasma encephalitis co-infected with HIV
Abstract
Background: Toxoplasma encephalitis is caused by the opportunistic protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Primary infection with T. gondii in immunocompetent individuals remains largely asymptomatic. In contrast, in immunocompromised individuals, reactivation of the parasite results in severe complications and mortality. Molecular changes at the protein level in the host central nervous system and proteins associated with pathogenesis of toxoplasma encephalitis are largely unexplored. We used a global quantitative proteomic strategy to identify differentially regulated proteins and affected molecular networks in the human host during T. gondii infection with HIV co-infection.
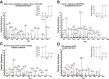
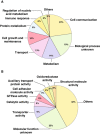
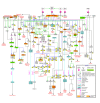
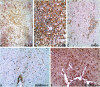
Results: We identified 3,496 proteins out of which 607 proteins were differentially expressed (≥1.5-fold) when frontal lobe of the brain from patients diagnosed with toxoplasma encephalitis was compared to control brain tissues. We validated differential expression of 3 proteins through immunohistochemistry, which was confirmed to be consistent with mass spectrometry analysis. Pathway analysis of differentially expressed proteins indicated deregulation of several pathways involved in antigen processing, immune response, neuronal growth, neurotransmitter transport and energy metabolism.
Conclusions: Global quantitative proteomic approach adopted in this study generated a comparative proteome profile of brain tissues from toxoplasma encephalitis patients co-infected with HIV. Differentially expressed proteins include previously reported and several new proteins in the context of T. gondii and HIV infection, which can be further investigated. Molecular pathways identified to be associated with the disease should enhance our understanding of pathogenesis in toxoplasma encephalitis.
Keywords: Chronic meningitis; Immunosuppression; LTQ-Orbitrap Velos; Neuroinfections; Opportunistic infections; iTRAQ labeling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
iTRAQ-based differential proteomic analysis in Mongolian gerbil brains chronically infected with Toxoplasma gondii.J Proteomics. 2017 May 8;160:74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.03.012. Epub 2017 Mar 18. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28323244
-
Global iTRAQ-based proteomic profiling of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts during sporulation.J Proteomics. 2016 Oct 4;148:12-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.07.010. Epub 2016 Jul 12. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27422377
-
Brain proteomic differences between wild-type and CD44- mice induced by chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection.Parasitol Res. 2018 Aug;117(8):2623-2633. doi: 10.1007/s00436-018-5954-z. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Parasitol Res. 2018. PMID: 29948204
-
[Highly Active AntiRetroviral Therapy and opportunistic protozoan infections].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):89-93. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305694 Review. Italian.
-
Characteristics and critical function of CD8+ T cells in the Toxoplasma-infected brain.Semin Immunopathol. 2015 May;37(3):261-70. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0487-3. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Semin Immunopathol. 2015. PMID: 25898888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomic signature of mouse cerebral cortex following Toxoplasma gondii infection.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Jul 29;12(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3623-4. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31358041 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal transcriptomic changes in long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs involved in the host immune and metabolic response during Toxoplasma gondii lytic cycle.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Jan 10;15(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-05140-3. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35012632 Free PMC article.
-
An optimised method for the proteomic profiling of full thickness human skin.Biol Proced Online. 2016 Jul 21;18:15. doi: 10.1186/s12575-016-0045-y. eCollection 2016. Biol Proced Online. 2016. PMID: 27445641 Free PMC article.
-
Global Metabolomic Profiling of Mice Brains following Experimental Infection with the Cyst-Forming Toxoplasma gondii.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 2;10(10):e0139635. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139635. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26431205 Free PMC article.
-
Global proteomic profiling of multiple organs of cats (Felis catus) and proteome-transcriptome correlation during acute Toxoplasma gondii infection.Infect Dis Poverty. 2022 Sep 14;11(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s40249-022-01022-7. Infect Dis Poverty. 2022. PMID: 36104766 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
