Toxin-antitoxin systems in the mobile genome of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
- PMID: 25384039
- PMCID: PMC4226512
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112226
Toxin-antitoxin systems in the mobile genome of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
Abstract
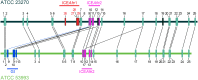
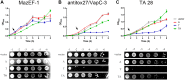
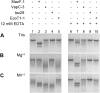
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems are genetic modules composed of a pair of genes encoding a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin that inhibits toxin activity. They are widespread among plasmids and chromosomes of bacteria and archaea. TA systems are known to be involved in the stabilization of plasmids but there is no consensus about the function of chromosomal TA systems. To shed light on the role of chromosomally encoded TA systems we analyzed the distribution and functionality of type II TA systems in the chromosome of two strains from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (ATCC 23270 and 53993), a Gram-negative, acidophilic, environmental bacterium that participates in the bioleaching of minerals. As in other environmental microorganisms, A. ferrooxidans has a high content of TA systems (28-29) and in twenty of them the toxin is a putative ribonuclease. According to the genetic context, some of these systems are encoded near or within mobile genetic elements. Although most TA systems are shared by both strains, four of them, which are encoded in the active mobile element ICEAfe1, are exclusive to the type strain ATCC 23270. We demonstrated that two TA systems from ICEAfe1 are functional in E. coli cells, since the toxins inhibit growth and the antitoxins counteract the effect of their cognate toxins. All the toxins from ICEAfe1, including a novel toxin, are RNases with different ion requirements. The data indicate that some of the chromosomally encoded TA systems are actually part of the A. ferrooxidans mobile genome and we propose that could be involved in the maintenance of these integrated mobile genetic elements.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive comparative-genomic analysis of type 2 toxin-antitoxin systems and related mobile stress response systems in prokaryotes.Biol Direct. 2009 Jun 3;4:19. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-4-19. Biol Direct. 2009. PMID: 19493340 Free PMC article.
-
Functionality of tRNAs encoded in a mobile genetic element from an acidophilic bacterium.RNA Biol. 2018;15(4-5):518-527. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1349049. Epub 2017 Aug 29. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 28708455 Free PMC article.
-
sRNAs in bacterial type I and type III toxin-antitoxin systems.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015 May;39(3):413-27. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv003. Epub 2015 Mar 25. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25808661 Review.
-
The chromosomal relBE2 toxin-antitoxin locus of Streptococcus pneumoniae: characterization and use of a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer assay to detect toxin-antitoxin interaction.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Feb;59(4):1280-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05027.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16430700
-
Divergently overlapping cis-encoded antisense RNA regulating toxin-antitoxin systems from E. coli: hok/sok, ldr/rdl, symE/symR.RNA Biol. 2012 Dec;9(12):1520-7. doi: 10.4161/rna.22757. Epub 2012 Nov 6. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 23131729 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological Functions of Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2021 Jun 11;9(6):1276. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061276. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34208120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a functional toxin-antitoxin system located in the genomic island PYG1 of piezophilic hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus yayanosii.Extremophiles. 2018 May;22(3):347-357. doi: 10.1007/s00792-018-1002-2. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Extremophiles. 2018. PMID: 29335804
-
Characterization and Comparative Overview of Complete Sequences of the First Plasmids of Pandoraea across Clinical and Non-clinical Strains.Front Microbiol. 2016 Oct 14;7:1606. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01606. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27790203 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of HigBA toxin-antitoxin system in an Arctic bacterium, Bosea sp. PAMC 26642.J Microbiol. 2022 Feb;60(2):192-206. doi: 10.1007/s12275-022-1619-9. Epub 2022 Feb 1. J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35102526
-
Nucleotide Second Messenger-Based Signaling in Extreme Acidophiles of the Acidithiobacillus Species Complex: Partition Between the Core and Variable Gene Complements.Front Microbiol. 2019 Mar 7;10:381. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00381. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30899248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamaguchi Y, Park J-H, Inouye M (2011) Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacteria and archaea. Annu Rev Genet 45: 61–79. - PubMed
-
- Gerdes K, Christensen SK, Løbner-Olesen A (2005) Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin stress response loci. Nat Rev Microbiol 3: 371–382. - PubMed
-
- Riley MA, Wertz JE (2002) Bacteriocins: evolution, ecology, and application. Annu Rev Microbiol 56: 117–137. - PubMed
-
- Hayes CS, Aoki SK, Low DA (2010) Bacterial contact-dependent delivery systems. Annu Rev Genet 44: 71–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

