Nordihydroguaiaretic Acid Extends the Lifespan of Drosophila and Mice, Increases Mortality-Related Tumors and Hemorrhagic Diathesis, and Alters Energy Homeostasis in Mice
- PMID: 25380600
- PMCID: PMC4631105
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glu190
Nordihydroguaiaretic Acid Extends the Lifespan of Drosophila and Mice, Increases Mortality-Related Tumors and Hemorrhagic Diathesis, and Alters Energy Homeostasis in Mice
Abstract
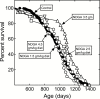
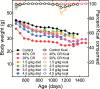
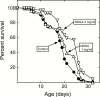
Mesonordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA) extends murine lifespan. The studies reported here describe its dose dependence, effects on body weight, toxicity-related clinical chemistries, and mortality-related pathologies. In flies, we characterized its effects on lifespan, food consumption, body weight, and locomotion. B6C3F1 mice were fed AIN-93M diet supplemented with 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, or 4.5 g NDGA/kg diet (1.59, 2.65, 3.71 and 4.77 mg/kg body weight/day) beginning at 12 months of age. Only the 3.5 mg/kg diet produced a highly significant increase in lifespan, as judged by either the Mantel-Cox log-rank test (p = .008) or the Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test (p = .009). NDGA did not alter food intake, but dose-responsively reduced weight, suggesting it decreased the absorption or increased the utilization of calories. NDGA significantly increased the incidence of liver, lung, and thymus tumors, and peritoneal hemorrhagic diathesis found at necropsy. However, clinical chemistries found little evidence for overt toxicity. While NDGA was not overtly toxic at its therapeutic dosage, its association with severe end of life pathologies does not support the idea that NDGA consumption will increase human lifespan or health-span. The less toxic derivatives of NDGA which are under development should be explored as anti-aging therapeutics.
Keywords: Dose; Lifespan; Longevity; NDGA; Therapeutic; response.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Gerontological Society of America.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acarbose, 17-α-estradiol, and nordihydroguaiaretic acid extend mouse lifespan preferentially in males.Aging Cell. 2014 Apr;13(2):273-82. doi: 10.1111/acel.12170. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Aging Cell. 2014. PMID: 24245565 Free PMC article.
-
Longer lifespan in male mice treated with a weakly estrogenic agonist, an antioxidant, an α-glucosidase inhibitor or a Nrf2-inducer.Aging Cell. 2016 Oct;15(5):872-84. doi: 10.1111/acel.12496. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Aging Cell. 2016. PMID: 27312235 Free PMC article.
-
Nordihydroguaiaretic acid and aspirin increase lifespan of genetically heterogeneous male mice.Aging Cell. 2008 Oct;7(5):641-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2008.00414.x. Aging Cell. 2008. PMID: 18631321 Free PMC article.
-
Nordihydroguaiaretic Acid in Therapeutics: Beneficial to Toxicity Profiles and the Search for its Analogs.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020;20(2):86-103. doi: 10.2174/1568009619666191022141547. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 31642411 Review.
-
Paradoxical cellular effects and biological role of the multifaceted compound nordihydroguaiaretic acid.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2014 Oct;347(10):685-97. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201400159. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2014. PMID: 25100573 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetyl-CoA Metabolism and Histone Acetylation in the Regulation of Aging and Lifespan.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 8;10(4):572. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040572. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33917812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions to Slow Aging in Humans: Are We Ready?Aging Cell. 2015 Aug;14(4):497-510. doi: 10.1111/acel.12338. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Aging Cell. 2015. PMID: 25902704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Creosote bush-derived NDGA attenuates molecular and pathological changes in a novel mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019 Dec 1;498:110538. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2019.110538. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31415794 Free PMC article.
-
Aging metabolism: intervention strategies.Virulence. 2017 Jul 4;8(5):571-576. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1305532. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Virulence. 2017. PMID: 28287893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Perspective in the Discovery of Anti-aging Agents from Natural Products.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2017 Oct;7(5):335-404. doi: 10.1007/s13659-017-0135-9. Epub 2017 May 31. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2017. PMID: 28567542 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tyler VE. The Honest Herbal, a Sensible Guide to the Use of Herbs and Related Remedies. Binghamton, NY: Pharmaceutical Products Press; 1994; 3, pp. 375.
-
- Obermeyer WR, Musser SM, Betz JM, Casey RE, Pohland AE, Page SW. Chemical studies of phytoestrogens and related compounds in dietary supplements: flax and chaparral. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1995;208:6–12. - PubMed
-
- Arteaga S, Andrade-Cetto A, Cárdenas R. Larrea tridentata (Creosote bush), an abundant plant of Mexican and US-American deserts and its metabolite nordihydroguaiaretic acid. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;98:231–239. - PubMed
-
- Grice HC, Becking G, Goodman T. Toxic properties of nordihydroguaiaretic acid. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1968;6:155–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

